node-less-otp
Version:
A super lightweight library for generating and verifying one-time passwords (OTPs) without the database interaction and additional dependencies.
297 lines (208 loc) • 8.26 kB
Markdown
# node-less-otp
A super lightweight Node.js stateless authentication library for generating and verifying one-time passwords (OTPs) without the database interaction and additional dependencies. TS is fully supported out of the box.
## Table of Contents
- [Installation](#installation)
- [Usage](#usage)
- [API Documentation](#api-documentation)
- [LessOtpConfig](#lessotpconfig)
- [GenerateOptions](#generateoptions)
- [LessOtp Class](#lessotp-class)
- [constructor](#constructor)
- [gen](#gen)
- [verify](#verify)
- [Examples](#examples)
- [License](#license)
## Installation
You can install the `node-less-otp` library via npm:
```bash
npm install node-less-otp
```
## Usage
To use the `node-less-otp` library, import the class and create an instance by passing your configuration. You can then generate and verify OTPs.
```javascript
import LessOtp from "node-less-otp";
const otp = new LessOtp({
secretSalt: "your_secret_salt", // Optional
algorithm: "aes-256-cbc", // Optional
ivLength: 16, // Optional
enableSet: false, // Optional, not recommended (default: true)
});
```
## API Documentation
### Example Use Case
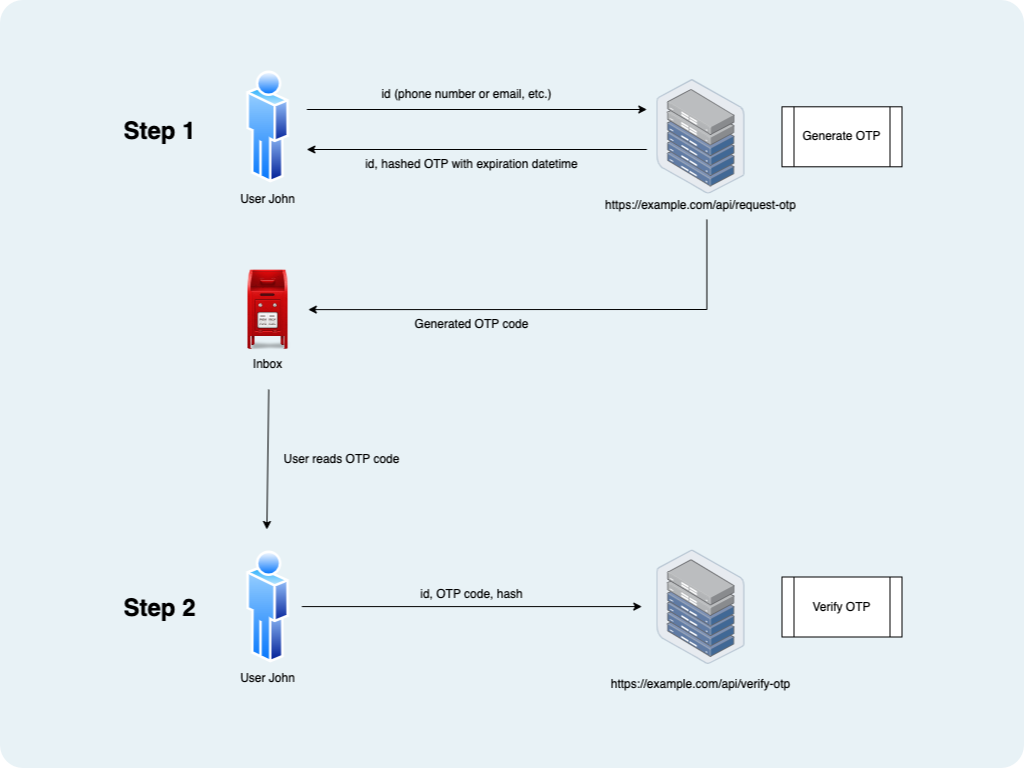
### LessOtpConfig
The configuration for the `LessOtp` instance:
| Parameter | Type | Description |
| ------------ | ------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| `secretSalt` | string | Optional secret salt used for encryption (if left blank, the random key is generated). |
| `algorithm` | string | Optional encryption algorithm (default: 'aes-256-cbc'). |
| `ivLength` | number | Optional initialization vector length (default: 16). |
| `enableSet` | boolean | Optional flag that indicates whether to enable the OTP hash set to ensure each code is only used once (enabled by default, setting to false is not recommended). |
### GenerateOptions
Options for OTP generation:
| Parameter | Type | Description |
| ---------- | ------ | --------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| `template` | string | Optional template for OTP generation (see examples). |
| `ttl` | number | Optional time-to-live in seconds for the generated OTP (default: Infinity). |
### LessOtp Class
#### constructor
Creates an instance of the `LessOtp` class.
```javascript
const otp = new LessOtp(config: LessOtpConfig);
```
#### gen
Generates an OTP based on a unique identifier and generation options.
```javascript
const { otp, hash } = await otp.gen(id: string, options: GenerateOptions);
```
- **Parameters**:
- `id`: Unique identifier (e.g., phone number, email, username).
- `options`: Generation options.
- **Returns**: An object containing the generated OTP and its encrypted hash.
#### verify
Verifies the OTP by comparing it with the decrypted OTP hash.
```javascript
const isValid = otp.verify(id: string, hash: string, submitted: string);
```
- **Parameters**:
- `id`: Unique identifier.
- `hash`: Encrypted OTP hash.
- `submitted`: Submitted OTP to verify.
- **Returns**: `true` if the OTP is valid; otherwise, `false`.
### Data
The data returned after generating an OTP (internal type, you can ignore it in this context):
| Parameter | Type | Description |
| ----------- | ------ | ------------------------------------------ |
| `otp` | string | The generated OTP. |
| `expiresAt` | number | Timestamp indicating when the OTP expires. |
## Examples
### Generating an OTP
#### Example 1: Numeric OTP
```javascript
const otp = new LessOtp({ secretSalt: "your_secret_salt" });
const { otp: generatedOtp, hash } = await otp.gen("user@example.com", {
template: "N{6}",
ttl: 300,
});
console.log("Generated Numeric OTP:", generatedOtp); // e.g., 491945
console.log("Encrypted Hash:", hash);
```
#### Example 2: Alphanumeric OTP
```javascript
const { otp: generatedOtp, hash } = await otp.gen("user@example.com", {
template: "A{8}",
ttl: 300,
});
console.log("Generated Alphanumeric OTP:", generatedOtp); // e.g., 1aB2cD3e
console.log("Encrypted Hash:", hash);
```
#### Example 3: Mixed-case Letters with Numbers
```javascript
const { otp: generatedOtp, hash } = await otp.gen("user@example.com", {
template: "M{4}-N{2}",
ttl: 300,
});
console.log("Generated Mixed-case OTP:", generatedOtp); // e.g., AbcD-12
console.log("Encrypted Hash:", hash);
```
#### Example 4: Custom Template
```javascript
const { otp: generatedOtp, hash } = await otp.gen("user@example.com", {
template: "N{2}-M{3}-U{2}",
ttl: 300,
});
console.log("Generated Custom OTP:", generatedOtp); // e.g., 12-abc-XY
console.log("Encrypted Hash:", hash);
```
### Verifying an OTP
```javascript
const isValid = otp.verify("user@example.com", hash, "832-059");
console.log("Is OTP valid?", isValid);
```
### Example of use with Express.js
```javascript
const express = require("express");
const LessOtp = require("less-otp");
const PORT = 3000;
const app = express();
const auth = new LessOtp({
// options
});
app.use(express.json());
// Request OTP endpoint
app.post("/request-otp", async (req, res) => {
const { email } = req.body;
if (!email) {
return res.status(400).json({ error: "Email is required" });
}
try {
const { otp, hash } = auth.gen(email, {
template: "N{3}-N{3}", // 912-753
ttl: 300, // 5 min
});
// Example of sending via Nodemailer
const transporter = createTransport({
service: "Gmail",
host: "smtp.gmail.com",
port: 465,
secure: true,
auth: {
user: "youraddress@gmail.com",
pass: "yourpassword",
},
});
const mailOptions = {
from: "youraddress@gmail.com",
to: email,
subject: "OTP Code",
text: `Your OTP code is: ${otp}`,
};
const info = await transporter.sendMail(mailOptions);
console.log(info);
// Return hash in response
res.json({ hash });
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error generating OTP:", error);
res.status(500).json({ error: "An error occurred" });
}
});
// Verify OTP endpoint
app.post("/verify-otp", (req, res) => {
const { email, otp, hash } = req.body;
if (!email || !otp || !hash) {
res.status(400).json({ error: "Email, OTP, and hash are required" });
return;
}
const isValid = auth.verify(email, hash, otp);
if (!isValid) {
res.status(401).json({ error: "Invalid OTP or OTP has expired" });
return;
}
res.json({ message: "OTP verified successfully" });
});
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`Server is running on ${PORT}`);
});
```
## Changelog
### [0.0.8] - 2024-11-05
Minor fix
### [0.0.7] - 2024-11-05
Fixed: Types and exports
Updated: package.json
### [0.0.6] - 2024-11-05
Added: Babel transpiler and Rollup Terser plugin to reduce dist size.
Updated: README.md
### [0.0.5] - 2024-11-05
Added: Unit tests using Vitest.
Added: New enableSet flag in the class constructor to control whether OTPs should be stored in a hash set, ensuring that each OTP can only be used once (defaults to true).
Usage: To disable storing OTPs in the hash set (not recommended), set enableSet to false when initializing the class:
```javascript
const lessOtp = new LessOtp({ enableSet: false });
```
Updated: `secretSalt` is now optional and, if not provided, will be generated automatically with a random length between 32 and 64 characters (16 to 32 bytes).
Updated: README.md
Code clean up
## License
This project is licensed under the [Apache-2.0 License](LICENSE).