react-native-localize
Version:
A toolbox for your React Native app localization.
433 lines (295 loc) • 9.47 kB
Markdown
# 🌍 react-native-localize
A toolbox for your React Native app localization.
[](https://badge.fury.io/js/react-native-localize) [](https://www.npmjs.org/package/react-native-localize)   [](https://github.com/prettier/prettier)
<img width="400" height="auto" center src="https://github.com/react-native-community/react-native-localize/blob/master/docs/screenshot.png?raw=true" />
## Support
| package name | version | react-native version |
| ---------------------- | ------- | -------------------- |
| react-native-localize | 1.0.0+ | 0.56.0+ |
| react-native-languages | 2.0.1 | 0.48.0 - 0.55.4 |
## Setup
```bash
$ npm install --save react-native-localize
# --- or ---
$ yarn add react-native-localize
```
_Don't forget to run `pod install` after that !_
## 🆘 Manual linking
Because this package targets React Native 0.60.0+, you will probably don't need to link it manually. Otherwise if it's not the case, follow this additional instructions:
<details>
<summary><b>👀 See manual linking instructions</b></summary>
### iOS
Add this line to your `ios/Podfile` file, then run `pod install`.
```bash
target 'YourAwesomeProject' do
# …
pod 'RNLocalize', :path => '../node_modules/react-native-localize'
end
```
### Android
1. Add the following lines to `android/settings.gradle`:
```gradle
include ':react-native-localize'
project(':react-native-localize').projectDir = new File(rootProject.projectDir, '../node_modules/react-native-localize/android')
```
2. Add the implementation line to the dependencies in `android/app/build.gradle`:
```gradle
dependencies {
// ...
implementation project(':react-native-localize')
}
```
3. Add the import and link the package in `MainApplication.java`:
```java
import com.reactcommunity.rnlocalize.RNLocalizePackage; // <- add the RNLocalizePackage import
public class MainApplication extends Application implements ReactApplication {
// …
@Override
protected List<ReactPackage> getPackages() {
@SuppressWarnings("UnnecessaryLocalVariable")
List<ReactPackage> packages = new PackageList(this).getPackages();
// …
packages.add(new RNLocalizePackage());
return packages;
}
// …
}
```
</details>
## Web support
This package supports `react-native-web`. Follow their [official guide](https://github.com/necolas/react-native-web/blob/master/docs/guides/multi-platform-apps.md) to configure `webpack`.
## Basic usage example
```js
import * as RNLocalize from "react-native-localize";
console.log(RNLocalize.getLocales());
console.log(RNLocalize.getCurrencies());
RNLocalize.addEventListener("change", () => {
// do localization related stuff…
});
```
## API
### getLocales()
Returns the user preferred locales, in order.
#### Method type
```ts
type getLocales = () => Array<{
languageCode: string;
scriptCode?: string;
countryCode: string;
languageTag: string;
isRTL: boolean;
}>;
```
#### Usage example
```js
console.log(RNLocalize.getLocales());
/* -> [
{ countryCode: "GB", languageTag: "en-GB", languageCode: "en", isRTL: false },
{ countryCode: "US", languageTag: "en-US", languageCode: "en", isRTL: false },
{ countryCode: "FR", languageTag: "fr-FR", languageCode: "fr", isRTL: false },
] */
```
### getNumberFormatSettings()
Returns number formatting settings.
#### Method type
```ts
type getNumberFormatSettings = () => {
decimalSeparator: string;
groupingSeparator: string;
};
```
#### Usage example
```js
console.log(RNLocalize.getNumberFormatSettings());
/* -> {
decimalSeparator: ".",
groupingSeparator: ",",
} */
```
### getCurrencies()
Returns the user preferred currency codes, in order.
#### Method type
```ts
type getCurrencies = () => Array<string>;
```
#### Usage example
```js
console.log(RNLocalize.getCurrencies());
// -> ["EUR", "GBP", "USD"]
```
### getCountry()
Returns the user current country code (based on its device locale, **not** on its position).
#### Method type
```ts
type getCountry = () => string;
```
#### Usage example
```js
console.log(RNLocalize.getCountry());
// -> "FR"
```
### getCalendar()
Returns the user preferred calendar format.
#### Method type
```ts
type getCalendar = () => "gregorian" | "japanese" | "buddhist";
```
#### Usage example
```js
console.log(RNLocalize.getCalendar());
// -> "gregorian"
```
### getTemperatureUnit()
Returns the user preferred temperature unit.
#### Method type
```ts
type getTemperatureUnit = () => "celsius" | "fahrenheit";
```
#### Usage example
```js
console.log(RNLocalize.getTemperatureUnit());
// -> "celsius"
```
### getTimeZone()
Returns the user preferred timezone (based on its device settings, **not** on its position).
#### Method type
```ts
type getTimeZone = () => string;
```
#### Usage example
```js
console.log(RNLocalize.getTimeZone());
// -> "Europe/Paris"
```
### uses24HourClock()
Returns `true` if the user prefers 24h clock format, `false` if he prefers 12h clock format.
#### Method type
```ts
type uses24HourClock = () => boolean;
```
#### Usage example
```js
console.log(RNLocalize.uses24HourClock());
// -> true
```
### usesMetricSystem()
Returns `true` if the user prefers metric measure system, `false` if he prefers imperial.
#### Method type
```ts
type usesMetricSystem = () => boolean;
```
#### Usage example
```js
console.log(RNLocalize.usesMetricSystem());
// -> true
```
### usesAutoDateAndTime()
Tells if the automatic date & time setting is enabled on the phone. **Android only**
#### Method type
```ts
type Option<T> = T | undefined;
type usesAutoDateAndTime = () => Option<boolean>;
```
#### Usage example
```js
console.log(RNLocalize.usesAutoDateAndTime()); // true or false
```
### usesAutoTimeZone()
Tells if the automatic time zone setting is enabled on the phone. **Android only**
#### Method type
```ts
type Option<T> = T | undefined;
type usesAutoTimeZone = () => Option<boolean>;
```
#### Usage example
```js
console.log(RNLocalize.usesAutoTimeZone());
```
### addEventListener() / removeEventListener()
Allows you to listen for any localization change.
#### Methods type
```ts
type addEventListener = (type: "change", handler: Function) => void;
type removeEventListener = (type: "change", handler: Function) => void;
```
#### Usage example
```js
function handleLocalizationChange() {
console.log(RNLocalize.getLocales());
}
RNLocalize.addEventListener("change", handleLocalizationChange);
// …later (ex: component unmount)
RNLocalize.removeEventListener("change", handleLocalizationChange);
```
### findBestAvailableLanguage()
Returns the best language tag possible and its reading direction (⚠️ **it respects the user preferred languages list order, see [explanations](https://github.com/react-native-community/react-native-localize/issues/57#issuecomment-508456427)**). Useful to pick the best translation available.
#### Method type
```ts
type findBestAvailableLanguage = (
languageTags: Array<string>,
) => { languageTag: string; isRTL: boolean } | void;
```
#### Usage example
```js
console.log(RNLocalize.findBestAvailableLanguage(["en-US", "en", "fr"]));
// -> { languageTag: "en-US", isRTL: false }
```
## Examples with [i18n-js](https://github.com/fnando/i18n-js)
Browse the files in the [/example](https://github.com/react-native-community/react-native-localize/tree/master/example) directory.
## How to test your code
Because it's a native module, you might need to mock this package to run your tests flawlessly.<br />
Here is an example for Jest, adapt it to your needs :
```js
// __mocks__/react-native-localize.js
const getLocales = () => [
// you can choose / add the locales you want
{ countryCode: "US", languageTag: "en-US", languageCode: "en", isRTL: false },
{ countryCode: "FR", languageTag: "fr-FR", languageCode: "fr", isRTL: false },
];
// use a provided translation, or return undefined to test your fallback
const findBestAvailableLanguage = () => ({
languageTag: "en-US",
isRTL: false,
});
const getNumberFormatSettings = () => ({
decimalSeparator: ".",
groupingSeparator: ",",
});
const getCalendar = () => "gregorian"; // or "japanese", "buddhist"
const getCountry = () => "US"; // the country code you want
const getCurrencies = () => ["USD", "EUR"]; // can be empty array
const getTemperatureUnit = () => "celsius"; // or "fahrenheit"
const getTimeZone = () => "Europe/Paris"; // the timezone you want
const uses24HourClock = () => true;
const usesMetricSystem = () => true;
const addEventListener = jest.fn();
const removeEventListener = jest.fn();
export {
findBestAvailableLanguage,
getLocales,
getNumberFormatSettings,
getCalendar,
getCountry,
getCurrencies,
getTemperatureUnit,
getTimeZone,
uses24HourClock,
usesMetricSystem,
addEventListener,
removeEventListener,
};
```
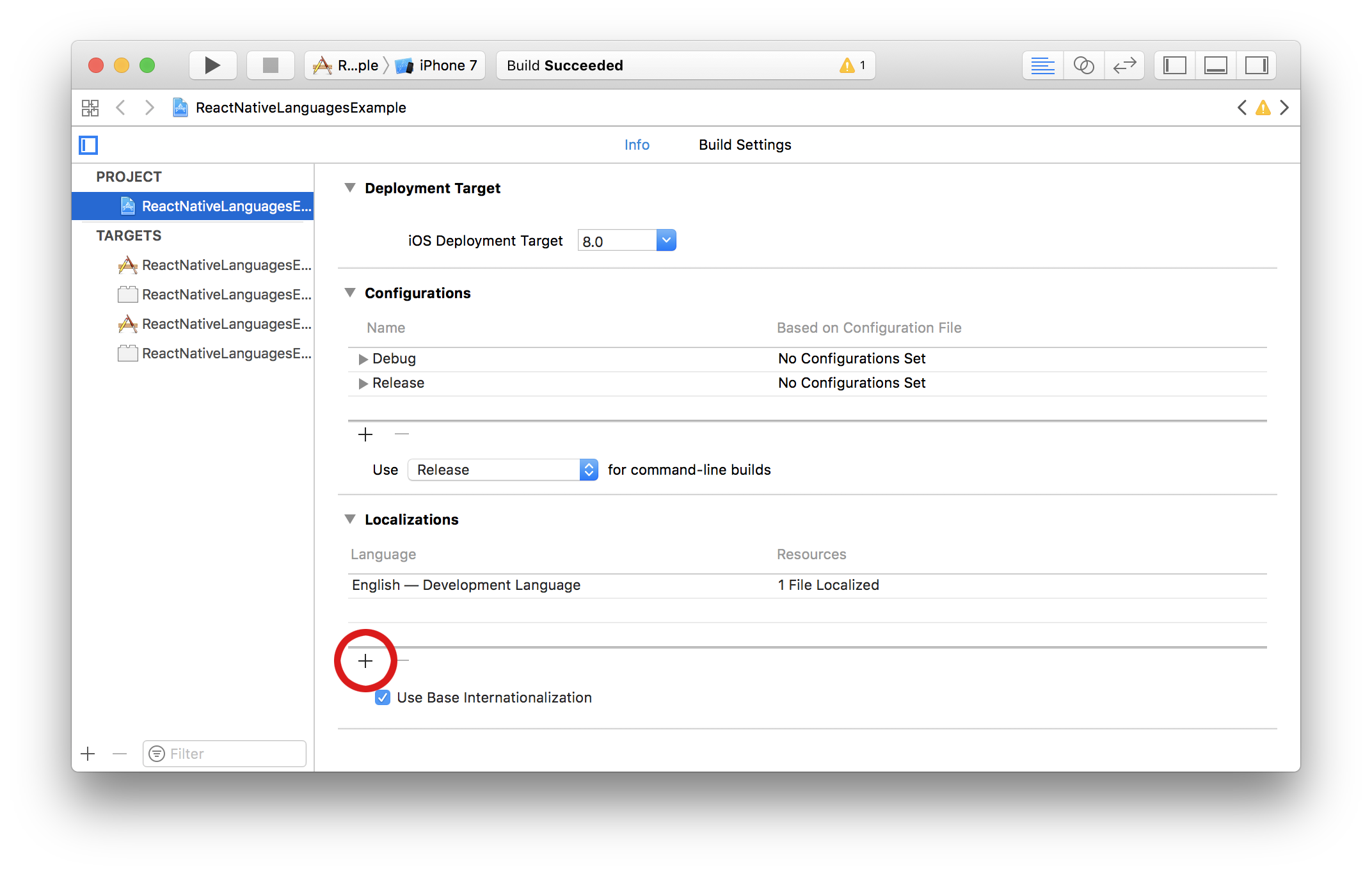
## Add project's supported localizations (iOS)