@huggingface/tasks
Version:
List of ML tasks for huggingface.co/tasks
95 lines (63 loc) • 5.45 kB
Markdown
## Different Types of Vision Language Models
Vision language models come in three types:
- **Base:** Pre-trained models that can be fine-tuned. A good example of base models is the [PaliGemma models family](https://huggingface.co/models?sort=trending&search=google%2Fpaligemma-3b-pt) by Google.
- **Instruction:** Base models fine-tuned on instruction datasets. A good example of instruction fine-tuned models is [idefics2-8b](https://huggingface.co/HuggingFaceM4/idefics2-8b).
- **Chatty/Conversational:** Base models fine-tuned on conversation datasets. A good example of chatty models is [deepseek-vl-7b-chat](https://huggingface.co/deepseek-ai/deepseek-vl-7b-chat).
## Use Cases
### Multimodal Dialogue
Vision language models can be used as multimodal assistants, keeping context about the conversation and keeping the image to have multiple-turn dialogues.
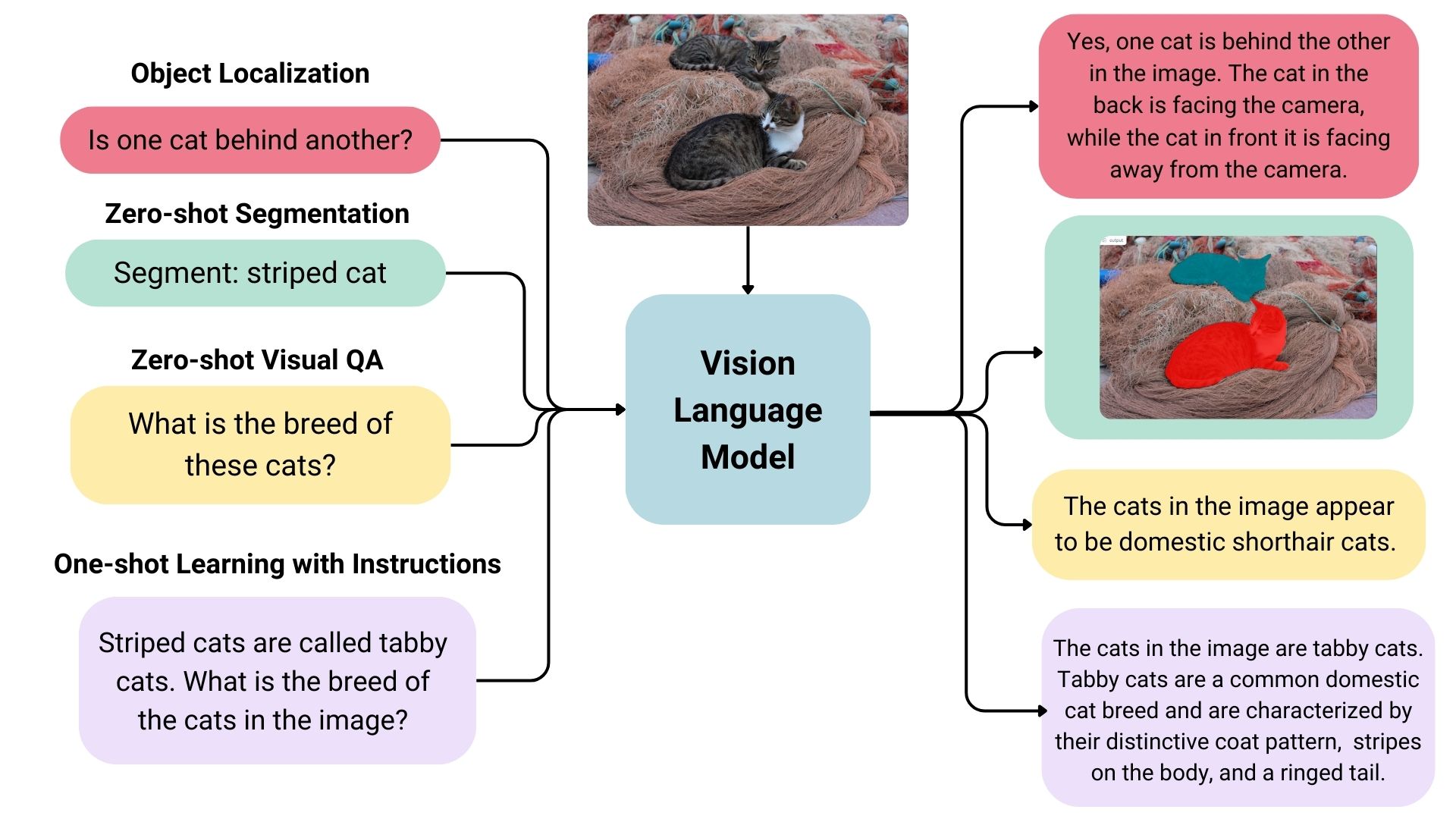
### Zero-shot Object Detection, Image Segmentation and Localization
Some vision language models can detect or segment a set of objects or describe the positions or relative positions of the objects. For example, one could prompt such a model to ask if one object is behind another. Such a model can also output bounding box coordination or segmentation masks directly in the text output, unlike the traditional models explicitly trained on only object detection or image segmentation.
### Visual Question Answering
Vision language models trained on image-text pairs can be used for visual question answering and generating captions for images.
### Document Question Answering and Retrieval
Documents often consist of different layouts, charts, tables, images, and more. Vision language models trained on formatted documents can extract information from them. This is an OCR-free approach; the inputs skip OCR, and documents are directly fed to vision language models. To find the relevant documents to be fed, models like [ColPali](https://huggingface.co/blog/manu/colpali) are used. An example workflow can be found [here](https://github.com/merveenoyan/smol-vision/blob/main/ColPali_%2B_Qwen2_VL.ipynb).
### Image Recognition with Instructions
Vision language models can recognize images through descriptions. When given detailed descriptions of specific entities, it can classify the entities in an image.
### Computer Use
Image-text-to-text models can be used to control computers with agentic workflows. Models like [ShowUI](https://huggingface.co/showlab/ShowUI-2B) and [OmniParser](https://huggingface.co/microsoft/OmniParser) are used to parse screenshots to later take actions on the computer autonomously.
## Inference
You can use the Transformers library to interact with [vision-language models](https://huggingface.co/models?pipeline_tag=image-text-to-text&transformers). Specifically, `pipeline` makes it easy to infer models.
Initialize the pipeline first.
```python
from transformers import pipeline
pipe = pipeline("image-text-to-text", model="llava-hf/llava-interleave-qwen-0.5b-hf")
```
The model's built-in chat template will be used to format the conversational input. We can pass the image as an URL in the `content` part of the user message:
```python
messages = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{
"type": "image",
"image": "https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/bee.jpg",
},
{"type": "text", "text": "Describe this image."},
],
}
]
```
We can now directly pass in the messages to the pipeline to infer. The `return_full_text` flag is used to return the full prompt in the response, including the user input. Here we pass `False` to only return the generated text.
```python
outputs = pipe(text=messages, max_new_tokens=60, return_full_text=False)
outputs[0]["generated_text"]
# The image captures a moment of tranquility in nature. At the center of the frame, a pink flower with a yellow center is in full bloom. The flower is surrounded by a cluster of red flowers, their vibrant color contrasting with the pink of the flower. \n\nA black and yellow bee is per
```
You can also use the Inference API to test image-text-to-text models. You need to use a [Hugging Face token](https://huggingface.co/settings/tokens) for authentication.
```bash
curl https://router.huggingface.co/hf-inference/models/meta-llama/Llama-3.2-11B-Vision-Instruct \
-X POST \
-d '{"messages": [{"role": "user","content": [{"type": "image"}, {"type": "text", "text": "Can you describe the image?"}]}]}' \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer hf_***"
```
## Useful Resources
- [Vision Language Models (Better, Faster, Stronger)](https://huggingface.co/blog/vlms-2025)
- [Vision Language Models Explained](https://huggingface.co/blog/vlms)
- [Welcome PaliGemma 2 – New vision language models by Google](https://huggingface.co/blog/paligemma2)
- [SmolVLM - small yet mighty Vision Language Model](https://huggingface.co/blog/smolvlm)
- [Multimodal RAG using ColPali and Qwen2-VL](https://github.com/merveenoyan/smol-vision/blob/main/ColPali_%2B_Qwen2_VL.ipynb)
- [Preference Optimization for Vision Language Models with TRL](https://huggingface.co/blog/dpo_vlm)
- [Image-text-to-text task guide](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/tasks/image_text_to_text)