prismaql-cli
Version:
CLI tool for managing and editing Prisma schema files using PrismaQL DSL.
365 lines (249 loc) • 13.5 kB
Markdown
# PrismaQL CLI - Command-Line Interface for Prisma Schema Management
[](https://www.npmjs.com/package/prismaql-cli)
[](LICENSE.md)
[](https://github.com/unbywyd/prismaql-cli/issues)
[](https://github.com/unbywyd/prismaql-cli)
## Introduction
**PrismaQL CLI** is a command-line tool that leverages the **PrismaQL Core** engine to manage and edit **Prisma schemas** via a **SQL-like DSL**. It allows you to execute **query** and **mutation** commands directly in your terminal, enabling everything from listing models to creating complex relations.
Key advantages:
- **Declarative Command Syntax** – Intuitive and human-readable commands like `GET MODELS`, `ADD FIELD`, and more.
- **Query & Mutation Separation** – Clear distinction between read-only operations (`GET`, `PRINT`, `VALIDATE`) and modifying ones (`ADD`, `DELETE`, `UPDATE`).
- **Configurable Workflow** – Easily extend and integrate custom handlers for queries and mutations.
- **Safe & Reversible Edits** – Built-in validation with automatic backups to ensure data integrity.
- **Flexible Relation Management** – Supports **1:1, 1:M, and M:N** relationships, including **pivot table-based relations**. Allows both **direct** and **indirect** (foreign-key-only) associations, with the ability to choose the **FK holder side** for precise schema control.
## How It Works
1. **Parsing DSL** – Raw text commands (e.g. `GET MODEL User;`) go through the **PrismaQlDslParser**, producing a structured object.
2. **Chained Commands** – You can chain multiple commands in a single line, separated by semicolons, and they will be executed sequentially.
3. **Validation & Execution** – Queries simply inspect the schema; mutations modify it, ensuring AST-level integrity.
4. **Backup & Save** – Each mutation can undergo a dry run, then save changes. Old versions are stored in `.prisma/backups`.
5. **Extensible Handlers** – You can register **query** or **mutation** handlers to shape how commands are processed.
### Example Commands
```bash
prismaql "ADD MODEL User ({name String}); ADD MODEL Profile ({age Int})(empty); ADD RELATION User AND Profile (type=1:M, fkHolder=Profile); GET RELATIONS Profile;" --dry
```
#### 📸 Result
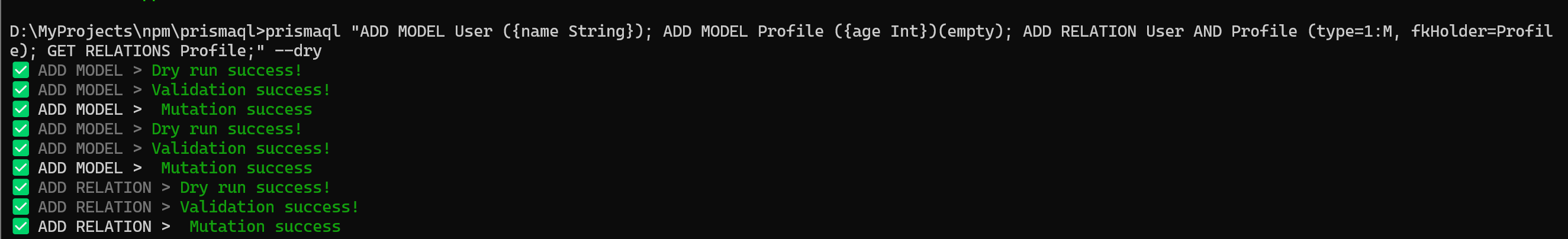
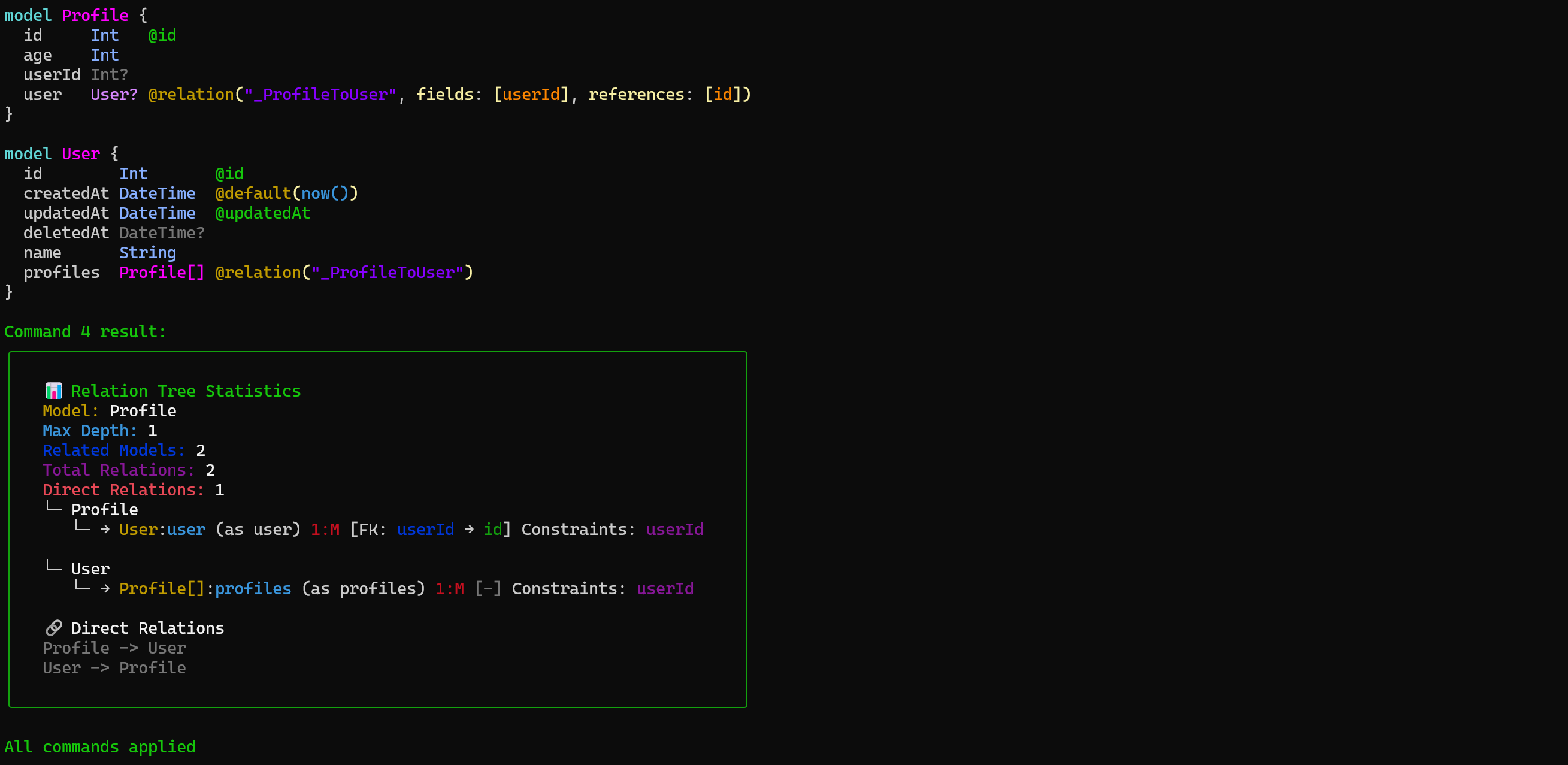
---
## Installation
Install globally using npm:
```bash
npm install -g prismaql-cli
```
This will give you the `prismaql` command in your terminal.
---
## Command Pattern
A command typically follows this structure:
```
ACTION COMMAND ...args ({PRISMA_BLOCK}) (OPTIONS);
```
- **ACTION** – One of `GET`, `PRINT`, `VALIDATE`, `ADD`, `DELETE`, `UPDATE`.
- **COMMAND** – A specific target (e.g., `MODEL`, `RELATION`, `ENUM`, `GENERATORS`, `GENERATOR`).
- **ARGS** – Varies by command (e.g., `User`, `User,Post`, `fieldName`).
- **PRISMA_BLOCK** – An optional Prisma snippet in `({ ... })` format, used for model/field definitions.
- **OPTIONS** – Additional parameters in `(key=value, flag, ...)` format.
---
## Basic Usage
```bash
prismaql <command> [--dry]
```
- **`<command>`** – A PrismaQL DSL command like `GET MODELS;`, `ADD FIELD name TO User ({String});`, etc.
- **`--dry`** – (Optional) Performs a dry run without applying any changes to the schema.
### Examples
```bash
# Query all models
prismaql "GET MODELS;"
# Add a new field
prismaql "ADD FIELD email TO User ({String @unique});"
# Remove a model
prismaql "DELETE MODEL TempData;"
```
---
## Supported Commands
PrismaQL CLI supports the same **Query** and **Mutation** commands as the core library:
### 1. Query Commands
- `GET MODELS` – List all models with highlighting.
- `GET MODEL <name> (empty?)` – Show details for a specific model (fields, relations, etc.).
- `GET ENUM_RELATIONS <enum>` – Show references to a specific enum across models.
- `GET FIELDS <model>` – List fields for a model.
- `GET FIELDS <field,field2> IN <model>` – Show specific fields.
- `GET RELATIONS <model,model2> (depth?=1)` – Display relations; optionally set a depth.
- `GET ENUMS (raw?)` / `GET ENUMS <enum, ...>` – Show one or more enums.
- `GET MODELS_LIST` – Display a sorted list of all models.
- `PRINT` – Print the entire schema in color.
- `GET DB` – Show the current database connection.
- `GET GENERATORS` – List all generators.
- `VALIDATE` – Validate the schema.
### 2. Mutation Commands
- `ADD MODEL <name> ({...})` – Create a new model with a Prisma block.
- `ADD FIELD <name> TO <model> ({String})` – Add a field to a model.
- `ADD RELATION <modelA> AND <modelB> (type=1:M, ...)` – Create a relation between two models.
- `ADD ENUM <name> ({A|B|C})` – Create a new enum.
- `DELETE MODEL <name>` – Delete a model.
- `DELETE FIELD <name> IN <model>` – Remove a field.
- `DELETE RELATION <modelA>, <modelB> (relationName=...)` – Remove a relation.
- `DELETE ENUM <name>` – Delete an enum.
- `UPDATE FIELD <name> IN <model> ({...})` – Recreate a field (caution).
- `UPDATE ENUM <name> ({A|B}) (replace=?)` – Append or replace enum values.
- `UPDATE DB (url='...', provider='...')` – Update the database connection.
- `UPDATE GENERATOR <name> ({...}) (provider='...', output='...')` – Update a generator.
- `ADD GENERATOR <name> ({...})` – Add a new generator.
- `DELETE GENERATOR <name>` – Remove a generator.
Each command follows the **`ACTION COMMAND ARGS (PRISMA_BLOCK) (OPTIONS)`** pattern.
---
## Query Commands (READ-ONLY)
### `GET MODELS`
- **Description**: Lists all models with syntax highlighting.
- **Usage**: `GET MODELS;`
### `GET MODEL <name>`
- **Description**: Shows a detailed view of a specific model, including required fields and relations.
- **Usage**: `GET MODEL User;`
### `GET ENUM_RELATIONS <enum>`
- **Description**: Displays all models and fields referencing a specific enum.
- **Usage**: `GET ENUM_RELATIONS UserRoleEnum;`
### `GET FIELDS <model>`
- **Description**: Lists all fields of a given model.
- **Usage**: `GET FIELDS User;`
### `GET FIELDS <field, field2> IN <model>`
- **Description**: Retrieves and filters specific fields of a model.
- **Usage**: `GET FIELDS name, email IN User;`
### `GET RELATIONS <model, model2> (depth?=1)`
- **Description**: Shows relations among specified models. Accepts an optional depth.
- **Usage**: `GET RELATIONS User, Post (depth=2);`
### `GET DB`
- **Description**: Outputs the provider's current database connection and url.
- **Usage**: `GET DB;`
### `GET GENERATORS`
- **Description**: Lists all generators in the schema.
- **Usage**: `GET GENERATORS;`
### `GET ENUMS (raw?)`
- **Description**: Lists all enums in a formatted or raw representation.
- **Usage**: `GET ENUMS (raw=true);`
### `GET ENUMS <enum, enum>`
- **Description**: Filters and displays specific enums.
- **Usage**: `GET ENUMS UserRole, AnotherEnum;`
### `GET MODELS_LIST`
- **Description**: Outputs all model names in a sorted list.
- **Usage**: `GET MODELS_LIST;`
### `PRINT`
- **Description**: Prints the entire schema with color formatting.
- **Usage**: `PRINT;`
### `VALIDATE`
- **Description**: Validates the current schema, checking for errors.
- **Usage**: `VALIDATE;`
---
## Mutation Commands (WRITE OPERATIONS)
### `ADD MODEL <name> ({...})`
- **Description**: Creates a new model. Requires two parameters: `name` and a **Prisma block** with fields.
- **Example**: `ADD MODEL User ({ id Int @id @default(autoincrement()) | name String });`
- **`empty`** – If specified, the model is created without fields (creadtAt, updatedAt, deletedAt are added by default).
### `ADD FIELD <name> TO <model> ({String})`
- **Description**: Adds a new field to a model. Requires the field name, the model name, and a Prisma block describing field attributes.
- **Example**: `ADD FIELD email TO User ({String @unique});`
### `ADD RELATION <modelA> AND <modelB> (...options)`
- **Description**: Creates a relation between two models. Supports multiple options:
- **`type`** (required): Defines the relation type: `"1:1" | "1:M" | "M:N"`.
- **`pivotTable`** (optional): `string | true`. If `true`, a pivot table is created automatically. In `1:1` or `1:M`, it can create an intermediate table.
- **`fkHolder`** (optional): Specifies which model holds the foreign key.
- **`required`** (optional): Marks the relation as required (`true`) or optional (`false`). Defaults to `true`.
- **`relationName`** (optional): Custom relation name. If omitted, a name is generated.
- **Example**:
```
ADD RELATION User TO Profile (
type=1:1,
pivotTable=true,
fkHolder=User,
required=false,
relationName=UserProfile
);
```
### `ADD ENUM <name> ({A|B|C})`
- **Description**: Creates a new enum. The block can include values separated by `|`.
- **Example**: `ADD ENUM Role ({ADMIN|USER|SUPERUSER});`
### `DELETE MODEL <name>`
- **Description**: Removes a model by name.
- **Example**: `DELETE MODEL TempData;`
### `DELETE FIELD <name> IN <model>`
- **Description**: Removes a specific field from a model.
- **Example**: `DELETE FIELD email IN User;`
### `DELETE RELATION <modelA>, <modelB> (...options)`
- **Description**: Unlinks relations between two models. If no options are passed, **all** relations between them are removed.
- **`fieldA`** (optional): Field name on Model A.
- **`fieldB`** (optional): Field name on Model B.
- **`relationName`** (optional): If a relation was named via `@relation("myRel")`, specify it here.
- **Example**:
```
DELETE RELATION User, Post (
fieldA=userId,
fieldB=authorId,
relationName=UserPosts
);
```
### `DELETE ENUM <name>`
- **Description**: Removes an existing enum.
- **Example**: `DELETE ENUM Role;`
### `UPDATE FIELD <name> IN <model> ({...})`
- **Description**: Recreates the specified field in a model, which can break migrations if used carelessly.
- **Example**: `UPDATE FIELD email IN User ({String @unique @db.VarChar(255)});`
### `UPDATE ENUM <name> ({A|B})(replace?)`
- **Description**: Updates an enum. By default, new values are appended; with `replace=true`, the existing enum is replaced.
- **Example**:
```
UPDATE ENUM Role ({ADMIN|SUPERADMIN}) (replace=true);
```
### `UPDATE DB (url='...', provider='...')`
- **Description**: Updates the database connection URL and provider.
- **Example**:
```
UPDATE DB (
url='mysql://user:password@localhost:3306/db',
provider='mysql'
);
```
### `UPDATE GENERATOR <name> ({...})(provider='...', output='...')`
- **Description**: Updates a generator with new options.
- **Example**:
```
UPDATE GENERATOR client ({provider='prisma-client-js', output='@prisma/client'});
```
### `ADD GENERATOR <name> ({...})`
- **Description**: Adds a new generator to the schema.
- **Example**:
```
ADD GENERATOR client ({provider='', output=''});
```
### `DELETE GENERATOR <name>`
- **Description**: Removes a generator from the schema.
- **Example**:
```
DELETE GENERATOR client;
```
---
## Dry Run and Confirmation
- **`--dry`** – When you append this flag, the command simulates changes but **does not** modify the schema. This is useful for verifying correctness.
- **Confirmation Hooks** – If you integrate the CLI with a script, you can prompt users for confirmation after seeing the changes (the CLI provides a confirmation mechanism in interactive scenarios).
---
## Backup and Restore
By default, whenever the CLI applies a **mutation**, it stores the previous schema version under `.prisma/backups`. This helps to:
- **Rollback** if something breaks.
- **Track** incremental changes over time.
---
## CLI Workflow
1. **Prepare your Prisma schema** – Typically located in `prisma/schema.prisma`.
2. **Issue commands** – Use DSL statements like `GET MODELS`, `ADD FIELD`, etc.
3. **(Optional) Dry Run** – Evaluate changes with `--dry`.
4. **Apply & Backup** – The CLI commits changes to the schema, backing up the old version.
5. **Validate** – Run `VALIDATE` to ensure the schema remains consistent.
---
## Common Tips
- **Always Validate** – Use `VALIDATE` after major changes.
- **Use Dry Runs** – For complex changes, do a dry run first to ensure correctness.
- **Look for .prisma/backups** – If something goes wrong, you can restore from backups.
- **Combine Commands** – You can pass multiple statements separated by semicolons.
---
## Project Status
- **Contributions Welcome** – Please report issues and PRs on [GitHub](https://github.com/unbywyd/prismaql-cli).
---
## License
PrismaQL CLI is licensed under the **MIT License**.
© 2025 [Artyom Gorlovetskiy](https://unbywyd.com).