rpi-io
Version:
Nodejs module to control Raspberry Pi GPIO
439 lines (299 loc) • 11.2 kB
Markdown
# rpi-io
    
**rpi-io** is a lite [ESM](https://nodejs.org/api/esm.html#modules-ecmascript-modules) module for **Node.js** to control **Raspberry Pi** GPIO: access (in, out), input event detection and [PWM](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pulse-width_modulation) peripheral control.
**rpi-io** supports only recent versions of Raspberry and related OS and middlewares :
- Raspberry Pi models: *RPi 5,* *RPi 4B* and *RPi Zero 2.*
- Raspberry Pi OS (64-bit): Debian *Bookworm* and *Trixie*.
- Middlewares (installed by default with OS distribution):
- Input/Output - [libgpiod](https://libgpiod.readthedocs.io/en/stable/) v1.6.3 (*Bookworm*) and v2.2.1 (*Trixie*)
- PWM - [sysfs](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sysfs) interface.
## Installation
````shell
npm install rpi-io
````
## Configuration
By default rpi-io does not require specific configuration.
If you want to use [hardware-based PWM](https://pinout.xyz/pinout/pwm) peripherals, some configuration is required:
- Open the file `/boot/firmware/config.txt` and add the required [dtoverlay](https://www.raspberrypi.com/documentation/computers/configuration.html#part3.1) configuration for PWM as showed in the examples below.
```shell
# Examples of PWM configuration to add to/boot/firmware/config.txt
# Default one-channel config: GPIO 18 as channel 0
[all]
dtoverlay=pwm
# Default two-channel config: GPIO 18 as channel 0 and GPIO 19 as channel 1
[all]
dtoverlay=pwm-2chan
# Custom two-channel config: GPIO 12 as channel 0 and GPIO 13 as channel 1
[all]
dtoverlay=pwm-2chan,pin=12,func=4,pin2=13,func2=4
```
- Reboot the Raspberry Pi.
- Test the PWM configuration.
```shell
# Testing PWM configuration after reboot
pinctrl get 12
# 12: a0 pd | lo // GPIO12 = PWM0_CHAN0
pinctrl get 13
# 13: a0 pd | lo // GPIO13 = PWM0_CHAN1
pinctrl get 18
# 18: no pd | -- // GPIO18 = none
pinctrl get 19
# 19: no pd | -- // GPIO19 = none
```
## Usage
PLEASE NOTE: In all this document, GPIOs numbers are the BCM ones as defined in https://pinout.xyz/.
### *OUT* operations
#### LED control
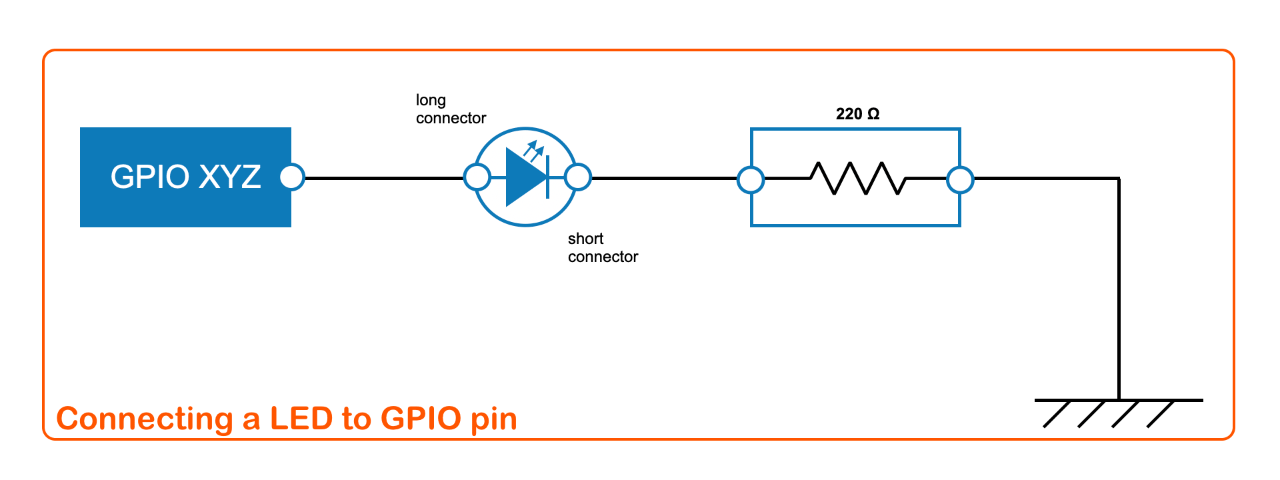
```javascript
// Import rpi-io module
import {Rio} from "rpi-io";
// Define instance for OUT operation on some GPIO
const led = new Rio(17, "out");
// Turn the led on
led.set(1);
// Turn the led off
led.set(0);
```
#### Active buzzer beep
`set` method has an optional *time* parameter to invert the command after some delay (ms). It may be useful to beep a buzzer.
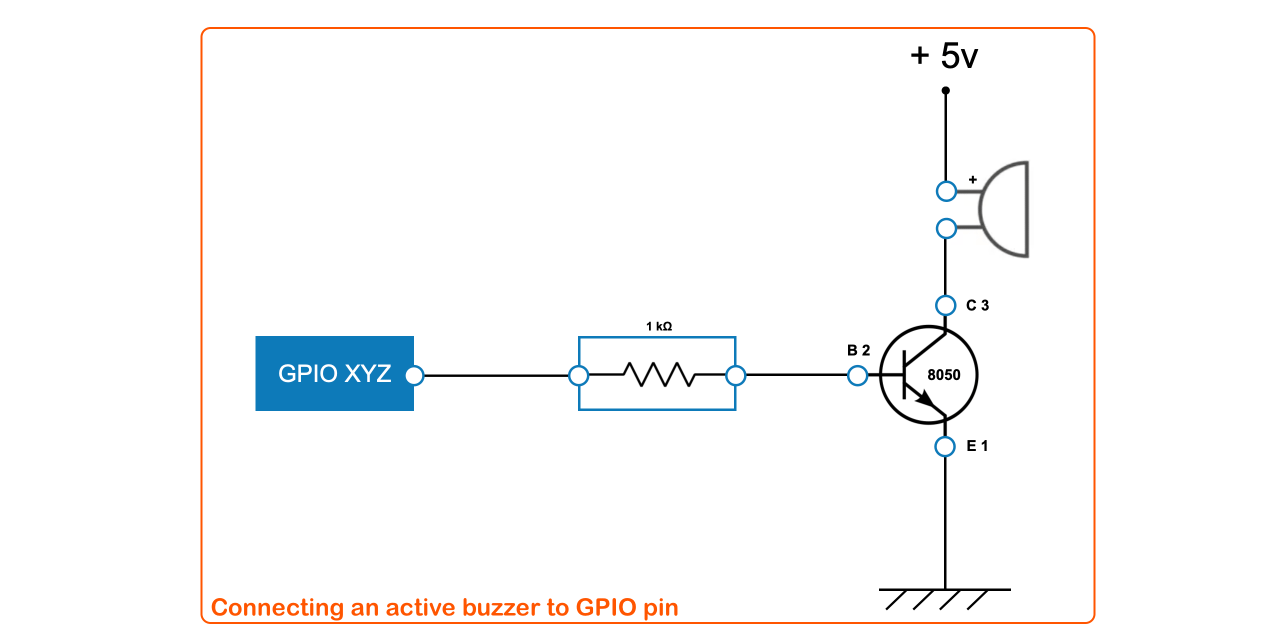
```javascript
// Import rpi-io module
import {Rio} from "rpi-io";
// Define instance for OUT operation on some GPIO
const buzzer = new Rio(23, "out");
// Turn the buzzer on for 3 seconds
buzzer.set(1, 3000);
```
### *IN* operations
#### Getting button status and listening to input events
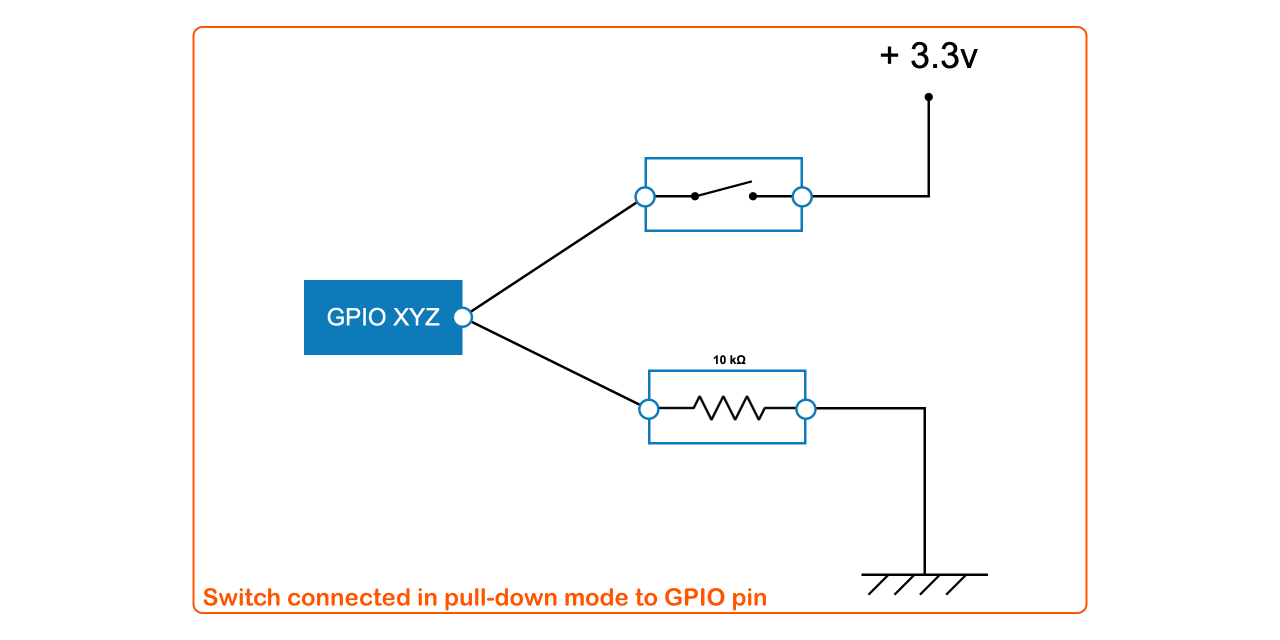
```javascript
// Import rpi-io module
import {Rio} from "rpi-io";
// Define instance for IN operation on some GPIO
const button = new Rio(18, "in");
// Get the instant value of the button
button.get(); // Return 0 (opened) or 1 (closed)
// Monitor button events ("rising, "falling" or "both")
// and receive results in callback function
button.monitor("both", (event) => {
// event.edge = "rising" or "falling"
// event.time = timestamp
console.log("event:", event.edge, event.time)
});
```
### PWM operations with servo motor in hardware mode
REMINDER: PWM peripherals used in hardware mode need some specific [configuration](#Configuration).
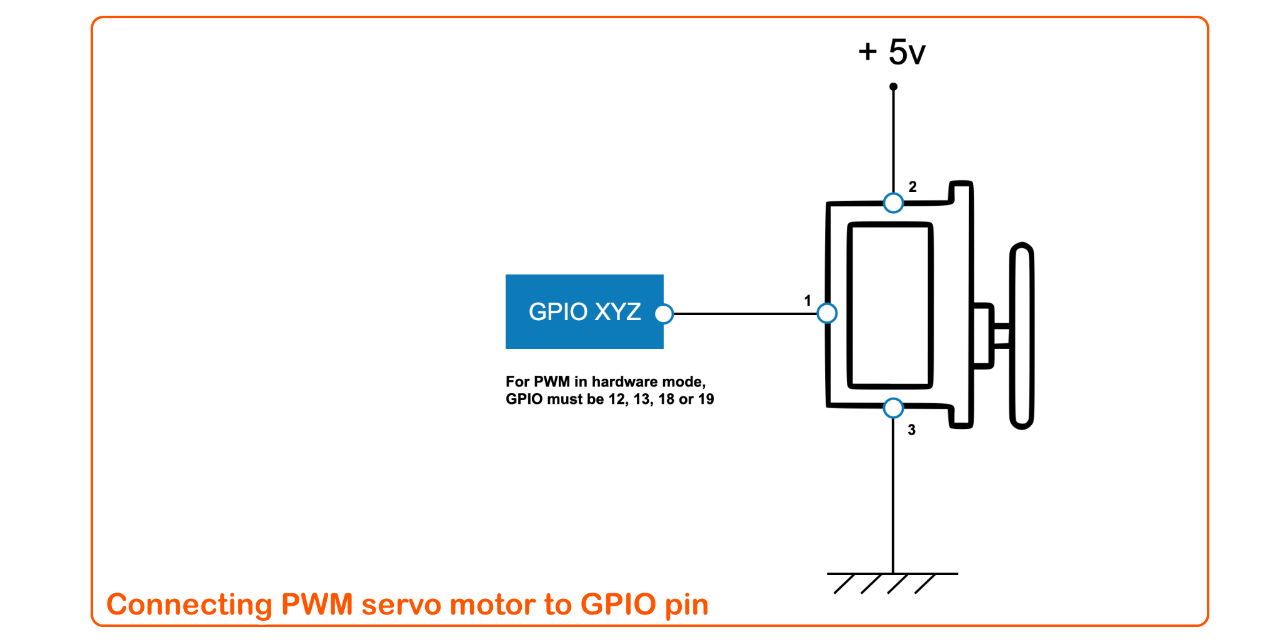
```javascript
// Import rpi-io module
import {Rio} from "rpi-io";
// Define instance for PWM operation on some PWM GPIO
const servoMotor = new Rio(13, "pwm");
// PWM servo motor parameters depends motor specifications.
// - period = 20,000,000 nano-seconds = 20 milli-seconds ~ frequency = 50 Hz
// - duty cycle on start = 500,000 nano-seconds = 0.5 milli-seconds
// - dutyMin = 0.5 ms ~ 0°
// - dutyMax = 2.5 ms ~ 180°
servoMotor.pwmInit(20000000, 500000, {
dutyMin: 500000,
dutyMax: 2500000
});
console.log("servo position = 0°");
// Wait 2s then change duty cyle to 1.5 ms
setTimeout(() => {
servo.pwmDuty(1500000);
console.log("servo position = 90°");
}, 2000);
```
## API
The **rpi-io** API is based on the class `Rio` with instance methods and static functions.
### Constructor and generic methods
#### Constructor - Rio(gpio, type)
##### Example
```javascript
import {Rio} from "rpi-io";
const myOutput = new Rio(17, 'out');
```
##### Parameters
- **gpio** *{Number}* Must be one of the GPIO number as defined in [pinout.xyz](https://pinout.xyz).
- **type** *{String}* Must be one of the following values: 'in', 'out', 'pwm'.
##### Detected errors
- Operating system version is not supported
- *libgpiod* version is not supported
- **gpio** is not defined as GPIO in [pinout.xyz](https://pinout.xyz).
- **gpio** is already used by another instance.
- **type** value is not recognized.
- **type**='pwm' and **gpio** is not properly configured.
#### Method - disable()
To remove an instance from the list.
##### Example
```javascript
myOutput.disable();
```
### Methods for instances where type='out'
#### set(value, duration)
To set some *out* GPIO to 0 or 1.
##### Example
```javascript
import {Rio} from "rpi-io";
const myOutput = new Rio(17, 'out');
myOutput.set(1, 3000);
```
##### Parameters
- **value** *{Number}* 0 or 1
- **duration** *{Number}* Time in ms. When defined, at the end of the defined time the output is inverted.
##### Detected errors
- Instance type is not 'out'.
- Instance is disabled or undefined.
### Methods for instances where type='in'
#### get()
To read instant value of some *in* GPIO.
##### Example
```javascript
import {Rio} from "rpi-io";
const myInput = new Rio(18, 'in');
let currentValue = myInput.get();
```
##### Returned value
0 or 1
##### Detected errors
- Instance type is not 'in'.
- Instance is disabled or undefined.
#### monitor(edge, callback)
To monitor activities on some *in* GPIO and receive events in a callback function.
##### Example
```javascript
import {Rio} from "rpi-io";
const myButton = new Rio(18, 'in');
myButton.monitor("both", event => {
console.log("event:", event.edge, event.time)
});
```
##### Parameters
- **edge** *{String}* 'rising', 'falling' or 'both'. Any other value stops instance monitoring.
- **callback** *{Function}* Callback function with one Object parameter for input events on instance e.g. `event = {edge: 'rising,' time: 'Thu Oct 30 2025 18:12:35 GMT+0100'}`
##### Detected errors
- Instance type is not 'in'.
- Instance is disabled or undefined.
### Methods for instances where type='pwm'
#### pwmInit(period, duty, options)
To initialize some *pwm* GPIO according to connected device specifications.
##### Example
```javascript
import {Rio} from "rpi-io";
const servoMotor = new Rio(13, "pwm");
servoMotor.pwmInit(20000000, 500000, {
dutyMin: 500000,
dutyMax: 2500000
});
console.log("servo position = 0°");
```
##### Parameters
All time parameters are defined in nanoseconds (ns).
- **period** *{Number}* Time period in which [duty cycle](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pulse-width_modulation) varies.
- **duty** *{Number}* Initial duty cycle.
- **options** *{Object}*
- **dutyMin** *{Number}* Default = 0. Minimum duty cycle (ns) as defined in connected device specifications.
- **dutyMax** *{Number}* Default = 1,000,000,000. Maximum duty cycle (ns) as defined in connected device specifications.
##### Detected errors
- Instance type is not 'pwm'.
- Instance is disabled or undefined.
- **period** is out-of-range [100, 1,000,000,000]
- **duty** < **options.dutyMin**
- **duty** > **options.dutyMax**
#### pwmStop()
To stop PWM modulation on some *pwm* GPIO.
##### Example
```javascript
servoMotor.pwmStop()
```
##### Detected errors
- Instance type is not 'pwm'.
- Instance is disabled or undefined.
#### pwmDuty(time)
To update duty cycle of some *pwm* GPIO.
##### Example
```javascript
servo.pwmDuty(1500000)
```
##### Parameters
- **time** *{Number}* Duty cycle (ns)
##### Detected errors
- Instance type is not 'pwm'.
- PWM instance is not properly initialized.
- **time** is out of range [dutyMin, dutyMax]
### Utility functions
#### Rio.stopMonitoring()
To stop monitoring subprocess when leaving your app script or in case of failure. This prevents having a runaway subprocess that could block a new call to the `monitor()` method.
##### Example
```javascript
Rio.stopMonitoring()
```
#### Rio.config(gpio)
To return configuration of some GPIO
##### Example
```javascript
import {Rio} from "rpi-io";
console.log(Rio.config(13))
// '13': 'pwm0_chan1'
```
#### Rio.info()
Javascript equivalent of command `gpioinfo`.
##### Example
```javascript
import {Rio} from "rpi-io";
console.log(Rio.info())
```
#### Rio.detect()
Javascript equivalent of command `gpiodetect`.
##### Example
```javascript
import {Rio} from "rpi-io";
console.log(Rio.detect())
```
#### Rio.version()
To retrieve libgpiod version.
##### Example
```javascript
import {Rio} from "rpi-io";
console.log(Rio.version())
// 'v1.6.3',
```
#### Rio.os()
To retrieve Raspberry Pi OS info.
##### Example
```javascript
import {Rio} from "rpi-io";
console.log(Rio.os())
// {id: '12', name: 'Bookworm'}
```
#### Rio.isSystemSupported()
To check if device is supported by **rpi-io** (device, model, os, middleware). It returns *true/false* and displays details in console.
#### Rio.log(level)
To set the level of console used in the module:
- 0: no console
- 1: console only for errors and warnings (default).
- 2: more logged data
##### Example
```javascript
import {Rio} from "rpi-io";
Rio.log(0)
Rio.isSystemSupported() // Nothing displayed in console
Rio.log(2)
Rio.isSystemSupported() // See console below
// 08:15:16.506 🔎 👍 Hardware is Raspberry Pi
// 08:15:16.539 🔎 👍 Raspberry Pi 5 Model B Rev 1.0 is supported
// 08:15:16.543 🔎 👍 Bookworm OS is supported
// 08:15:16.545 🔎 👍 libgpiod version v1.6.x is supported
// 08:15:16.545 🔎 👍 Systems requirements for rpi-io are met
```
## Benchmark
The following table summarizes GPIO *set* average times with rpi-io v1.1.0 and various hardware and OS.
| | RPi 5B | RPi 4B | RPi Zero2 |
|----------|---------|------------|------------|
| Bookworm | 1.37 ms | 4.56 ms | 9.07 ms |
| Trixie | 3.82 ms | not tested | not tested |
---