aki-angular-secure-config
Version:
The `aki-angular-secure-config` is a new npm package developed to address a security vulnerability in Angular applications. This package ensures that sensitive configuration data in `config.json` is protected from being inspected or extracted via browser
300 lines (218 loc) • 10.3 kB
Markdown
# AKI Angular Secure Configuration
## Overview
`aki-angular-secure-config` is a new npm package developed to address a security vulnerability in Angular applications. This package ensures that sensitive configuration data in `config.json` is protected from being inspected or extracted via browser network tools or debugging features.
## Problem Statement
Many developers switch from `environment.ts` to `config.json` for application configuration. This change requires an HTTP request to access the `config.json` at runtime, exposing the file to potential security risks.
## Solution
`aki-angular-secure-config` resolves this issue by encrypting the `config.json` file before the application starts. Upon startup, the application decrypts the file in `main.ts` and stores the data in a static variable, ensuring the configuration remains secure.
## Features
- **Encryption:** Secure your configuration data by encrypting the `config.json` file.
- **Decryption:** Seamlessly decrypt the configuration data in the `main.ts` file.
- **Dockerfile:** Provides a Dockerfile for containerizing your Angular application with secure configuration handling.
- **Obfuscation:** Adds a layer of security by obfuscating the application source.
- **Integration with Vault:** Utilizes Vault for securely managing sensitive data.
- **Config-Map Compatibility:** Works with Kubernetes ConfigMaps to replace actual values from Vault before encryption.
## Demo
You can find a complete implementation at [Stackblatz - Angular Secure Config](https://stackblitz.com/edit/stackblitz-starters-ufyypl)
## Getting Started
1. **Create a new angular application**
```sh
ng new angular-app
```
2. **Install the package**
```sh
npm install -g aki-angular-secure-config
```
```sh
yarn add global aki-angular-secure-config
```
3. **Run the package**
- Run package help:
```sh
aki-angular-secure-config help
```
- Run package and its dependancies via NPM:
```sh
aki-angular-secure-config run
```
- Run package and its dependancies via YARN:
```sh
aki-angular-secure-config run --use-yarn
```
- Run package and its dependancies with custom package:
```sh
aki-angular-secure-config run --npmrc-src my-registry --npmrc-username my-username --npmrc-pat my-pat
```
> **The custom registry URL:** https://SOURCE-CONTROL/ORGANIZATION-NAME/PROJECT-NAME/_packaging/FEED/npm/registry/
>
> **my-registry:** SOURCE-CONTROL/ORGANIZATION-NAME/PROJECT-NAME/_packaging/FEED
>
> **my-username:** Your feed username
>
> **my-pat:** Your organization Personal Access Token in Base64 format
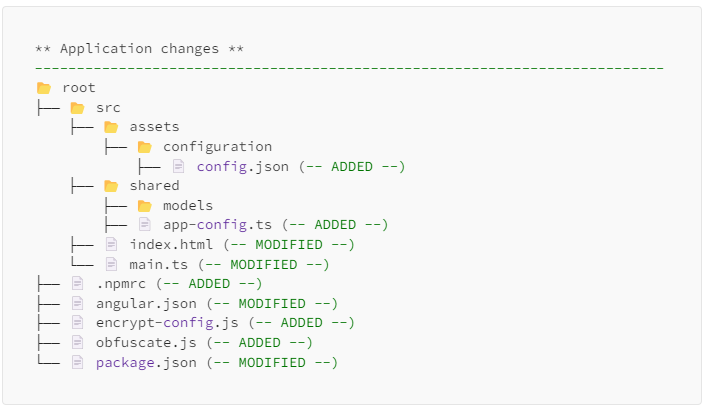
- Specify the name of the configuration file **(default: config.json)**:
```sh
aki-angular-secure-config run --config-file-name custom-config.json
```
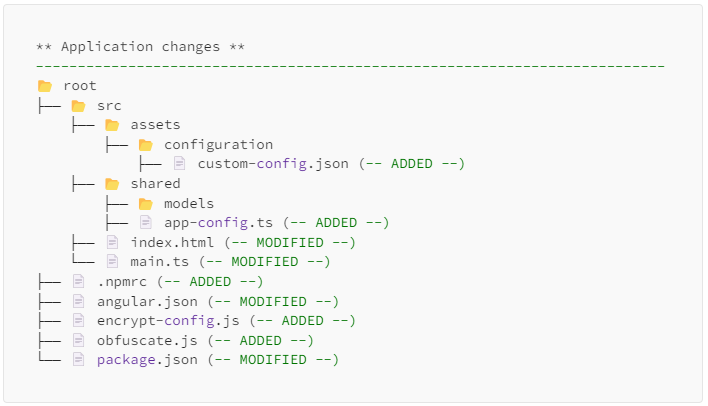
- Run package and include docker dependencies:
```sh
aki-angular-secure-config run --include-dockerfile --config-file-name custom-config.json
```
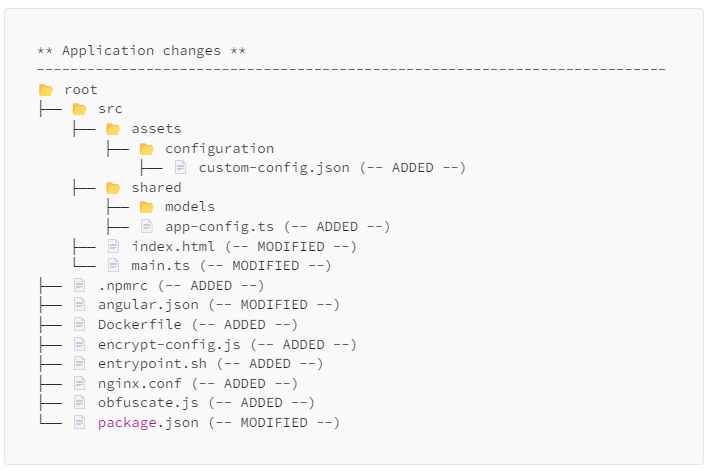
4. **Update `config.json` and `AppConfig`**
```json
{
"production": false,
"title": "AKI Angular Secure Config",
"version": "V 1.0.0",
"app": {
"baseUrl": "http://localhost:4200"
}
}
```
```ts
export interface AppConfig {
production: boolean;
title: string;
version: string;
app: App;
}
export interface App {
baseUrl: string;
}
```
> Note: Verify that the `config.json` changes were added to the `AppConfig` model to be up-to-date.
5. **Update `app.module.ts`**
You can ensure that configuration settings are loaded before the Angular application starts by using the `APP_INITIALIZER` token. This guide explains how to inject `APP_INITIALIZER` into your Angular module to initialize the configuration service.
## Step-by-Step Guide to Injecting APP_INITIALIZER
### 1. Import Required Modules
Begin by importing the necessary modules and services into your `AppModule`.
```typescript
import { NgModule, APP_INITIALIZER } from "@angular/core";
import { BrowserModule } from "@angular/platform-browser";
import { AppRoutingModule } from "./app-routing.module";
import { AppComponent } from "./app.component";
import { ConfigService } from "aki-resources";
import { AppConfig } from "../shared/models/app-config";
```
### 2. Create Configuration Loader Function
Define a function that initializes the `ConfigService`. This function will be used by the `APP_INITIALIZER` to load configuration settings before the application starts.
```typescript
function appConfigLoader(ConfigService: ConfigService<AppConfig>) {
return () => ConfigService.init();
}
```
### 3. Configuring the `APP_INITIALIZER`
Configure the `APP_INITIALIZER` provider to use the `appConfigLoader` function into the `AppModule`. This ensures that the configuration settings are loaded and available when the application starts.
```typescript
@NgModule({
declarations: [AppComponent],
imports: [BrowserModule, AppRoutingModule],
providers: [
{
provide: APP_INITIALIZER,
multi: true,
deps: [ConfigService],
useFactory: appConfigLoader,
},
],
bootstrap: [AppComponent],
})
export class AppModule {}
```
## Usage
The `ConfigService` from the `aki-resources` package provides a streamlined way to manage and access your application's configuration settings. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to integrate and use the `ConfigService` in your Angular components.
## Example: Displaying Application Configuration Data
The following example demonstrates how to use `ConfigService` within an Angular component to read and display application configuration data.
## Step-by-Step Integration
### 1. Import Required Modules
Begin by importing the necessary modules and services into your component.
```typescript
import { Component } from "@angular/core";
import { ConfigService } from "aki-resources";
import { AppConfig, App } from "../shared/models/app-config";
```
### 2. Define the Component
Create your Angular component. In this example, we'll use `AppComponent` to display configuration data.
```typescript
@Component({
selector: "app-root",
template: `
<h2>App Config Data</h2>
<p><b>Title:</b> {{ appConfig?.title }}</p>
<p><b>Version:</b> {{ appConfig?.version }}</p>
<p><b>BaseUrl:</b> {{ appConfig?.app?.baseUrl }}</p>
`,
})
export class AppComponent {
public appConfig: AppConfig | null = null;
public appBaseUrl: string = "";
constructor(private configService: ConfigService<AppConfig>) {
this.appConfig = ConfigService.readConfig<AppConfig>();
this.appConfig.app = {
baseUrl: configService.getOne("app")?.baseUrl || "",
} as App;
}
}
```
### 3. Reading Configuration
The `ConfigService.readConfig` method is used to read the configuration data at runtime. This method fetches the configuration settings and assigns them to the `appConfig` property.
```typescript
this.appConfig = ConfigService.readConfig<AppConfig>();
```
### 4. Accessing Nested Configuration
To access nested configuration properties, such as `app.baseUrl`, the `ConfigService.getOne` method is utilized. This ensures that even nested configuration properties are correctly retrieved and used within your component.
```typescript
this.appConfig.app = {
baseUrl: configService.getOne("app")?.baseUrl || "",
} as App;
```
### 5. Displaying Configuration Data
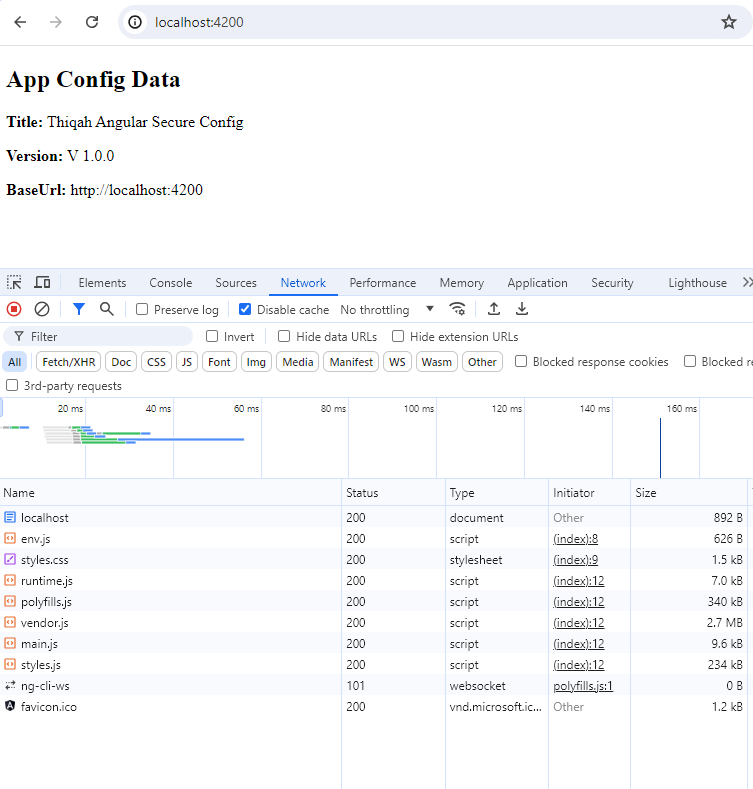
Finally, the configuration data is displayed in the component’s template using Angular’s data binding. This example shows how to display the application's title, version, and base URL.
```html
<h2>App Config Data</h2>
<p><b>Title:</b> {{ appConfig?.title }}</p>
<p><b>Version:</b> {{ appConfig?.version }}</p>
<p><b>BaseUrl:</b> {{ appConfig?.app?.baseUrl }}</p>
```
## Run the application
```sh
node encrypt-config.js && ng serve -o
```
```sh
npm start
```
<hr>
## Deployment
1. **Manual**
- Build the production version of your application:
```sh
ng build --configuration production && node obfuscate.js
```
> After running the command above, your deployment files will be ready in the `dist` folder.
>
> Open `angular.json`, and navigate to **'architect.build.options.outputPath'**.
2. **Docker**
- Build the Dockerfile using docker engine:
```sh
docker build -f "Dockerfile" -t angular-app:1.0 .
```
```sh
docker run -d -p 4100:8080 angular-app:1.0
```
By following this guide, you can ensure your Angular application configuration is securely managed, preventing unauthorized access and enhancing the overall security of your application.
## Changelog
### Version 1.0.24 (Latest)
- **Fixed:** Resolved issue with `.npmrc` file not being included in published package
- **Changed:** Renamed `.npmrc` to `npmrc-template` to avoid npm exclusion of dotfiles
- **Improved:** CLI now properly copies and renames `npmrc-template` to `.npmrc` during installation
- **Enhanced:** Better handling of configuration templates for npm publishing
### Version 1.0.23
- **Updated:** Improved CLI logic for local resource copying
- **Enhanced:** Better `.npmrc` handling and dependency installation
- **Changed:** Switched from `@thiqah/shared-lib` to `aki-resources` in install commands
## License
MIT