otp-without-db
Version:
Database less OTP verification with cryptography
95 lines (53 loc) • 4.18 kB
Markdown
## OTP verification using Cryptography and without any Database
#### Background
This module is derived from my blog post on the technique. You can read the [blog post here](https://blog.anam.co/otp-verification-without-using-a-database/) to understand the technique and motivation.
#### Dependencies:
This module depends on the [Crypto](https://nodejs.org/api/crypto.html) built in module on nodeJS. This is the only dependency and should work in any system that has crypto support (Which is technocally majority of the systems at this moment)
This module also uses some modern JavaScript features like Template literals, Default arguments and modern object literal. This might be a problem if you are planning to use it with older versions of nodeJS
#### Installation
You can use npm to install the package with the following code
npm install --save otp-without-db
#### Usage
You need additional tool to create OTP, and send SMS. This module only takes care of the verification part.
You can take a look at the [otp-generator](https://www.npmjs.com/package/otp-generator) module to create OTP for your users.
#### Verification process
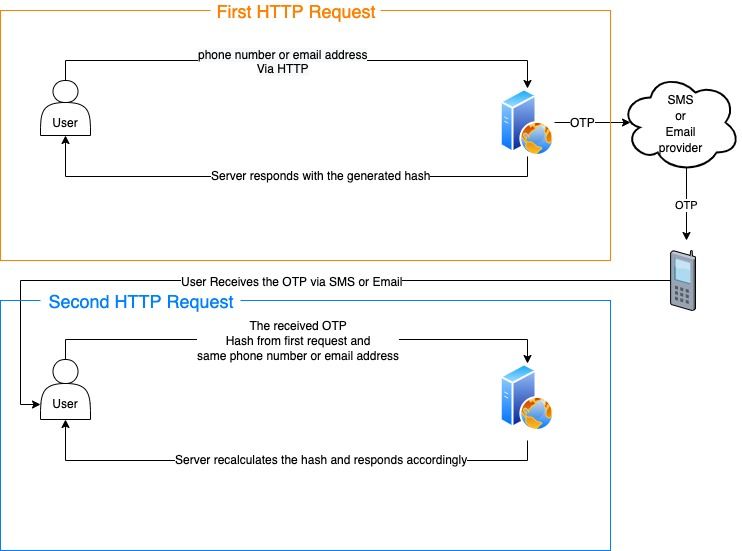
OTP verification is done in the following steps:
1. A hash is created with the phone number/email address and then sent to the user.
2. The user also receives the OTP via SMS, email or any other method.
3. The user sends back the hash, OTP and phone/email used in the first request.
4. The server verifies the information and returns true if they match.
Here's a diagram that shows the whole process:
#### Generating OTP Hash
We will use the [otp-generator](https://www.npmjs.com/package/otp-generator) tool mentioned previously to create OTP. You can use any other tool or technique.
const otpGen = require("otp-generator");
const otpTool = require("otp-without-db");
const key = "secretKey"; // Use unique key and keep it secret
let phone = "88017009090";
let otp = otpGen.generate(6, { upperCase: false, specialChars: false, alphabets: false });
let hash = otpTool.createNewOTP(phone,otp,key);
You can then send this hash to the user as response. The generate method takes these following arguments (In particular order),
createNewOTP(phoneOrEmail,otp,key="",expiresAfter=5,algorithm="sha256")
| Argument | Required | default | Description |
| ------------- | -------- | ------- | -------------- |
| phoneOrEmail | true | N/A | Phone or email |
| otp | true | N/A | OTP |
| key | false | "" | unique and secret key for HMAC see: [createHmac](https://nodejs.org/api/crypto.html#crypto_crypto_createhmac_algorithm_key_options)|
| expiresAfter | false | 5 | Expirty in minutes|
| algorithm | false | `sha256`| Algorithm used for hashing the data. Any supported algorithm from OpenSSL|
#### Verifying OTP hash
The user should get the hash from the HTTP request and should get the real OTP via SMS or email.
Then when the user sends back the information, they can be verified with the following code:
otpTool.verifyOTP(phone,otp,hash,key);
This method returns a **Boolean**. If the verification is successful, it will return true.
This method also takes the following arguments in particular order:
verifyOTP(phone,otp,hash,key="",algorithm="sha256")
| Argument | Required | default | Description |
| ------------- | -------- | ------- | -------------- |
| phoneOrEmail | true | N/A | Phone or email |
| otp | true | N/A | OTP |
| hash | true | N/A | The hash that was returned from the user |
| key | false | "" | unique and secret key for HMAC see: [createHmac](https://nodejs.org/api/crypto.html#crypto_crypto_createhmac_algorithm_key_options)|
| algorithm | false | `sha256`| Algorithm used for hashing the data. Any supported algorithm from OpenSSL|
******
This product is created with 🖤 by [Anam Ahmed](https://anam.co), Any improvements and PR is welcome.