ember-qunit
Version:
QUnit helpers for testing Ember.js applications
62 lines (39 loc) • 2.81 kB
Markdown
# Debugging Async Leakage Using Test Isolation Validation
## Overview
The `ember-qunit` test isolation validation feature allows you to opt-in to enabling automatic detection of async execution that extends beyond when the test is considered complete. This can be a particularly difficult problem to detect in your tests, and can contribute to non-deterministic test execution.
## Installation
The test isolation validation functionality is available on `ember-qunit` version `4.2.0` or higher.
```bash
ember install ember-qunit
```
## How to use
In order to enable test isolation validation, you'll need to configure the option, `setupTestIsolationValidation: true` in `ember-qunit`'s `start` function, which starts your application or addon's test run.
```js
// tests/test-helper.js
import Application from '../app';
import config from '../config/environment';
import { setApplication } from '@ember/test-helpers';
import { start } from 'ember-qunit';
setApplication(Application.create(config.APP));
start({
setupTestIsolationValidation: true
});
```
## Finding non-isolated tests
Once a test run is started with test isolation validation turned on, analysis will occur on a test-by-test basis. Once a failure is detected, a new assertion will be added that will fail the test, indicating that the test is not isolated.
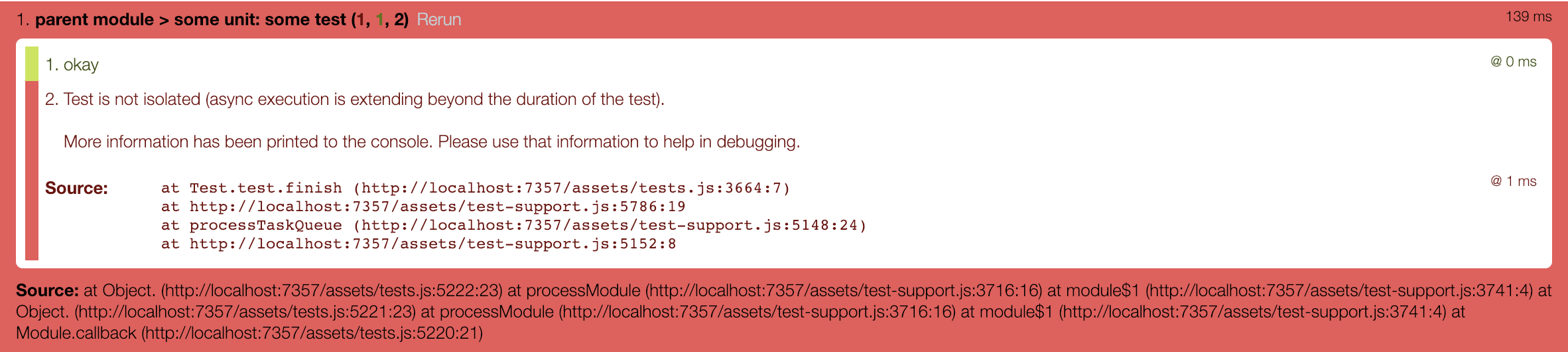
As indicated by the assertion message, important (and more useful) information is printed to the console.
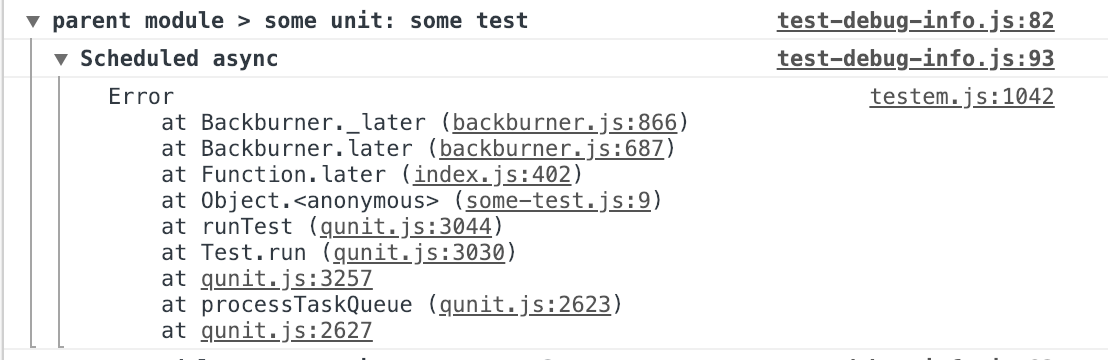
As you can see, the following information is provided for each test that fails isolation validation:
- The test module and test name
- The category of failure, one of
- Pending AJAX requests
- Pending test waiters
- Scheduled async
- Scheduled autorun
- The stack trace of the code that caused the isolation failure (Scheduled async or Scheduled autoruns only)
In the case of pending **AJAX requests** and **test waiters**, we see those categorizations of the failures. In the case of **scheduled async** or **scheduled autoruns**, we get a bit more information - stack traces that point to the code that scheduled the async call.
By viewing this information output to the console, we can traverse the stack from top to bottom, clicking the associated file/line number to get a more detailed view of the callee.
In line 9 below, we can see that an async call was scheduled via `Ember.run.later`:

Having this information will enable you to evaluate the best way to address the particular case of async leakage detected.