lexer-state
Version:
Lightweight state machine library to define and manage state transition declaratively
241 lines (192 loc) • 6.32 kB
Markdown
<p align="center">
<img src="http://baraabytes.com/wp-content/uploads/lexerState.png" alt="lexer-state logo" height="150" />
</p>
Lexer state is a lightweight easy to use state management library, that’s allow you to handle and model your state transition declaratively using a state machine.
Install lexer state with npm
```bash
cd my-project
npm install lexer-state
```
State machine or finite Automata has a finite set of states edges lead from one state to another, and each edge is labeled with a symbol. One state is the start state, and certain of the states are distinguished as final states.
We can describe a finite state machine that accept (identify) real numbers in the following diagram. Each circle represent a state in the machine, and the arrows are showing the type of input that’ll trigger a transition to the next state.
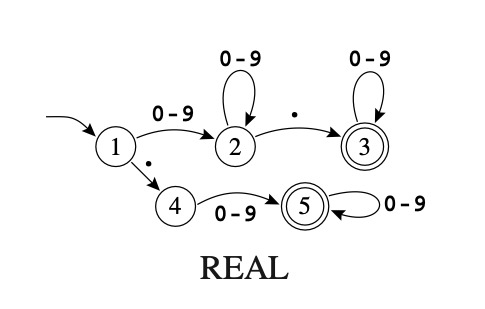
## Example
Let's create a simple state machine that accept or identify (if) in a string.
such a state machine can be represent in this diagram.
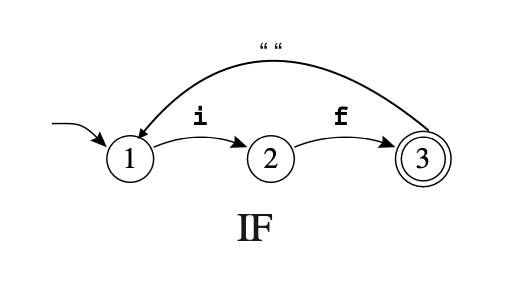
We can implements that easily using Lexer-state by first defining our set of states and the transition events. Then create a transition table. After which we create an instance of machine from a transition table. to drive the state machine to goto next state we call next() with input value.
```javascript
import {
LexerState,
Transition,
isItMatch,
Machine,
} from 'lexer-state/packages/machine';
const myStates = {
firstState: 'firstState',
secondState: 'secondState',
ifState: 'if',
} as const;
const myEvents = {
i_event: 'i',
f_event: 'f',
space_event: ' ',
} as const;
// creating transition events
const receiveI = LexerState(myEvents).create('i_event');
const receiveF = LexerState(myEvents).create('f_event');
const receiveSpace = LexerState(myEvents).create('space_event');
// creating set of states
const firstState = LexerState(myStates).create('firstState');
const secondState = LexerState(myStates).create('secondState');
const ifState = LexerState(myStates).create('ifState');
// defining transition table
const transition = new Transition('simple');
transition
.at(firstState)
.add(
isItMatch(receiveI).moveTo(secondState),
isItMatch(receiveSpace).moveTo(firstState),
)
.at(secondState)
.add(
isItMatch(receiveF).moveTo(ifState),
isItMatch(receiveSpace).moveTo(firstState),
)
.at(ifState)
.add(isItMatch(receiveSpace).moveTo(firstState));
const machine = new Machine(transition).at(
// set the starting state of the machine
myStates.firstState,
);
// call next() with input value to goto next state
console.log('current state ', machine.next('i'));
//output: current state secondState
console.log('current state: ', machine.next('f'));
//output: current state: if
```
- create state and event object
```javascript
export const TrafficLightStates = {
redState: 'redState',
yellowState: 'yellowState',
greenState: 'greenState',
} as const;
export const TrafficLightEvent = {
next_event: 'next_event',
} as const;
```
- Instantiate lexerState states and events
```javascript
// src/service/index.ts
import {
LexerState,
Transition,
isItMatch,
Machine,
} from 'lexer-state/packages/machine';
// Instantiate States & events
const redState = LexerState(TrafficLightStates).create(
'redState',
);
const yellowState = LexerState(TrafficLightStates).create(
'yellowState',
);
const greenState = LexerState(TrafficLightStates).create(
'greenState',
);
// Instantiate transition events
const nextEvent = LexerState(TrafficLightEvent).create(
'next_event',
);
```
- Define all possible transitions associated with each state.
- do() allows you to execute some actions on certain transition
```javascript
// src/service/index.ts
// Define transitions
const transition = new Transition('trafficLights');
transition
// defining red state
.at(redState)
// add red transition conditions
.add(isItMatch(nextEvent).moveTo(yellowState))
// defining yellow state
.at(yellowState)
.add(
isItMatch(nextEvent)
.moveTo(greenState)
.do(async (arg) =>console.log('Traffic light switching to grean go now!'))
)
// defining green state
.at(greenState)
.add(isItMatch(nextEvent).moveTo(redState));
```
- Create traffic lights machine
```javascript
// src/service/index.ts
export const trafficMachine = new Machine(transition).at(
// set the starting state of the machine
TrafficLightStates.redState,
);
```
- Setup traffic light state machine with LexerState provider
```javascript
// src/index.tsx
import { LexerStateProvider } from 'lexer-state/packages/machine';
import { trafficMachine } from './service';
function Index() {
return (
<LexerStateProvider machine={trafficMachine}>
<App />
</LexerStateProvider>
);
}
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(
document.getElementById('app'),
);
root.render(<Index />);
```
- useLexerState hook to get the current state or to transition to next state by dispatching a transition event to the state machine.
```javascript
// src/App.tsx
import { useLexerState } from 'lexer-state/packages/machine';
import { TrafficLightEvent } from './service.ts';
import { trafficMachine } from './service';
function App() {
const { currentState, dispatchEvent } = useLexerState<typeof TrafficLightEvent>(trafficMachine);
const onNext = () => {
dispatchEvent(TrafficLightEvent.next_event);
};
return (
<div>
<h1>Traffic light is in {currentState}</h1>
<button onClick={onNext}>NEXT</button>
</div>
);
}
```
```javascript
// src/index.tsx
import { LexerStateProvider } from 'lexer-state/packages/machine';
import { trafficMachine, simpleMachine } from './service';
function Index() {
return (
<LexerStateProvider machines={[trafficMachine,simpleMachine]}>
<App />
</LexerStateProvider>
);
}
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(
document.getElementById('app'),
);
root.render(<Index />);
```