react-native-attitude
Version:
Obtain device attitude (roll, pitch and heading)
271 lines (151 loc) • 6.15 kB
Markdown
# react-native-attitude
** THIS MODULE IS NO LONGER MAINTAINED **
PLEASE USE MY NEW MODULE [react-native-ahrs](https://github.com/dpyeates/react-native-ahrs)
This module provides device attitude (Roll, Pitch & Heading) in degrees for iOS and Android.<br/>
It uses a reference frame that assumes the user is looking 'through' the screen - typical to many augmented reality applications.<br/>
It uses Core Motion Quaternions on iOS and the Rotation Vector sensor on Android.
## Getting started
`yarn add react-native-attitude`
or
`npm install react-native-attitude --save`
Since ****react-native 0.60**** and higher, [autolinking](https://github.com/react-native-community/cli/blob/master/docs/autolinking.md) makes the installation process simpler.<br/>
If you are using React Native 0.60 or higher, no other installation steps are required.
### Manual installation (react-native 0.59 and lower)
<details>
<summary>Manually link the library on iOS</summary>
### `Open RNAttitude.xcodeproj in Xcode`
Drag `RNAttitude.xcodeproj` to your project on Xcode (usually under the Libraries group on Xcode):
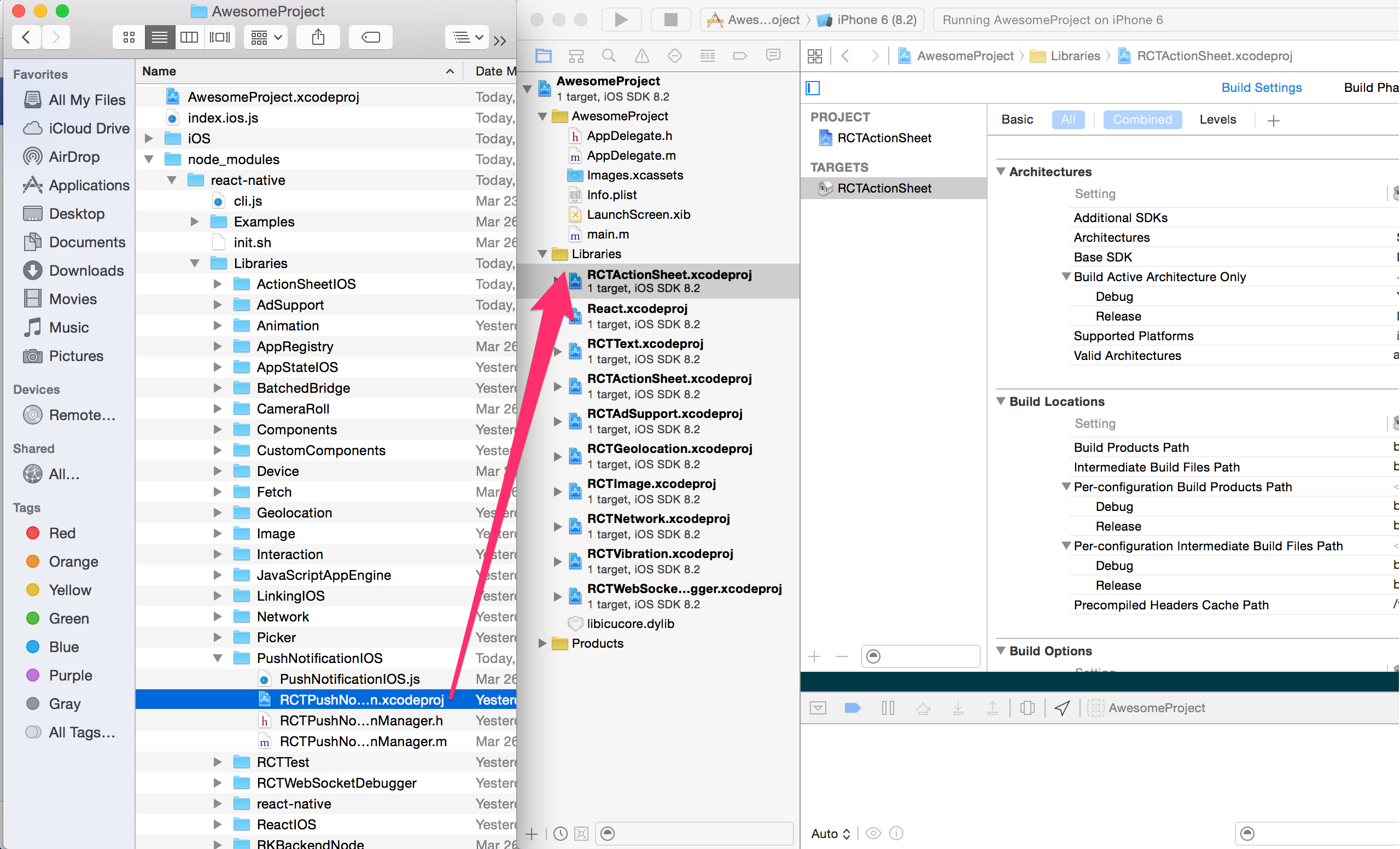
### Link `libRNAttitude.a` binary with libraries
Click on your main project file (the one that represents the `.xcodeproj`) select `Build Phases` and drag the static library from the `Products` folder inside the Library you are importing to `Link Binary With Libraries` (or use the `+` sign and choose library from the list):

### Using CocoaPods
Update your `Podfile`
```
pod 'react-native-attitude', path: '../node_modules/react-native-attitude'
```
</details>
<details>
<summary>Manually link the library on Android</summary>
#### `android/settings.gradle`
```groovy
include ':react-native-attitude'
project(':react-native-attitude').projectDir = new File(rootProject.projectDir, '../node_modules/react-native-attitude/android')
```
#### `android/app/build.gradle`
```groovy
dependencies {
...
implementation project(':react-native-attitude')
}
```
#### `android/app/src/main/.../MainApplication.java`
On top, where imports are:
```java
import com.sensorworks.RNAttitudePackage;
```
Add the `RNAttitudePackage` class to your list of exported packages.
```java
@Override
protected List<ReactPackage> getPackages() {
return Arrays.asList(
new MainReactPackage(),
new RNAttitudePackage()
);
}
```
</details>
## Usage
### Example
```javascript
import Attitude from 'react-native-attitude';
Attitude.watch((payload) => {});
```
## Methods
* [`isSupported`](#issupported)
* [`setInterval`](#setinterval)
* [`setRotation`](#setRotation)
* [`zero`](#zero)
* [`reset`](#reset)
* [`watch`](#watch)
* [`clearWatch`](#clearwatch)
* [`stopObserving`](#stopobserving)
## Details
#### `isSupported()`
Checks to see if attitude updates are supported on the device.<br/>
This always returns true on iOS devices.
```javascript
const isSupported = await Attitude.isSupported();
```
#### `setInterval()`
Optionally request an update interval in ms. The default update rate is (approx) 20ms, i.e. 5Hz.<br/>
This is a request - updates may come slower than the rate you specify, but never faster.
```javascript
// request updates once every second
Attitude.setInterval(1000);
```
#### `setRotationl(['none', 'left' or 'right']])`
Optionally tell the module if you would like the results rotated. This is typically used when the phone/device is in a rotated state. The module defaults to 'none', which for most devices means no rotation or 'portrait' screen orientation. Passing 'left' to setRotation is used when the device has rotated to landscape left (top of phone/device when you look at it is rotated left by 90 degrees). Passing 'right' to setRotation is used when the device has rotated to landscape right (top of phone/device when you look at it is rotated right by 90 degrees)
NOTE: Version 1 of this module did this automatically within the module but this sometimes meant there was a conflict between the native side and the javascript side. Version 2 of this modules pulls this out and makes it explicit.
```javascript
// set the device rotation to either 'none', 'left' or 'right'
Attitude.setRotation('none'); // default
Attitude.setRotation('left');
Attitude.setRotation('right');
```
#### `zero()`
Levels pitch and roll according to the current attitude. This can be used to null the device if it is oriented away from level.
```javascript
// level both pitch and roll
Attitude.zero();
```
#### `reset()`
Resets any previous calls to `zero()`.
```javascript
Attitude.reset();
```
#### `watch()`
```javascript
Attitude.watch(success);
```
Invokes the success callback whenever the attitude changes.
The payload delivered via the callback is defined in the example below.
Returns a `watchId` (number).
****Parameters:****
| Name | Type | Required | Description |
| ------- | -------- | -------- | ----------------------------------------- |
| success | function | Yes | Invoked at a default interval of 5hz This can be changed by using the setInterval method. |
****Example:****
```javascript
const watchId = Attitude.watch((payload) =>{
/*
payload.timestamp - sample time in ms referenced to January 1, 1970 UTC
payload.roll - roll in degrees -180<-->180
payload.pitch - pitch in degrees -90<-->90
payload.heading - heading in degrees 0-->360
*/
);
```
#### `clearWatch()`
```javascript
Attitude.clearWatch(watchID);
```
****Parameters:****
| Name | Type | Required | Description |
| ------- | ------ | -------- | ------------------------------------ |
| watchID | number | Yes | Id as returned by `watch()`. |
#### `stopObserving()`
```javascript
Attitude.stopObserving();
```
Stops observing for all attitude updates.
In addition, it removes all listeners previously registered.
Note that this method does nothing if the `Attitude.watch(successCallback)` method has not previously been called.