node-red-contrib-tak-registration
Version:
A Node-RED node to register to TAK and to help wrap files as datapackages to send to TAK
88 lines (51 loc) • 5.12 kB
Markdown
node-red-contrib-tak-registration
=================================
A <a href="http://nodered.org" target="_new">Node-RED</a> node to register to a TAK server, to help wrap and send
files as datapackages for TAK, and to create and update markers from json messages.
**NOTE**: NOT yet for production use.
## Install
Either use the Menu - Manage Palette - Install option, or run the following command in your Node-RED user
directory - typically `~/.node-red`
npm i node-red-contrib-tak-registration
## TAK-Registration Node Usage
Registers a TAK gateway node and sets up a heartbeat.
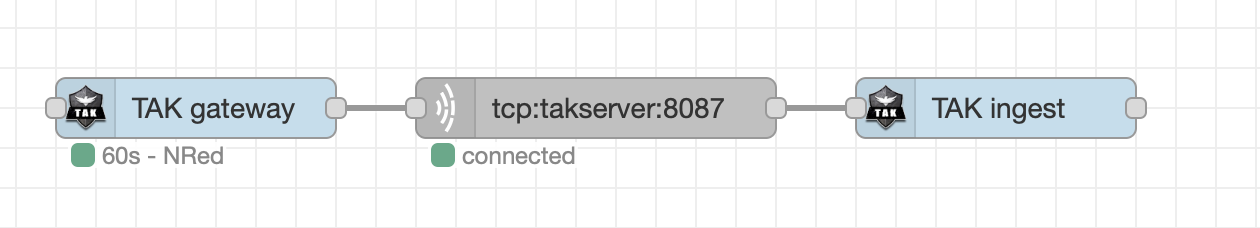
It must be connected to a TCP request node, configured to point to the TAK server tcp address and port
(usually 8087 or 8089), set to return strings, <i>keep connection open</i> mode, and split on "</event>".
It can send various types of messages to TAK.
It should be configured with a name, and location.
As it registers to the gateway it should be possible for other team members to send messages and markers to the gateway.
### Standard COT event
If the `msg.payload` is an XML string it will be passed directly though. It should be a correctly formatted CoT XML message of course.
### Sending marker position...
To create or update a simple marker send a msg with the following property
- **payload** - *object* - a "standard" node-red worldmap format - IE a msg.payload containing `name, lat, lon, SIDC or cottype or aistype, (alt), (speed), (bearing), (layer), (remarks)`, where `SIDC` is the standard mil 2525C code, eg SFGPU, `cottype` is the CoT type, eg a-f-g-u, or `aistype` is the AIS ship type number, eg 80 for a tanker. The `layer` will get turned into a hashtag which can then be selected on/off in the TAK app layers control, and any `remarks` will get added to the CoT remarks field.
### Simple GeoChat messages
requires a `msg` containing the following properties
- **sendTo** - *string | array* - can either be an individual TAK callsign, a comma separted list of callsigns, an array of callsigns, or **broadcast** to send to all users.
- **payload** - *string* - the text of the message to send.
### Sending data packages...
requires a `msg` containing the following properties
- **sendTo** - *string | array* - can either be an individual TAK callsign, an array of callsigns, or **broadcast** to send to all users, or **public** to just upload the package to the TAK server.
- **topic** - *string* - the overall package name - IE what you want it to be called on the TAK device (keep it short).
- **attachments** - *array of objects* - each object must contain at least a **filename** (string) and **content** a buffer of the file/data, for example `[{filename:"foo.kml", content: <buffer of the file>}]`
- **from** - *string* - (optional) callsign of the person sending the file - defaults to the gateway node callsign.
- **lat** - *number | (string)* - (optional) latitude of the marker for the file.
- **lon** - *number | (string)* - (optional) longitude of the marker for the file.
If you just need to send a single file then instead of msg.attachments you can use `msg.filename` to set the filename, and the `msg.payload` should be a binary buffer.
### Sending drawing layer...
The node will also accept drawing type messages incoming from the drawing layer of the
[node-red-contrib-web-worldmap](https://flows.nodered.org/node/node-red-contrib-web-worldmap),
and convert them to CoT objects for display. To do this configure a *worldmap-in* node to pass on drawing layer messages.
### Updating the gateway position...
To update the location of the gateway dynamically the node can accept a payload
- **payload** - *string | object* - Either an NMEA string starting `$GPGGA` (for example from a locally attached serial GPS device) - or an object containing only `lat` and `lon` and optional `alt` properties (**but no name** property).
### Details
This should work almost directly with messages received from an email-in node for example - but you will need to add the recipients in the sendTo property and may need to filter out unwanted messages first.
## TAK-Ingest Node Usage
This node can accept input direct from a TCP request node, configured to point to the TAK server tcp address and port (usually 8087 or 8089), set to return strings, *keep connection open* mode, and split on "</event>". This can be same TCP node as used by the TAK-registration node above.
It will produce a well formatted JSON object containing the event. It is returned as **msg.payload.event**
**msg.topic** is set to the COT type.
If an event arrives with a *fileshare* link, it will fetch the file and add **msg.filename** and **msg.datapackage** to the output msg. The datapackage will be a buffer.
It can also accept input from a UDP node configured to listen to *multicast* on group 239.2.3.1 port 6969. The JSON object produced contains similar information but formatted/organised slightly differently. (Very annoying).
It is returned as **msg.payload.cotEvent**