react-native-background-geolocation
Version:
The most sophisticated cross-platform background location-tracking & geofencing module with battery-conscious motion-detection intelligence
1,206 lines (1,157 loc) • 70.5 kB
TypeScript
/// <reference path="types.d.ts" />
/// <reference path="interfaces/Config.d.ts" />
/// <reference path="interfaces/ConnectivityChangeEvent.d.ts" />
/// <reference path="interfaces/CurrentPositionRequest.d.ts" />
/// <reference path="interfaces/Geofence.d.ts" />
/// <reference path="interfaces/GeofenceEvent.d.ts" />
/// <reference path="interfaces/GeofencesChangeEvent.d.ts" />
/// <reference path="interfaces/HeartbeatEvent.d.ts" />
/// <reference path="interfaces/HeadlessEvent.d.ts" />
/// <reference path="interfaces/HttpEvent.d.ts" />
/// <reference path="interfaces/Location.d.ts" />
/// <reference path="interfaces/LocationAuthorizationAlert.d.ts" />
/// <reference path="interfaces/Logger.d.ts" />
/// <reference path="interfaces/MotionActivityEvent.d.ts" />
/// <reference path="interfaces/MotionChangeEvent.d.ts" />
/// <reference path="interfaces/ProviderChangeEvent.d.ts" />
/// <reference path="interfaces/Sensors.d.ts" />
/// <reference path="interfaces/State.d.ts" />
/// <reference path="interfaces/WatchPositionRequest.d.ts" />
/// <reference path="interfaces/DeviceSettings.d.ts" />
/// <reference path="interfaces/Notification.d.ts" />
/// <reference path="interfaces/SQLQuery.d.ts" />
/// <reference path="interfaces/DeviceInfo.d.ts" />
/// <reference path="interfaces/Authorization.d.ts" />
/// <reference path="interfaces/AuthorizationEvent.d.ts" />
/// <reference path="interfaces/TransistorAuthorizationToken.d.ts" />
/// <reference path="interfaces/Subscription.d.ts" />
declare module "react-native-background-geolocation" {
/**
* Primary API of the SDK.
* @break
*
* ## 📚 Help
* - 📘 [Philosophy of Operation](github:wiki/Philosophy-of-Operation)
* - 📘 [[HttpEvent | HTTP Guide]].
* - 📘 [[Geofence | Geofencing Guide]].
* - 📘 [Android Headless Mode](github:wiki/Android-Headless-Mode).
* - 📘 [Debugging Guide](github:wiki/Debugging).
*
* ## ⚡️ Events
*
* [[BackgroundGeolocation]] is event-based. Interacting with the SDK is largely through implementing listeners on the following events:
*
* | Method | Description |
* |------------------------|-----------------------------------------|
* | [[onLocation]] | Fired with each recorded [[Location]] |
* | [[onMotionChange]] | Fired when the plugin changes state between *moving* / *stationary* |
* | [[onHttp]] | Fired with each HTTP response from your server. (see [[Config.url]]). |
* | [[onActivityChange]] | Fired with each change in device motion-activity. |
* | [[onProviderChange]] | Fired after changes to device location-services configuration. |
* | [[onHeartbeat]] | Periodic timed events. See [[heartbeatInterval]]. iOS requires [[preventSuspend]]. |
* | [[onGeofence]] | Fired with each [[Geofence]] transition event (`ENTER, EXIT, DWELL`). |
* | [[onGeofencesChange]] | Fired when the list of actively-monitored geofences changed. See [[geofenceProximityRadius]]. |
* | [[onSchedule]] | Fired for [[schedule]] events. |
* | [[onConnectivityChange]] | Fired when network-connectivity changes (connected / disconnected). |
* | [[onPowerSaveChange]] | Fired when state of operating-system's "power-saving" feature is enabled / disabled. |
* | [[onEnabledChange]] | Fired when the plugin is enabled / disabled via its [[start]] / [[stop]] methods. |
* | [[onAuthorization]] | Fired when a response from [[Authorization.refreshUrl]] is received. |
* | [[onNotificationAction]] | __Android only__: Fired when a button is clicked on a custom [[Notification.layout]] of a foreground-service notification. |
*
* ## 🔧 [[Config]] API
*
* [[BackgroundGeolocation]] is highly configurable. See the [[Config]] API for more information.
*
* There are three main steps to using `BackgroundGeolocation`
* 1. Wire up event-listeners.
* 2. [[ready]] the SDK.
* 3. [[start]] tracking.
*
* @example
* ```typescript
*
* ////
* // 1. Wire up event-listeners
* //
*
* // This handler fires whenever bgGeo receives a location update.
* BackgroundGeolocation.onLocation(location => {
* console.log("[location] ", location);
* }, error => {
* console.log("[location] ERROR: ", error);
* });
*
* // This handler fires when movement states changes (stationary->moving; moving->stationary)
* BackgroundGeolocation.onMotionChange(location => {
* console.log("[motionchange] ", location);
* });
*
* // This handler fires on HTTP responses
* BackgroundGeolocation.onHttp(response => {
* console.log("[http] ", response);
* });
*
* // This event fires when a change in motion activity is detected
* BackgroundGeolocation.onActivityChange(activityEvent => {
* console.log("[activitychange] ", activityEvent);
* });
*
* // This event fires when the user toggles location-services authorization
* BackgroundGeolocation.onProviderChange(providerEvent => {
* console.log("[providerchange] ", providerEvent);
* });
*
* ////
* // 2. Execute #ready method (required)
* //
* BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
* // Geolocation Config
* desiredAccuracy: BackgroundGeolocation.DESIRED_ACCURACY_HIGH,
* distanceFilter: 10,
* // Activity Recognition
* stopTimeout: 1,
* // Application config
* debug: true, // <-- enable this hear debug sounds.
* logLevel: BackgroundGeolocation.LOG_LEVEL_VERBOSE,
* stopOnTerminate: false, // <-- Allow the background-service to continue tracking when app terminated.
* startOnBoot: true, // <-- Auto start tracking when device is powered-up.
* // HTTP / SQLite config
* url: "http://yourserver.com/locations",
* batchSync: false, // <-- Set true to sync locations to server in a single HTTP request.
* autoSync: true, // <-- Set true to sync each location to server as it arrives.
* headers: { // <-- Optional HTTP headers
* "X-FOO": "bar"
* },
* params: { // <-- Optional HTTP params
* "auth_token": "maybe_your_server_authenticates_via_token_YES?"
* }
* }, (state) => {
* console.log("- BackgroundGeolocation is configured and ready: ", state.enabled);
*
* if (!state.enabled) {
* ////
* // 3. Start tracking!
* //
* BackgroundGeolocation.start(function() {
* console.log("- Start success");
* });
* }
* });
*
* ```
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
* distanceFilter: 10,
* stopOnTerminate: false,
* logLevel: BackgroundGeolocation.LOG_LEVEL_VERBOSE,
* debug: true
* }, (state) => {
* console.log("- BackgroundGeolocation is ready: ", state);
* });
* ```
*
* ### ⚠️ Warning:
* Do not execute *any* API method which will require accessing location-services until the callback to [[ready]] executes (eg: [[getCurrentPosition]], [[watchPosition]], [[start]]).
*
* ### Promise API
*
* The `BackgroundGeolocation` Javascript API supports [Promises](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Promise) for *nearly* every method (the exceptions are [[watchPosition]] and adding event-listeners via **`#onEventName`** methods.)
* @example
* ```typescript
* // Traditional API still works:
* BackgroundGeolocation.ready({desiredAccuracy: 0, distanceFilter: 50}).then(state => {
* console.log("- BackgroundGeolocation is ready: ", state);
* }).catch(error => {
* console.log("- BackgroundGeolocation error: ", error);
* });
* ```
*/
export class BackgroundGeolocation {
static EVENT_BOOT: Event;
static EVENT_TERMINATE: Event;
static EVENT_LOCATION: Event;
static EVENT_MOTIONCHANGE: Event;
static EVENT_HTTP: Event;
static EVENT_HEARTBEAT: Event;
static EVENT_PROVIDERCHANGE: Event;
static EVENT_ACTIVITYCHANGE: Event;
static EVENT_GEOFENCE: Event;
static EVENT_GEOFENCESCHANGE: Event;
static EVENT_ENABLEDCHANGE: Event;
static EVENT_CONNECTIVITYCHANGE: Event;
static EVENT_SCHEDULE: Event;
static EVENT_POWERSAVECHANGE: Event;
static EVENT_NOTIFICATIONACTION: Event;
static EVENT_AUTHORIZATION: Event;
static LOG_LEVEL_OFF: LogLevel;
static LOG_LEVEL_ERROR: LogLevel;
static LOG_LEVEL_WARNING: LogLevel;
static LOG_LEVEL_INFO: LogLevel;
static LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG: LogLevel;
static LOG_LEVEL_VERBOSE: LogLevel;
static DESIRED_ACCURACY_NAVIGATION:LocationAccuracy;
static DESIRED_ACCURACY_HIGH:LocationAccuracy;
static DESIRED_ACCURACY_MEDIUM:LocationAccuracy;
static DESIRED_ACCURACY_LOW:LocationAccuracy;
static DESIRED_ACCURACY_VERY_LOW:LocationAccuracy;
static DESIRED_ACCURACY_LOWEST:LocationAccuracy;
static AUTHORIZATION_STATUS_NOT_DETERMINED:AuthorizationStatus;
static AUTHORIZATION_STATUS_RESTRICTED:AuthorizationStatus;
static AUTHORIZATION_STATUS_DENIED:AuthorizationStatus;
static AUTHORIZATION_STATUS_ALWAYS:AuthorizationStatus;
static AUTHORIZATION_STATUS_WHEN_IN_USE:AuthorizationStatus;
static NOTIFICATION_PRIORITY_DEFAULT:NotificationPriority;
static NOTIFICATION_PRIORITY_HIGH:NotificationPriority;
static NOTIFICATION_PRIORITY_LOW:NotificationPriority;
static NOTIFICATION_PRIORITY_MAX:NotificationPriority;
static NOTIFICATION_PRIORITY_MIN:NotificationPriority;
static ACTIVITY_TYPE_OTHER:ActivityType;
static ACTIVITY_TYPE_AUTOMOTIVE_NAVIGATION:ActivityType;
static ACTIVITY_TYPE_FITNESS:ActivityType;
static ACTIVITY_TYPE_OTHER_NAVIGATION:ActivityType;
static ACTIVITY_TYPE_AIRBORNE:ActivityType;
static PERSIST_MODE_ALL: PersistMode;
static PERSIST_MODE_LOCATION: PersistMode;
static PERSIST_MODE_GEOFENCE: PersistMode;
static PERSIST_MODE_NONE: PersistMode;
static ACCURACY_AUTHORIZATION_FULL: AccuracyAuthorization;
static ACCURACY_AUTHORIZATION_REDUCED: AccuracyAuthorization;
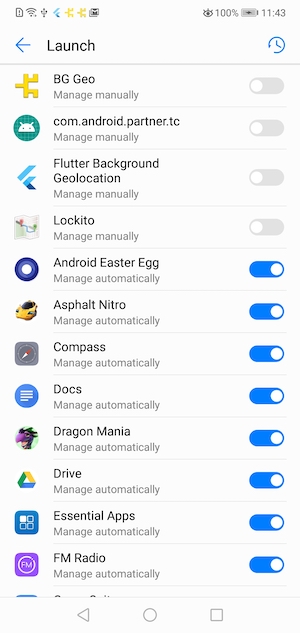
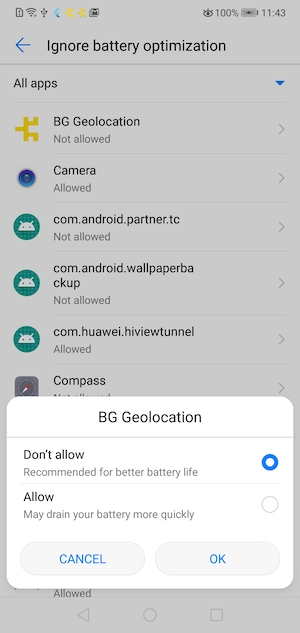
/**
* [[DeviceSettings]] API
*
* Provides an API to show Android & vendor-specific Battery / Power Management settings screens that can affect performance of the Background Geolocation SDK on various devices.
*
* The site [Don't Kill My App](https://dontkillmyapp.com/) provides a comprehensive list of poor Android vendors which throttle background-services that this plugin relies upon.
*
* This [[DeviceSettings]] API is an attempt to provide resources to direct the user to the appropriate vendor-specific settings screen to resolve issues with background operation.
*
* 
* 
*
*/
static deviceSettings: DeviceSettings;
/**
* [[Logger]] API
*/
static logger: Logger;
/**
* @hidden
*/
static addListener(event: string, success:Function, failure?:Function):void;
/**
* @hidden
*/
static on(event: string, success:Function, failure?:Function):void;
/**
* @deprecated. Use [[Subscription]] returned from __`BackgroundGeolocation.onXXX`__ to remove listeners.
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* const subscription = BackgroundGeolocation.onLocation((location) => {
* console.log('[onLocation]', location);
* });
* .
* .
* .
* // Remove listener
* subscription.remove();
* ```
*
* ---------------------------------------------------------------------
* ### ⚠️ [Deprecated]
*
* Removes an event listener. You must supply the *type* of event to remove in addition to a reference to the *exact* function you
* used to subscribe to the event.
*
*
* | Event |
* |----------------------|
* | `location` |
* | `motionchange` |
* | `activitychange` |
* | `providerchange` |
* | `geofence` |
* | `geofenceschange` |
* | `heartbeat` |
* | `http` |
* | `powersavechange` |
* | `schedule` |
* | `connectivitychange` |
* | `enabledchange` |
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* const locationHandler = (location) => {
* console.log("[location] - ", location)
* }
* BackgroundGeolocation.onLocation(locationHandler)
* .
* .
* // Remove the listener providing a reference to the original callback.
* BackgroundGeolocation.removeListener("location", locationHandler)
* ```
*/
static removeListener(event: string, handler: Function, success?:Function, failure?:Function): void;
/**
* Alias for [[removeListener]].
* @ignore
*/
static un(event: string, handler: Function, success?:Function, failure?:Function): void;
/**
* Removes all event-listeners.
*
* Calls [[Subscription.remove]] on all subscriptions.
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* BackgroundGeolocation.removeListeners();
* ```
*/
static removeListeners(success?:Function, failure?:Function): Promise<void>;
/**
* Alias for [[removeListeners]]
*/
static removeAllListeners(success?:Function, failure?:Function): Promise<void>;
/**
* Subscribe to location events.
*
* Every location recorded by the SDK is provided to your `callback`, including those from [[onMotionChange]], [[getCurrentPosition]] and [[watchPosition]].
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* const subscription = BackgroundGeolocation.onLocation((location) => {
* console.log("[onLocation] success: ", location);
* }, (error) => {
* console.log("[onLocation] ERROR: ", error);
* });
* ```
*
* ### Error Codes
*
* If the native location API fails to return a location, the `failure` callback will be provided a [[LocationError]].
*
* ### ⚠️ Note [[Location.sample]]:
*
* When performing a [[onMotionChange]] or [[getCurrentPosition]], the plugin requests **multiple** location *samples* in order to record the most accurate location possible. These *samples* are **not** persisted to the database but they will be provided to your `callback`, for your convenience, since it can take some seconds for the best possible location to arrive.
*
* For example, you might use these samples to progressively update the user's position on a map. You can detect these *samples* in your `callback` via `location.sample == true`. If you're manually `POST`ing location to your server, you should ignore these locations.
*
* @event location
*/
static onLocation(success: (location:Location)=>void, failure?:(errorCode: LocationError) => void):Subscription;
/**
* Subscribe to Geofence transition events.
*
* Your supplied `callback` will be called when any monitored geofence crossing occurs.
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* const subscription = BackgroundGeolocation.onGeofence((event) => {
* console.log("[onGeofence] ", event);
* });
* ```
*
* ### ℹ️ See also:
* - 📘 [[Geofence | Geofencing Guide]]
*
* @event geofence
*/
static onGeofence(callback: (event: GeofenceEvent) => void):Subscription;
/**
* Subscribe to __`motionchange`__ events.
*
* Your `callback` will be executed each time the device has changed-state between **MOVING** or **STATIONARY**.
*
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* const subscription = BackgroundGeolocation.onMotionChange((event) => {
* if (event.isMoving) {
* console.log("[onMotionChange] Device has just started MOVING ", event.location);
* } else {
* console.log("[onMotionChange] Device has just STOPPED: ", event.location);
* }
* });
* ```
*
* ----------------------------------------------------------------------
* ### ⚠️ Warning: `autoSyncThreshold`
*
* If you've configured [[Config.autoSyncThreshold]], it **will be ignored** during a `onMotionChange` event — all queued locations will be uploaded, since:
* - If an `onMotionChange` event fires **into the *moving* state**, the device may have been sitting dormant for a long period of time. The plugin is *eager* to upload this state-change to the server as soon as possible.
* - If an `onMotionChange` event fires **into the *stationary* state**, the device may be about to lie dormant for a long period of time. The plugin is *eager* to upload all queued locations to the server before going dormant.
* ----------------------------------------------------------------------
*
* ### ℹ️ See also:
* - [[stopTimeout]]
* - 📘 [Philosophy of Operation](github:wiki/Philosophy-of-Operation)
*
* @event motionchange
*/
static onMotionChange(callback: (event:MotionChangeEvent) => void): Subscription;
/**
* Subscribe to HTTP responses from your server [[Config.url]].
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* const subscription = BackgroundGeolocation.onHttp((response) => {
* let status = response.status;
* let success = response.success;
* let responseText = response.responseText;
* console.log("[onHttp] ", response);
* });
* ```
* ### ℹ️ See also:
* - [[HttpEvent | HTTP Guide]]
*
* @event http
*/
static onHttp(callback: (response:HttpEvent) => void): Subscription;
/**
* Subscribe to changes in motion activity.
*
* Your `callback` will be executed each time the activity-recognition system receives an event (`still, on_foot, in_vehicle, on_bicycle, running`).
*
* ### Android
* Android [[MotionActivityEvent.confidence]] always reports `100`%.
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* const subscription = BackgroundGeolocation.onActivityChange((event) => {
* console.log("[onActivityChange] ", event);
* });
* ```
* @event activitychange
*/
static onActivityChange(callback: (event: MotionActivityEvent) => void): Subscription;
/**
* Subscribe to changes in device's location-services configuration / authorization.
*
* Your `callback` fill be executed whenever a change in the state of the device's **Location Services** has been detected. eg: "GPS ON", "WiFi only".
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* const subscription = BackgroundGeolocation.onProviderChange((event) => {
* console.log("[onProviderChange: ", event);
*
* switch(event.status) {
* case BackgroundGeolocation.AUTHORIZATION_STATUS_DENIED:
* // Android & iOS
* console.log("- Location authorization denied");
* break;
* case BackgroundGeolocation.AUTHORIZATION_STATUS_ALWAYS:
* // Android & iOS
* console.log("- Location always granted");
* break;
* case BackgroundGeolocation.AUTHORIZATION_STATUS_WHEN_IN_USE:
* // iOS only
* console.log("- Location WhenInUse granted");
* break;
* }
* });
* ```
*
* ### ℹ️ See also:
* - You can explicitly request the current state of location-services using [[getProviderState]].
*
* ### ⚠️ Note:
* - The plugin always force-fires an [[onProviderChange]] event whenever the app is launched (right after the [[ready]] method is executed), regardless of current state, so you can learn the the current state of location-services with each boot of your application.
*
* @event providerchange
*/
static onProviderChange(callback: (event:ProviderChangeEvent) => void): Subscription;
/**
* Subscribe to periodic heartbeat events.
*
* Your `callback` will be executed for each [[heartbeatInterval]] while the device is in **stationary** state (**iOS** requires [[preventSuspend]]: true as well).
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
* heartbeatInterval: 60,
* preventSuspend: true // <-- Required for iOS
* });
*
* const subscription = BackgroundGeolocation.onHeartbeat((event) => {
* console.log("[onHeartbeat] ", event);
*
* // You could request a new location if you wish.
* BackgroundGeolocation.getCurrentPosition({
* samples: 1,
* persist: true
* }).then((location) => {
* console.log("[getCurrentPosition] ", location);
* });
* })
* ```
*
* ### ⚠️ Note:
* - The [[Location]] provided by the [[HeartbeatEvent]] is only the last-known location. The *heartbeat* event does not actively engage location-services. If you wish to get the current location in your `callback`, use [[getCurrentPosition]].
* @event heartbeat
*/
static onHeartbeat(callback: (event: HeartbeatEvent) => void): Subscription;
/**
* Subscribe to changes in actively monitored geofences.
*
* Fired when the list of monitored-geofences changed. The BackgroundGeolocation SDK contains powerful geofencing features that allow you to monitor
* any number of circular geofences you wish (thousands even), in spite of limits imposed by the native platform APIs (**20 for iOS; 100 for Android**).
*
* The plugin achieves this by storing your geofences in its database, using a [geospatial query](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spatial_query) to determine
* those geofences in proximity (@see [[geofenceProximityRadius]]), activating only those geofences closest to the device's current location
* (according to limit imposed by the corresponding platform).
*
* When the device is determined to be moving, the plugin periodically queries for geofences in proximity (eg. every minute) using the latest recorded
* location. This geospatial query is **very fast**, even with tens-of-thousands geofences in the database.
*
* It's when this list of monitored geofences *changes*, that the plugin will fire the `onGeofencesChange` event.
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* const subscription = BackgroundGeolocation.onGeofencesChange((event) => {
* let on = event.on; //<-- new geofences activated.
* let off = event.off; //<-- geofences that were just de-activated.
*
* // Create map circles
* on.forEach((geofence) => {
* createGeofenceMarker(geofence)
* });
*
* // Remove map circles
* off.forEach((identifier) => {
* removeGeofenceMarker(identifier);
* }
* });
* ```
*
* ### ℹ️ See also:
* - 📘 [[Geofence | Geofencing Guide]]
* @event geofenceschange
*/
static onGeofencesChange(callback: (event: GeofencesChangeEvent) => void): Subscription;
/**
* Subscribe to [[schedule]] events.
*
* Your `callback` will be executed each time a [[schedule]] event fires. Your `callback` will be provided with the current [[State]]: **`state.enabled`**
* will reflect the state according to your [[schedule]].
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* const subscription = BackgroundGeolocation.onSchedule((state) => {
* if (state.enabled) {
* console.log("[onSchedule] scheduled start tracking");
* } else {
* console.log("[onSchedule] scheduled stop tracking");
* }
* });
* ```
* @event schedule
*/
static onSchedule(callback: (state:State) => void): Subscription;
/**
* Subscribe to changes in network connectivity.
*
* Fired when the state of the device's network-connectivity changes (enabled -> disabled and vice-versa). By default, the plugin will automatically fire
* a `connectivitychange` event with the current state network-connectivity whenever the [[start]] method is executed.
*
* ℹ️ The SDK subscribes internally to `connectivitychange` events — if you've configured the SDK's HTTP Service (See [[HttpEvent | HTTP Guide]]) and your app has queued locations,
* the SDK will automatically initiate uploading to your configured [[Config.url]] when network connectivity is detected.
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* const subscription = BackgroundGeolocation.onConnectivityChange((event) => {
* console.log("[onConnectivityChange] ", event);
* });
* ```
* @event connectivitychange
*/
static onConnectivityChange(callback: (event:ConnectivityChangeEvent) => void): Subscription;
/**
* Subscribe to state changes in OS power-saving system.
*
* Fired when the state of the operating-system's "Power Saving" mode changes. Your `callback` will be provided with a `bool` showing whether
* "Power Saving" is **enabled** or **disabled**. Power Saving mode can throttle certain services in the background, such as HTTP requests or GPS.
* @break
*
* ℹ️ You can manually request the current-state of "Power Saving" mode with the method [[isPowerSaveMode]].
*
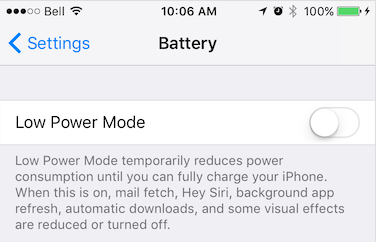
* ### iOS
*
* iOS Power Saving mode can be engaged manually by the user in **Settings -> Battery** or from an automatic OS dialog.
*
* 
*
* ### Android
*
* Android Power Saving mode can be engaged manually by the user in **Settings -> Battery -> Battery Saver** or automatically with a user-specified "threshold" (eg: 15%).
*
* 
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* const subscription = BackgroundGeolocation.onPowerSaveChange((isPowerSaveMode) => {
* console.log("[onPowerSaveChange: ", isPowerSaveMode);
* });
* ```
* @event powersavechange
*/
static onPowerSaveChange(callback: (enabled:boolean) => void): Subscription;
/**
* Subscribe to changes in plugin [[State.enabled]].
*
* Fired when the SDK's [[State.enabled]] changes. For example, executing [[start]] and [[stop]] will cause the `onEnabledChnage` event to fire.
* This event is primarily designed for use with the configuration option [[stopAfterElapsedMinutes]], which automatically executes the SDK's
* [[stop]] method.
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* const subscription = BackgroundGeolocation.onEnabledChange(isEnabled => {
* console.log("[onEnabledChanged] isEnabled? ", isEnabled);
* });
* ```
* @event enabledchange
*/
static onEnabledChange(callback: (enabled:boolean) => void): Subscription;
/**
* [__Android-only__] Subscribe to button-clicks of a custom [[Notification.layout]] on the Android foreground-service notification.
*/
static onNotificationAction(callback: (buttonId:string) => void): Subscription;
/**
* Subscribe to [[Authorization]] events.
*
* Fired when [[Authorization.refreshUrl]] responds, either successfully or not. If successful, [[AuthorizationEvent.success]] will be `true` and [[AuthorizationEvent.response]] will
* contain the decoded JSON response returned from the server.
*
* If authorization failed, [[AuthorizationEvent.error]] will contain the error message.
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* const subscription = BackgroundGeolocation.onAuthorization((event) => {
* if (event.success) {
* console.log("[authorization] ERROR: ", event.error);
* } else {
* console.log("[authorization] SUCCESS: ", event.response);
* }
* });
* ```
*
*/
static onAuthorization(callback: (event:AuthorizationEvent) => void): Subscription;
/**
* Registers a Javascript callback to execute in the Android "Headless" state, where the app has been terminated configured with
* [[stopOnTerminate]]`:false`. * The received `event` object contains a `name` (the event name) and `params` (the event data-object).
*
* ### ⚠️ Note Cordova & Capacitor
* - Javascript headless callbacks are not supported by Cordova or Capacitor. See [Android Headless Mode](github:wiki/Android-Headless-Mode)
*
* ### ⚠️ Warning:
* - You __must__ `registerHeadlessTask` in your application root file (eg: `index.js`).
*
* ### ⚠️ Warning:
* - Your `function` __must__ be declared as `async`. You must `await` all work within your task. Your headless-task will automatically be terminated after executing the last line of your function.
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* const BackgroundGeolocationHeadlessTask = async (event) => {
* const params = event.params;
* console.log("[BackgroundGeolocation HeadlessTask] -", event.name, params);
*
* switch (event.name) {
* case "terminate":
* // Use await for async tasks
* const location = await BackgroundGeolocation.getCurrentPosition({
* samples: 1,
* persist: false
* });
* console.log("[BackgroundGeolocation HeadlessTask] - getCurrentPosition:", location);
* break;
* }
* // You must await all work you do in your task.
* // Headless-tasks are automatically terminated after executing the last line of your function.
* await doWork();
* }
*
* BackgroundGeolocation.registerHeadlessTask(BackgroundGeolocationHeadlessTask);
* ```
*
* ### Debugging
*
* While implementing your headless-task It's crucial to observe your Android logs in a terminal via
*
* ```bash
* $ adb logcat *:S TSLocationManager:V ReactNativeJS:V
*
* TSLocationManager: [c.t.r.HeadlessTask onHeadlessEvent] 💀 event: connectivitychange
* TSLocationManager: [c.t.r.HeadlessTask createReactContextAndScheduleTask] initialize ReactContext
* TSLocationManager: [c.t.r.HeadlessTask onHeadlessEvent] 💀 event: providerchange
* TSLocationManager: [c.t.r.HeadlessTask onHeadlessEvent] 💀 event: terminate
* ReactNativeJS: '[BGGeoHeadlessTask] ', 'connectivitychange', taskId: 1
* TSLocationManager: [c.t.r.HeadlessTask invokeStartTask] taskId: 1
* TSLocationManager: [c.t.r.HeadlessTask invokeStartTask] taskId: 2
* TSLocationManager: [c.t.r.HeadlessTask invokeStartTask] taskId: 3
* ReactNativeJS: '[BGGeoHeadlessTask] ', 'providerchange', taskId: 2
* ReactNativeJS: '[BGGeoHeadlessTask] ', 'terminate', taskId: 3
* TSLocationManager: [c.t.l.u.BackgroundTaskManager$Task start] ⏳ startBackgroundTask: 1
* TSLocationManager: [c.t.l.u.BackgroundTaskManager$Task start] ⏳ startBackgroundTask: 2
* ReactNativeJS: *** [doWork] START
* ReactNativeJS: *** [doWork] START
* TSLocationManager: [c.t.l.u.BackgroundTaskManager$Task start] ⏳ startBackgroundTask: 3
* ReactNativeJS: *** [doWork] START
* .
* .
* .
* ReactNativeJS: *** [doWork] FINISH
* ReactNativeJS: *** [doWork] FINISH
* ReactNativeJS: *** [doWork] FINISH
* TSLocationManager: [c.t.l.u.BackgroundTaskManager$Task stop] ⏳ stopBackgroundTask: 1
* TSLocationManager: [c.t.l.u.BackgroundTaskManager$Task stop] ⏳ stopBackgroundTask: 2
* TSLocationManager: [c.t.l.u.BackgroundTaskManager$Task stop] ⏳ stopBackgroundTask: 3
* TSLocationManager: [c.t.r.HeadlessTask$1 onHeadlessJsTaskFinish] taskId: 1
* TSLocationManager: [c.t.r.HeadlessTask$1 onHeadlessJsTaskFinish] taskId: 2
* TSLocationManager: [c.t.r.HeadlessTask$1 onHeadlessJsTaskFinish] taskId: 3
* ```
*
* ### ℹ️ See also:
* - 📘 [Android Headless Mode](github:wiki/Android-Headless-Mode).
* - [[Config.enableHeadless]]
*
*/
static registerHeadlessTask(callback:(event:HeadlessEvent)=> Promise<void>): void;
/**
*
* Signal to the plugin that your app is launched and ready, proving the default [[Config]].
*
* The supplied [[Config]] will be applied **only at first install** of your app — for every launch thereafter,
* the plugin will automatically load its last-known configuration from persistent storage.
* The plugin always remembers the configuration you apply to it.
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
* desiredAccuracy: BackgroundGeolocation.DESIRED_ACCURACY_HIGH,
* distanceFilter: 10,
* stopOnTerminate: false,
* startOnBoot: true,
* url: "http://your.server.com",
* headers: {
* "my-auth-token": "secret-token"
* }
* }).then((state) => {
* console.log("[ready] success", state);
* });
* ```
*
* ### ⚠️ Warning: You must call __`.ready(confg)`__ **once** and **only** once, each time your app is launched.
* - Do not hide the call to `#ready` within a view which is loaded only by clicking a UI action. This is particularly important
* for iOS in the case where the OS relaunches your app in the background when the device is detected to be moving. If you don't ensure that `#ready` is called in this case, tracking will not resume.
*
* ### The [[reset]] method.
*
* If you wish, you can use the [[reset]] method to reset all [[Config]] options to documented default-values (with optional overrides):
*
* ### [[Config.reset]]: false
*
* Configuring the plugin with __`reset: false`__ should generally be avoided unless you know *exactly* what it does. People often find this from the *Demo* app. If you do configure `reset: false`, you'll find that your `Config` provided to `.ready` is consumed **only at first launch after install**. Thereafter, the plugin will ignore any changes you've provided there. The only way to change the config then is to use [[setConfig]].
*
* You will especially not want to use `reset: false` during development, while you're fine-tuning your `Config` options.
*
* The reason the *Demo* app uses `reset: false` is because it hosts an advanced "*Settings*" screen to tune the `Config` at runtime and we don't want those runtime changes to be overwritten by `.ready(config)` each time the app launches.
*
* ⚠️ If you *don't* undestand what __`reset: false`__ does, **NO NOT USE IT**. If you blindly copy/pasted it from the *Demo* app, **REMOVE IT** from your `Config`.
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* BackgroundGeolocation.reset();
* // Reset to documented default-values with overrides
* bgGeo.reset({
* distanceFilter: 10
* });
* ```
*/
static ready(config: Config, success?:(state:State) => void, failure?:(error:string) => void): Promise<State>;
/**
* @ignore
* __DEPRECATED__. Use [[ready]] instead.
*/
static configure(config: Config, success?:(state:State) => void, failure?:Function): Promise<State>;
/**
*
* Re-configure the SDK's [[Config]] parameters. This is the method to use when you wish to *change*
* the plugin [[Config]] *after* [[ready]] has been executed.
*
* The supplied [[Config]] will be appended to the current configuration and applied in realtime.
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* BackgroundGeolocation.setConfig({
* desiredAccuracy: Config.DESIRED_ACCURACY_HIGH,
* distanceFilter: 100.0,
* stopOnTerminate: false,
* startOnBoot: true
* }).then((state) => {
* console.log("[setConfig] success: ", state);
* })
* ```
*/
static setConfig(config: Config, success?:(state:State) => void, failure?:Function): Promise<State>;
/**
* Resets the plugin configuration to documented default-values.
*
* If an optional [[Config]] is provided, it will be applied *after* the configuration reset.
*
*/
static reset(config?:Config, success?:(state:State) => void, failure?:Function): Promise<State>;
/**
* Enable location + geofence tracking.
*
* This is the SDK's power **ON** button. The plugin will initially start into its **stationary** state, fetching an initial location before
* turning off location services. Android will be monitoring its **Activity Recognition System** while iOS will create a stationary geofence around
* the current location.
*
* ### ⚠️ Note:
* If you've configured a [[schedule]], this method will override that schedule and engage tracking immediately.
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* BackgroundGeolocation.start().then((state) => {
* console.log("[start] success - ", state);
* });
* ```
*
* ### ℹ️ See also:
* - [[stop]]
* - [[startGeofences]]
* - 📘 [Philosophy of Operation](github:wiki/Philosophy-of-Operation)
*/
static start(success?:(state:State) => void, error?:(error:string) => void): Promise<State>;
/**
* Disable location and geofence monitoring. This is the SDK's power **OFF** button.
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* BackgroundGeolocation.stop();
* ```
*
* ### ⚠️ Note:
* If you've configured a [[schedule]], **`#stop`** will **not** halt the Scheduler. You must explicitly [[stopSchedule]] as well:
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* // Later when you want to stop the Scheduler (eg: user logout)
* BackgroundGeolocation.stopSchedule();
* ```
*/
static stop(success?:(state:State) => void, error?: (error:string) => void): Promise<State>;
/**
* Manually toggles the SDK's **motion state** between **stationary** and **moving**.
*
* When provided a value of **`true`**, the plugin will engage location-services and begin aggressively tracking the device's location *immediately*,
* bypassing stationary monitoring.
*
* If you were making a "Jogging" application, this would be your **`[Start Workout]`** button to immediately begin location-tracking. Send **`false`**
* to turn **off** location-services and return the plugin to the **stationary** state.
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* BackgroundGeolocation.changePace(true); // <-- Location-services ON ("moving" state)
* BackgroundGeolocation.changePace(false); // <-- Location-services OFF ("stationary" state)
* ```
*/
static changePace(isMoving:boolean, success?: Function, failure?:(error:string) => void): Promise<void>;
/**
* Engages the geofences-only [[State.trackingMode]].
*
* In this mode, no active location-tracking will occur — only geofences will be monitored. To stop monitoring "geofences" [[TrackingMode]],
* simply use the usual [[stop]] method.
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* // Add a geofence.
* BackgroundGeolocation.addGeofence({
* notifyOnExit: true,
* radius: 200,
* identifier: "ZONE_OF_INTEREST",
* latitude: 37.234232,
* longitude: 42.234234
* });
*
* // Listen to geofence events.
* BackgroundGeolocation.onGeofence((event) => {
* console.log("[onGeofence] - ", event);
* });
*
* // Configure the plugin
* BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
* url: "http://my.server.com",
* autoSync: true
* }).then(((state) => {
* // Start monitoring geofences.
* BackgroundGeolocation.startGeofences();
* });
* ```
*
* ### ℹ️ See also:
* - [[stop]]
* - 📘 [[Geofence | Geofencing Guide]]
*/
static startGeofences(success?:(state:State) => void, failure?:(error:string) => void): Promise<State>;
/**
* Return the current [[State]] of the plugin, including all [[Config]] parameters.
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* let state = await BackgroundGeolocation.getState();
* console.log("[state] ", state.enabled, state.trackingMode);
* ```
*/
static getState(success?: (state:State) => void, failure?: (error:string) => void): Promise<State>;
/**
* Initiate the configured [[schedule]].
*
* If a [[schedule]] was configured, this method will initiate that schedule. The plugin will automatically be started or stopped according to
* the configured [[schedule]].
*
* To halt scheduled tracking, use [[stopSchedule]].
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* BackgroundGeolocation.startSchedule.then((state) => {
* console.log("[startSchedule] success: ", state);
* })
* ```
* ### ℹ️ See also:
* - [[schedule]]
* - [[startSchedule]]
*/
static startSchedule(success?: (state:State) => void, failure?: (error:string) => void): Promise<State>;
/**
* Halt scheduled tracking.
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* BackgroundGeolocation.stopSchedule.then((state) => {
* console.log("[stopSchedule] success: ", state);
* })
* ```
*
* ⚠️ [[stopSchedule]] will **not** execute [[stop]] if the plugin is currently tracking. You must explicitly execute [[stop]].
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* // Later when you want to stop the Scheduler (eg: user logout)
* await BackgroundGeolocation.stopSchedule().then((state) => {
* if (state.enabled) {
* BackgroundGeolocation.stop();
* }
* })
* ```
* ### ℹ️ See also:
* - [[startSchedule]]
*
*/
static stopSchedule(success?: (state:State) => void, failure?: (error:string) => void): Promise<State>;
/**
* Sends a signal to OS that you wish to perform a long-running task.
*
* The OS will keep your running in the background and not suspend it until you signal completion with the [[stopBackgroundTask]] method. Your callback will be provided with a single parameter `taskId`
* which you will send to the [[stopBackgroundTask]] method.
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* onLocation(location) {
* console.log("[location] ", location);
*
* // Perform some long-running task (eg: HTTP request)
* BackgroundGeolocation.startBackgroundTask().then((taskId) => {
* performLongRunningTask.then(() => {
* // When your long-running task is complete, signal completion of taskId.
* BackgroundGeolocation.stopBackgroundTask(taskId);
* }).catch(error) => {
* // Be sure to catch errors: never leave you background-task hanging.
* console.error(error);
* BackgroundGeolocation.stopBackgroundTask();
* });
* });
* }
* ```
*
* ### iOS
* The iOS implementation uses [beginBackgroundTaskWithExpirationHandler](https://developer.apple.com/documentation/uikit/uiapplication/1623031-beginbackgroundtaskwithexpiratio)
*
* ⚠️ iOS provides **exactly** 180s of background-running time. If your long-running task exceeds this time, the plugin has a fail-safe which will
* automatically [[stopBackgroundTask]] your **`taskId`** to prevent the OS from force-killing your application.
*
* Logging of iOS background tasks looks like this:
* ```
* ✅-[BackgroundTaskManager createBackgroundTask] 1
* .
* .
* .
*
* ✅-[BackgroundTaskManager stopBackgroundTask:]_block_invoke 1 OF (
* 1
* )
* ```
* ### Android
*
* The Android implementation launches a [`WorkManager`](https://developer.android.com/topic/libraries/architecture/workmanager) task.
*
* ⚠️ The Android plugin imposes a limit of **3 minutes** for your background-task before it automatically `FORCE KILL`s it.
*
*
* Logging for Android background-tasks looks like this (when you see an hourglass ⏳ icon, a foreground-service is active)
* ```
* I TSLocationManager: [c.t.l.u.BackgroundTaskManager onStartJob] ⏳ startBackgroundTask: 6
* .
* .
* .
* I TSLocationManager: [c.t.l.u.BackgroundTaskManager$Task stop] ⏳ stopBackgroundTask: 6
* ```
*
*/
static startBackgroundTask(success?: (taskId:number) => void, failure?: Function): Promise<number>;
/**
* Signal completion of [[startBackgroundTask]]
*
* Sends a signal to the native OS that your long-running task, addressed by `taskId` provided by [[startBackgroundTask]] is complete and the OS may proceed
* to suspend your application if applicable.
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* BackgroundGeolocation.startBackgroundTask().then((taskId) => {
* // Perform some long-running task (eg: HTTP request)
* performLongRunningTask.then(() => {
* // When your long-running task is complete, signal completion of taskId.
* BackgroundGeolocation.stopBackgroundTask(taskId);
* });
* });
* ```
*/
static stopBackgroundTask(taskId: number, success?: Function, failure?: Function): Promise<number>;
/**
* @alias [[stopBackgroundTask]]
* @deprecated
*/
static finish(taskId: number, success?: Function, failure?: Function): Promise<number>;
/**
* @private
* __[Android-only]__ Signals completion of an Android headless-task (see [[Config.enableHeadless]])
*/
static finishHeadlessTask(taskId: number, success?: Function, failure?: Function): Promise<number>;
/**
* Retrieves the current [[Location]].
*
* This method instructs the native code to fetch exactly one location using maximum power & accuracy. The native code will persist the fetched location to
* its SQLite database just as any other location in addition to POSTing to your configured [[Config.url]].
* If an error occurs while fetching the location, `catch` will be provided with an [[LocationError]].
* @break
*
* ### Options
*
* See [[CurrentPositionRequest]].
*
* ### Error Codes
*
* See [[LocationError]].
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* let location = await BackgroundGeolocation.getCurrentPosition({
* timeout: 30, // 30 second timeout to fetch location
* maximumAge: 5000, // Accept the last-known-location if not older than 5000 ms.
* desiredAccuracy: 10, // Try to fetch a location with an accuracy of `10` meters.
* samples: 3, // How many location samples to attempt.
* extras: { // Custom meta-data.
* "route_id": 123
* }
* });
* ```
* ### ⚠️ Note:
* - While [[getCurrentPosition]] will receive only **one** [[Location]], the plugin *does* request **multiple** location samples which will all be provided
* to the [[onLocation]] event-listener. You can detect these samples via [[Location.sample]] `== true`.
*/
static getCurrentPosition(options: CurrentPositionRequest, success?:(location:Location) => void, failure?:(errorCode:LocationError) => void): Promise<Location>;
/**
* Start a stream of continuous location-updates. The native code will persist the fetched location to its SQLite database
* just as any other location (If the SDK is currently [[State.enabled]]) in addition to POSTing to your configured [[Config.url]] (if you've enabled the HTTP features).
*
* ### ⚠️ Warning:
* `watchPosition` is **not** recommended for **long term** monitoring in the background — It's primarily designed for use in the foreground **only**. You might use it for fast-updates of the user's current position on the map, for example.
* The SDK's primary [Philosophy of Operation](github:wiki/Philosophy-of-Operation) **does not require** `watchPosition`.
*
* #### iOS
* `watchPosition` will continue to run in the background, preventing iOS from suspending your application. Take care to listen to `suspend` event and call [[stopWatchPosition]] if you don't want your app to keep running in the background, consuming battery.
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* onResume() {
* // Start watching position while app in foreground.
* BackgroundGeolocation.watchPosition((location) => {
* console.log("[watchPosition] -", location);
* }, (errorCode) => {
* console.log("[watchPosition] ERROR -", errorCode);
* }, {
* interval: 1000
* })
* }
*
* onSuspend() {
* // Halt watching position when app goes to background.
* BackgroundGeolocation.stopWatchPosition();
* }
* ```
*/
static watchPosition(success: (location:Location) => void, failure?: (errorCode:LocationError) => void, options?: WatchPositionRequest): void;
/**
* Stop watch-position updates initiated from [[watchPosition]].
* @example
* ```typescript
* onResume() {
* // Start watching position while app in foreground.
* BackgroundGeolocation.watchPosition((location) => {
* console.log("[watchPosition] -", location);
* }, (errorCode) => {
* console.log("[watchPosition] ERROR -", errorCode);
* }, {
* interval: 1000
* })
* }
*
* onSuspend() {
* // Halt watching position when app goes to background.
* BackgroundGeolocation.stopWatchPosition();
* }
* ```
* ### ℹ️ See also:
* - [[stopWatchPosition]]
*
*/
static stopWatchPosition(success?: Function, failure?: Function): Promise<void>;
/**
* Retrieve a List of [[Location]] currently stored in the SDK's SQLite database.
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* let locations = await BackgroundGeolocation.getLocations();
* ```
*/
static getLocations(success?:(locations:Array<Object>) => void, failure?:Function): Promise<Array<Object>>;
/**
* Retrieve the count of all locations current stored in the SDK's SQLite database.
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* let count = await BackgroundGeolocation.getCount();
* ```
*/
static getCount(success?:(count:number)=>void, failure?:Function): Promise<number>;
/**
* Remove all records in SDK's SQLite database.
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* let success = await BackgroundGeolocation.destroyLocations();
* ```
*/
static destroyLocations(success?:F