@tsmx/express-jwt-validator
Version:
Simple express middleware for validating JWT bearer tokens.
228 lines (150 loc) • 7.47 kB
Markdown
# [**@tsmx/express-jwt-validator**](https://github.com/tsmx/express-jwt-validator)
[](https://opensource.org/licenses/MIT)


[](https://img.shields.io/github/actions/workflow/status/tsmx/express-jwt-validator/git-build.yml?branch=master)
[](https://coveralls.io/github/tsmx/express-jwt-validator?branch=master)
> Simple express middleware for validating JWT bearer tokens.
Stop writing boilerplate code to protect [express](https://www.npmjs.com/package/express) routes with [JWT](https://www.npmjs.com/package/jsonwebtoken) bearer tokens in your projects.
Supports optional log output using [winston](https://www.npmjs.com/package/winston), [log4js](https://www.npmjs.com/package/log4js) or any other compatible logger. For details refer to the [log configuration](#logger) section
## Usage
```js
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const verifyToken = require('@tsmx/express-jwt-validator')({
secret: 'YOUR_JWT_SECRET'
});
app.get('/secret', verifyToken, (req, res) => {
// token payload available in req.authData
res.send('Only accessible with a valid JWT bearer token.');
});
```
For further customizing please refer to the [configuration options](#configuration-options).
## How it works
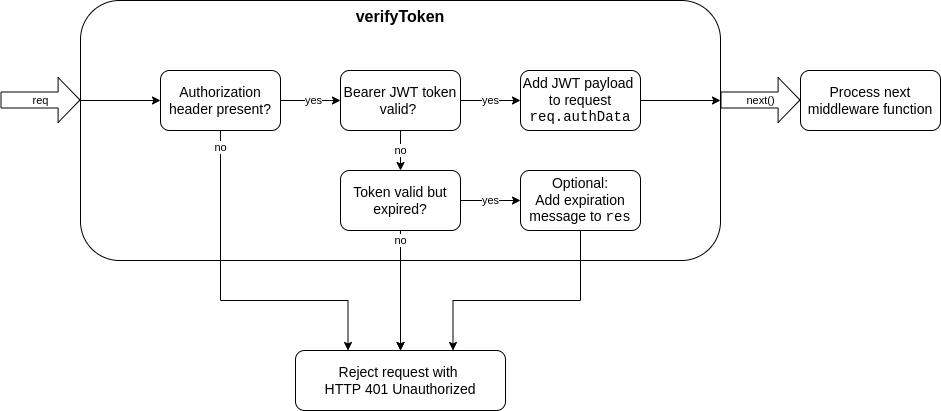
This module exports a middleware function for express to check a request for a valid JSON Web token authorization. The token must be provided as a bearer token in the HTTP request header according to the [RFC standard](https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc6750#section-2.1).
Requests with a failed JWT validation will be rejected with [HTTP status 401](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Status/401) by default. If the validations succeeds, the verified JWT payload will be added to the request and it will be passed to the next element of the middleware chain.
## Configuration options
When requiring in the middleware with...
```js
const verifyToken = require('@tsmx/express-jwt-validator')({
/* configuration object */
});
```
...the passed configuration object supports the following properties.
| Property | Description |
|----------|-------------|
| [secret](#secret) | The JWT validation secret |
| [header](#header) | Custom header HTTP name |
| [strictBearerValidation](#strictbearervalidation) | Enable/disable strict validation |
| [rejectHttpStatus](#rejecthttpstatus) | Custom HTTP response status for failed validations |
| [sendExpiredMessage](#sendexpiredmessage) | Enable/disable error message for expired tokens |
| [requestAuthProp](#requestauthprop) | Custom property name to store token data in `req` |
| [logger](#logger) | An optional logger to receive log output |
### secret
Type: `String`
Default: `undefined`
Mandatory: yes
The sceret used to verify the JWT bearer token. Must be present, otherwise an exception will be thrown.
Example:
```js
const verifyToken = require('@tsmx/express-jwt-validator')({
secret: 'MySecretKey-123456'
});
```
### header
Type: `String`
Default: `authorization`
Mandatory: no
Can be used if the bearer token will be supplied in another header field than `authorization` (Note: HTTP header field names are case-insensitive).
Example:
```js
const verifyToken = require('@tsmx/express-jwt-validator')({
secret: 'MySecretKey-123456',
header: 'auth'
});
```
### strictBearerValidation
Type: `Boolean`
Default: `false`
Mandatory: no
If set to true, the authorization header is strictly validated against the schema `Bearer <JWT>` (including the whitespace), like `Bearer eyJhb...`. If set to false (default), it is sufficient if the header consists of two strings separated by a whitespace whereas the second entry is considered to be the JWT.
Example:
```js
const verifyToken = require('@tsmx/express-jwt-validator')({
secret: 'MySecretKey-123456',
strictBearerValidation: true
});
```
### rejectHttpStatus
Type: `Number`
Default: `401`
Mandatory: no
The HTTP status to be sent back to the client if the bearer token validation fails. Defaults to 401 for `Unauthorized`, could also be set to 403 `Forbidden` for example. Please note that although any status is possible here you should use an appropriate [HTTP client error code](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Status#client_error_responses).
Example:
```js
const verifyToken = require('@tsmx/express-jwt-validator')({
secret: 'MySecretKey-123456',
rejectHttpStatus: 403
});
```
### sendExpiredMessage
Type: `Boolean`
Default: `true`
Mandatory: no
If set to true, the rejection response will contain a JSON body with one property `error` and value `TokenExpiredError` indicating the client that the token has expired. This can be useful to allow the client to check that the token must be refreshed.
If set to false, an expired token will be rejected without any response body.
Example:
```js
const verifyToken = require('@tsmx/express-jwt-validator')({
secret: 'MySecretKey-123456',
sendExpiredMessage: false
});
```
### requestAuthProp
Type: `String`
Default: `authData`
Mandatory: no
The name of the property in `req` where the JWT bearer token payload should be stored for further processing. Can be changed to any property name, please make sure it is unique and no other properties are overwritten.
Example:
```js
const verifyToken = require('@tsmx/express-jwt-validator')({
secret: 'MySecretKey-123456',
requestAuthProp: 'tokenPayload'
});
```
Token data would now be accessible with `req.tokenPayload` instead of `req.authData` in following middleware functions.
### logger
Type: `Object`
Default: `undefined`
Mandatory: no
You can pass a [winston](https://www.npmjs.com/package/winston) or [log4js](https://www.npmjs.com/package/log4js) logger instance (or any compatible) to get log output from the middleware. Compatible means that the logger must provide `info`, `warn` and `error` functions receiving a string to be logged.
Note: the package contains tests for winston and log4js.
The following events will be logged:
| Event | Log level |
|-------|-----------|
| Rejected - No auth header present | WARN |
| Rejected - No valid 'Bearer TOKEN' entry in auth header | WARN |
| Rejected - Strict Bearer validation failed | WARN |
| Rejected - Expired token was sent | WARN |
| Rejected - Invalid token was sent (potential attack) | ERROR |
| Passed - Valid Bearer token was sent | INFO |
Example for winston:
```js
const winston = require('winston');
winstonLogger = winston.createLogger({ /*... winston options ...*/ });
const verifyToken = require('@tsmx/express-jwt-validator')({
secret: 'MySecretKey-123456',
logger: winstonLogger
});
```
Example for log4js:
```js
const log4js = require('log4js');
log4js.configure({ /*... log4js options ...*/ });
log4jsLogger = log4js.getLogger();
const verifyToken = require('@tsmx/express-jwt-validator')({
secret: 'MySecretKey-123456',
logger: log4jsLogger
});
```