@huggingface/tasks
Version:
List of ML tasks for huggingface.co/tasks
130 lines (90 loc) • 6.58 kB
Markdown
Image-to-image pipelines can also be used in text-to-image tasks, to provide visual guidance to the text-guided generation process.
## Use Cases
### Image inpainting
Image inpainting is widely used during photography editing to remove unwanted objects, such as poles, wires, or sensor dust.
### Image colorization
Old or black and white images can be brought up to life using an image colorization model.
### Super Resolution
Super-resolution models increase the resolution of an image, allowing for higher-quality viewing and printing.
## Inference
You can use pipelines for image-to-image in 🧨diffusers library to easily use image-to-image models. See an example for `StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline` below.
```python
import torch
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForImage2Image
from diffusers.utils import make_image_grid, load_image
pipeline = AutoPipelineForImage2Image.from_pretrained(
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-refiner-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16, variant="fp16", use_safetensors=True
)
# this helps us to reduce memory usage- since SDXL is a bit heavy, this could help by
# offloading the model to CPU w/o hurting performance.
pipeline.enable_model_cpu_offload()
# prepare image
url = "https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/img2img-sdxl-init.png"
init_image = load_image(url)
prompt = "Astronaut in a jungle, cold color palette, muted colors, detailed, 8k"
# pass prompt and image to pipeline
image = pipeline(prompt, image=init_image, strength=0.5).images[0]
make_image_grid([init_image, image], rows=1, cols=2)
```
You can use [huggingface.js](https://github.com/huggingface/huggingface.js) to infer image-to-image models on Hugging Face Hub.
```javascript
import { InferenceClient } from "@huggingface/inference";
const inference = new InferenceClient(HF_TOKEN);
await inference.imageToImage({
data: await (await fetch("image")).blob(),
model: "timbrooks/instruct-pix2pix",
parameters: {
prompt: "Deblur this image",
},
});
```
## Uses Cases for Text Guided Image Generation
### Style Transfer
One of the most popular use cases of image-to-image is style transfer. With style transfer models:
- a regular photo can be transformed into a variety of artistic styles or genres, such as a watercolor painting, a comic book illustration and more.
- new images can be generated using a text prompt, in the style of a reference input image.
See 🧨diffusers example for style transfer with `AutoPipelineForText2Image` below.
```python
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForText2Image
from diffusers.utils import load_image
import torch
# load pipeline
pipeline = AutoPipelineForText2Image.from_pretrained("stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
pipeline.load_ip_adapter("h94/IP-Adapter", subfolder="sdxl_models", weight_name="ip-adapter_sdxl.bin")
# set the adapter and scales - this is a component that lets us add the style control from an image to the text-to-image model
scale = {
"down": {"block_2": [0.0, 1.0]},
"up": {"block_0": [0.0, 1.0, 0.0]},
}
pipeline.set_ip_adapter_scale(scale)
style_image = load_image("https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/0052a70beed5bf71b92610a43a52df6d286cd5f3/diffusers/rabbit.jpg")
generator = torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(26)
image = pipeline(
prompt="a cat, masterpiece, best quality, high quality",
ip_adapter_image=style_image,
negative_prompt="text, watermark, lowres, low quality, worst quality, deformed, glitch, low contrast, noisy, saturation, blurry",
guidance_scale=5,
num_inference_steps=30,
generator=generator,
).images[0]
image
```
### ControlNet
Controlling the outputs of diffusion models only with a text prompt is a challenging problem. ControlNet is a neural network model that provides image-based control to diffusion models. Control images can be edges or other landmarks extracted from a source image.

## Pix2Pix
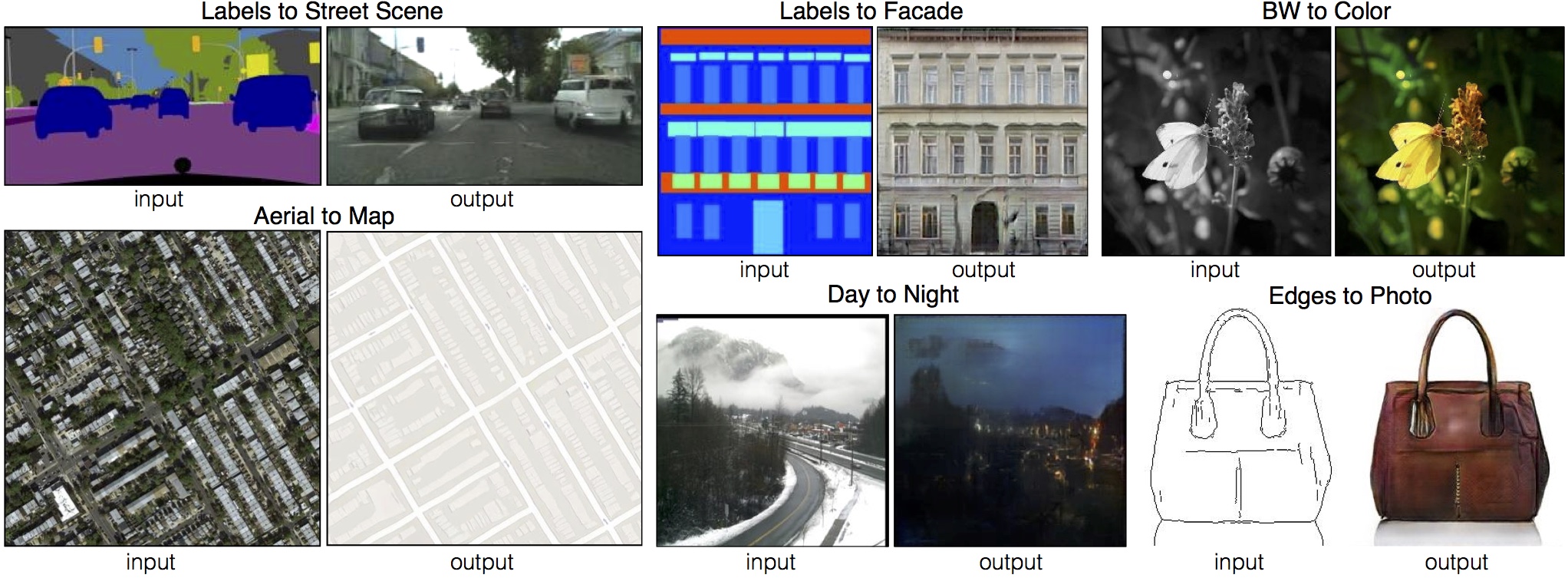
Pix2Pix is a popular model used for image-to-image translation tasks. It is based on a conditional-GAN (generative adversarial network) where instead of a noise vector a 2D image is given as input. More information about Pix2Pix can be retrieved from this [link](https://phillipi.github.io/pix2pix/) where the associated paper and the GitHub repository can be found.
The images below show some examples extracted from the Pix2Pix paper. This model can be applied to various use cases. It is capable of relatively simpler things, e.g., converting a grayscale image to its colored version. But more importantly, it can generate realistic pictures from rough sketches (can be seen in the purse example) or from painting-like images (can be seen in the street and facade examples below).
## Useful Resources
- [Image-to-image guide with diffusers](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/using-diffusers/img2img)
- Image inpainting: [inpainting with 🧨diffusers](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/inpaint), [demo](https://huggingface.co/spaces/diffusers/stable-diffusion-xl-inpainting)
- Colorization: [demo](https://huggingface.co/spaces/modelscope/old_photo_restoration)
- Super resolution: [image upscaling with 🧨diffusers](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/upscale#super-resolution), [demo](https://huggingface.co/spaces/radames/Enhance-This-HiDiffusion-SDXL)
- [Style transfer and layout control with diffusers 🧨](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/using-diffusers/ip_adapter#style--layout-control)
- [Train your ControlNet with diffusers 🧨](https://huggingface.co/blog/train-your-controlnet)
- [Ultra fast ControlNet with 🧨 Diffusers](https://huggingface.co/blog/controlnet)
- [List of ControlNets trained in the community JAX Diffusers sprint](https://huggingface.co/spaces/jax-diffusers-event/leaderboard)
## References
[1] P. Isola, J. -Y. Zhu, T. Zhou and A. A. Efros, "Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional Adversarial Networks," 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2017, pp. 5967-5976, doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.632.
This page was made possible thanks to the efforts of [Paul Gafton](https://github.com/Paul92) and [Osman Alenbey](https://huggingface.co/osman93).