@quickstat/nodejs
Version:
Effortlessly monitor Node.js metrics and export them to Prometheus for visualization in Grafana
181 lines (120 loc) • 8 kB
Markdown
# Node.js Runtime Monitoring Plugin
The QuickStat Node.js Plugin offers seamless integration with Node.js runtime, allowing effortless monitoring of key runtime metrics. It exports these metrics to Prometheus, enabling visualization in Grafana dashboards for comprehensive Node.js application performance monitoring.
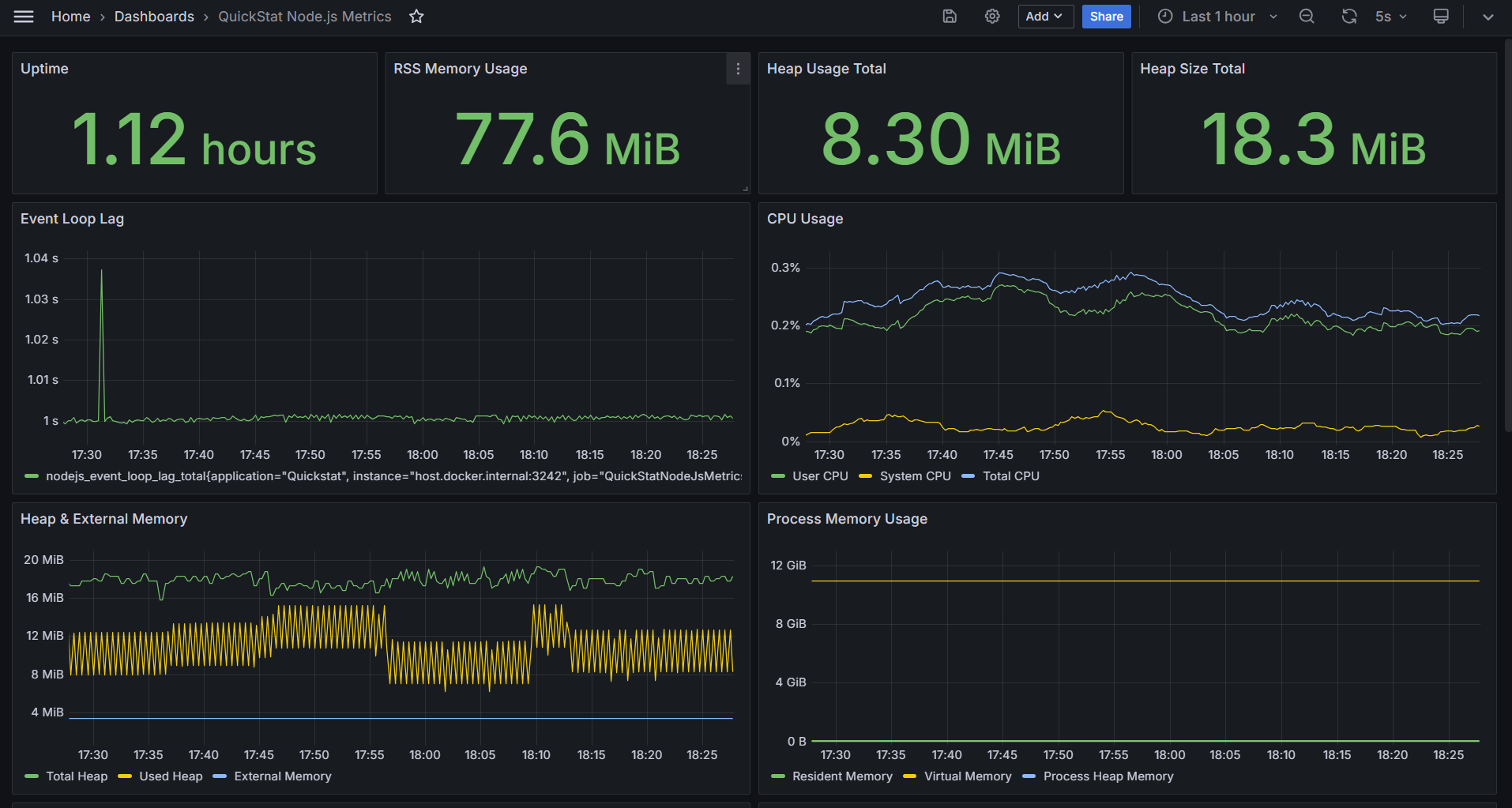
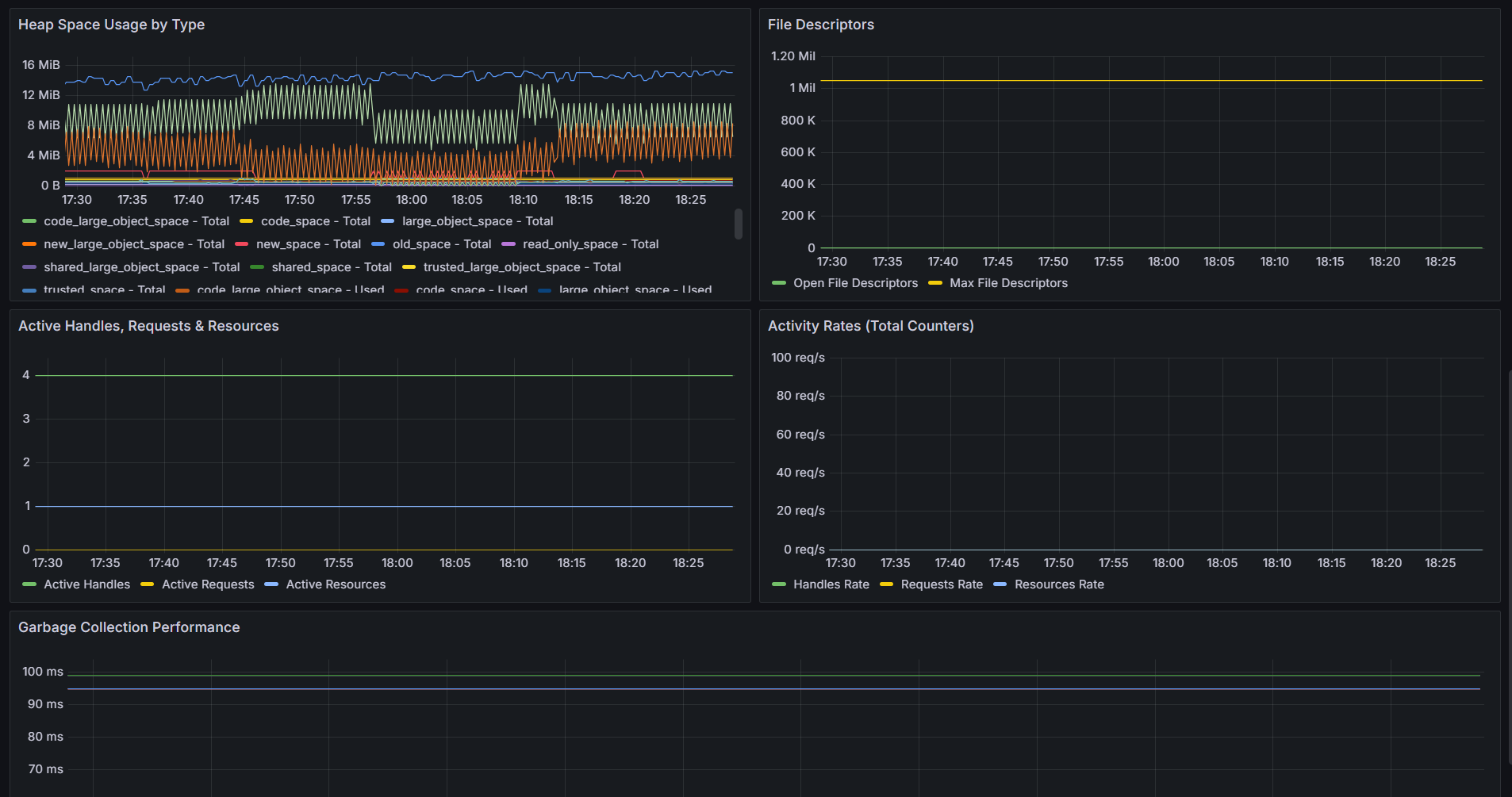
If you are new to QuickStat and its components, feel free to check the [official documentation](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@quickstat/core) for a detailed breakdown.
## Installation
Start by installing the QuickStat core package, the data source used by Grafana and then the Node.js plugin:
```bash
npm install @quickstat/core
npm install @quickstat/prometheus
npm install @quickstat/nodejs
```
## Getting Started
If you use docker and want to get started quickly, you can check the [following docker-setup](https://github.com/QuickStat/quickstat/tree/master/examples/plugins/nodejs), which allows you to skip the setup and directly use the plugin. Once you have setup docker, continue on Step 3.
If your unfamiliar with [QuickStat's plugins](https://github.com/QuickStat/quickstat/tree/master?tab=readme-ov-file#plugins), then keep in mind that you can also use other strategies such as (PushGateway) for exposing metrics or even combine your dashboard with other plugins.
If you want to set up Prometheus and Grafana manually, follow the steps below:
### 1. Setup Prometheus and Grafana
1. **Install Prometheus**: Follow the [official documentation](https://prometheus.io/docs/prometheus/latest/installation/) to install Prometheus on your system.
2. **Install Grafana**: Refer to the [official documentation](https://grafana.com/docs/grafana/latest/installation/) for instructions on installing Grafana.
3. **Configure Prometheus Data Source in Grafana**: After installing Grafana, configure Prometheus as a data source. Go to Grafana settings, add a new data source, and specify the URL where Prometheus is running.
### 2. Import Dashboard to Grafana
Once Prometheus and Grafana are set up, you can add [following Dashboard](https://grafana.com/grafana/dashboards/24130). Navigate to the Grafana dashboard page, click on "Import" and paste the dashboard template URL. Then, customize the dashboard as needed.
### 3. Expose Node.js Runtime Metrics
To expose the metrics to Prometheus using the QuickStat Node.js Plugin, use the following code snippet:
```javascript
import { Client as QuickStatClient } from '@quickstat/core'
import { NodeJsPlugin } from '@quickstat/nodejs'
import { PrometheusDataSource, ScrapeStrategy } from '@quickstat/prometheus'
import http from 'http'
// Create QuickStat Client
const quickStatClient = new QuickStatClient() < PrometheusDataSource < ScrapeStrategy >> ({
metrics: [],
plugins: [
// Register Node.js Plugin
new NodeJsPlugin({
excludeMetrics: [],
}),
],
// Register the data source
dataSource: new PrometheusDataSource({
strategy: new ScrapeStrategy(),
}),
})
// Let Prometheus scrape the metrics at http://localhost:3242
// WARNING: On production, properly secure the endpoint (if open)
http.createServer(async (req, res) => {
const response = await quickStatClient.dataSource?.strategy?.getResponse()
// Write the prometheus response file
if (response) {
res.writeHead(200, response.headers)
res.end(response.file)
}
}).listen(3242)
```
### 4. Start the Application
After setting up the code, start the application. The metrics will be available at `http://localhost:3242` in Prometheus format and will be scraped by Prometheus, which will then be used for visualization in Grafana.
## Available Metrics
The Node.js plugin provides comprehensive runtime metrics:
### Memory Metrics
- `nodejs_heap_size_total` - Total heap size in bytes
- `nodejs_heap_size_used` - Used heap size in bytes
- `nodejs_external_memory` - External memory size in bytes
- `nodejs_heap_space_size_total` - Total heap space size in bytes (by space)
- `nodejs_heap_space_size_used` - Used heap space size in bytes (by space)
- `nodejs_heap_space_size_available` - Available heap space size in bytes (by space)
- `nodejs_process_resident_memory` - Resident memory size in bytes
- `nodejs_process_virtual_memory` - Virtual memory size in bytes (Linux only)
- `nodejs_process_heap_memory` - Heap memory size in bytes
### Performance Metrics
- `nodejs_event_loop_lag` - Event loop lag in seconds
- `nodejs_gc_duration` - Garbage collection duration in seconds (by GC kind)
### CPU Metrics
- `nodejs_process_cpu_user_total` - Total user CPU time in seconds
- `nodejs_process_cpu_system_total` - Total system CPU time in seconds
- `nodejs_process_cpu_total` - Total CPU time in seconds
### Resource Metrics
- `nodejs_active_handles` - Number of active handles
- `nodejs_active_handles_total` - Total number of active handles
- `nodejs_active_requests` - Number of active requests
- `nodejs_active_requests_total` - Total number of active requests
- `nodejs_active_resources` - Number of active resources
- `nodejs_active_resources_total` - Total number of active resources
### File Descriptor Metrics (Linux/Unix only)
- `nodejs_process_max_fds` - Maximum number of file descriptors
- `nodejs_process_open_fds` - Number of open file descriptors
### Process Information
- `nodejs_start_time` - Start time of the Node.js process in seconds
- `nodejs_version` - Node.js version information
## Configuration
### DataSource
The example above uses the PrometheusDataSource with the ScrapeStrategy. The ScrapeStrategy exposes the prometheus file on the given endpoint for being scraped from prometheus. You can also use the PushGatewayStrategy to push the metrics to the PushGateway of Prometheus.
If you would like to use other data sources, you can take a look at the available data sources in the [@quickstat/core package](https://github.com/QuickStat/quickstat?tab=readme-ov-file#data-sources)
### Plugin
The Node.js Plugin automatically collects runtime metrics from the current Node.js process. You can exclude specific metrics which should not be processed by the plugin.
| Option | Description | Default |
| -------------- | --------------------------- | ------- |
| excludeMetrics | Array of metrics to exclude | [] |
### Platform Support
- **Full Support**: Linux/Unix systems (includes file descriptor metrics)
- **Core Support**: Windows/macOS (excludes platform-specific metrics like file descriptors)
- **GC Monitoring**: Available on Node.js versions that support PerformanceObserver
- **Event Loop Monitoring**: Available on all supported Node.js versions
### Memory Considerations
The plugin monitors the Node.js runtime with minimal overhead:
- Event loop monitoring: ~1KB memory, updates every second
- GC monitoring: Negligible overhead, only active during garbage collection
- Metric collection: Runs during scheduled collection intervals
## Example Use Cases
### Development Environment
Monitor your application's memory usage, event loop performance, and garbage collection patterns during development to identify potential performance issues early.
### Production Monitoring
Set up alerts on critical metrics like:
- High event loop lag (> 100ms)
- Memory leaks (continuously increasing heap usage)
- Excessive garbage collection frequency
- High CPU usage patterns
### Performance Optimization
Use heap space metrics to understand memory allocation patterns and optimize your application's memory usage across different heap spaces.
## Contributing and Issues
If you have any issues or feature requests, feel free to open an issue on the [GitHub repository](https://github.com/QuickStat/quickstat)