@d3vtool/hooks
Version:
Collection of custom React hooks to simplify tasks in your React projects.
1,461 lines (1,036 loc) • 44.6 kB
Markdown
# React Hooks Collection
A collection of custom React hooks designed to simplify common tasks in your React applications. Here’s the list of all the hooks:
- [**useMState**](#usemstate)
- It is a custom mutable version of useState that supports direct or
initializer-action-based initial state and enables state updates using the most recent mutable snapshot.
- [**useBoolean**](#useboolean)
- Manages boolean states with easy toggling actions.
- [**useClickOutside**](#useclickoutside)
- It's a custom hook that triggers a callback when a click occurs outside the referenced element, useful for scenarios like closing modals or dropdowns.
- [**usePersistentState**](#usepersistentstate)
- Manages state that persists in localStorage across tabs/window and components.
- [**useReadPersistentState**](#usereadpersistentstate)
- Reads a persistent state from localStorage without providing update capabilities across tabs/window and components.
- [**createHub**](#createhub)
- Creates a shared state hub to manage and synchronize state across multiple components.
- [**createComputedHub**](#createcomputedhub)
- Creates a computed hub that derives its state from an existing hub using a compute action.
- [**createPromiseHub**](#createpromisehub)
- Creates a hub to manage asynchronous state with a promise action, handling state, errors, and loading.
- [**useHub**](#usehub)
- Subscribes to a shared state hub and provides access to both the state and an update function.
- [**useReadHub**](#usereadhub)
- Reads the current state from a shared state hub without the ability to update it.
- [**useComputeHub**](#usecomputehub)
- Computes a derived state from a shared state hub using a custom compute function.
- [**useStoredHub**](#usestoredhub)
- `useStoredHub` is a custom hook that synchronizes a shared state hub with persistent storage across tabs and pages.
- [**usePromiseHub**](#usepromisehub)
- Manages state from a promise hub, providing access to current state, errors, loading status, and a retry action.
- [**usePromiseReadHub**](#usepromisereadhub)
- Reads the current state, error, and loading status from a promise hub without triggering updates.
- [**usePromiseHubAction**](#usepromisehubaction)
- `usePromiseHubAction` is a custom hook that allows you to manually trigger an asynchronous action within a `PromiseHub` and provides the current loading state and any errors.
- [**useSecId**](#usesecid)
- `useSecId` is a custom hook that returns a function to generate unique string identifiers with customizable length and character set.
- [**useForm**](#useform)
- `useForm` is a custom React hook for managing form state, validation, and asynchronous submission. It optimizes performance by minimizing re-renders, updating the component only on validation errors rather than input changes.
- [**useDebounce**](#usedebounce)
- `useDebounce` is a custom React hook that delays the execution of a function until after a specified delay, reducing unnecessary calls. It's useful for scenarios like search bars, where you want to avoid triggering an action on every keystroke.
---
## Installation
You can install the package using npm or yarn:
### npm
```bash
npm install @d3vtool/hooks
```
### yarn
```bash
yarn add @d3vtool/hooks
```
## Available Hooks
### `useMState`
`useMState` is a custom mutable version of `useState` hook for managing state in your React components. It can be used with a direct initial state value or with an initializer function for more complex state setups. It also supports updating state based on the most recent snapshot of the state in a mutable way.
#### API
```ts
const [state, setState] = useMState(initialState);
```
- `initialState`: Can be a direct initial value or a function that returns the initial value.
#### Examples
##### Using with a direct initial state value:
```ts
const [count, setCount] = useMState(0);
```
##### Using with an initializer function:
```ts
import { useMState } from "@d3vtool/hooks";
const [user, setUser] = useMState(() => ({ name: 'John', age: 30 }));
// Updating state based on previous state:
setUser(mostRecentSnapshot => {
mostRecentSnapshot.age += 1;
});
// It also accepts a second argument for deep cloning the `mostRecentSnapshot` of the state.
// By default, this is set to false, so it creates a shallow copy of `Object` types.
setUser(mostRecentSnapshot => {
mostRecentSnapshot.age += 5;
}, true);
```
##### Using with an Array:
```ts
import { useMState } from "@d3vtool/hooks";
const [fruits, setFruits] = useMState([]);
// Updating array state by mutating:
setUser(prevFruits => {
prevFruits.push('Banana');
prevFruits.push('Apple');
});
```
---
### `useBoolean`
`useBoolean` is a custom hook that provides an easy way to manage boolean states. It allows you to toggle the boolean state, set it to `true`, or set it to `false`.
#### API
```ts
const [state, actions] = useBoolean(initialValue: boolean);
```
- `initialValue`: The initial value of the boolean state.
#### Examples
##### Basic usage with initial value:
```ts
const [state, actions] = useBoolean(false);
```
This initializes the state to `false`.
##### Toggling the state:
```tsx
const [state, actions] = useBoolean(false);
return (
<div>
<p>The current state is: {state ? 'True' : 'False'}</p>
<button onClick={actions.toggle}>Toggle State</button>
</div>
);
```
##### Setting the state to `true` or `false`:
```tsx
const [state, actions] = useBoolean(false);
return (
<div>
<button onClick={actions.setTrue}>Set to True</button>
<button onClick={actions.setFalse}>Set to False</button>
</div>
);
```
- **`toggle`**: Flips the current state between `true` and `false`.
- **`setTrue`**: Sets the state to `true`.
- **`setFalse`**: Sets the state to `false`.
---
### `useClickOutside`
`useClickOutside` is a custom hook that triggers a callback when a click event occurs outside the referenced element. It allows you to detect clicks outside a specific component and can be useful for scenarios like closing modals or dropdowns.
#### API
```ts
const ref = useClickOutside(action: VoidFunction);
```
- `action`: The function to be triggered when a click occurs outside the referenced element.
#### Example
```tsx
import { useClickOutside } from "@d3vtool/hooks";
const DropdownComponent: React.FC = () => {
const dropdownRef = useClickOutside(() => {
console.log("Clicked outside the dropdown");
});
return (
<div>
<div ref={dropdownRef} style={{ padding: "20px", backgroundColor: "lightblue" }}>
<p>Dropdown content</p>
<button>Click me</button>
</div>
<p>Click outside the box to trigger the action.</p>
</div>
);
};
export default DropdownComponent;
```
---
### `usePersistentState`
`usePersistentState` is a custom hook that manages state and persists it in `localStorage`. It allows you to store and retrieve state values across sessions and tabs, with optional features like clearing the state when the component unmounts, delayed saving, `useLayout` ensures the state is synchronized and fetched from storage immediately during the layout phase when the component is rendered for the first time and custom serialization and deserialization function for user-defined type.
#### Supported Data Types:
1. **Primitive Types**: e.g. `numbers`, `strings`, `booleans`.
2. **Object Types**: e.g. `plain objects` and `arrays`.
3. **Special Object Types**:
- `Map`, `Set`, `Date`, `BigInt`, `RegExp`.
4. **User-defined Types**: You can provide custom serialization and deserialization functions within config for complex types like classes or non-JSON-serializable objects.
#### Key Features:
1. **Persistent State Across Tabs**: Synchronize state across multiple browser windows or tabs in real-time.
2. **Optimized Caching**: Once a state is fetched from `localStorage`, it is cached for improved performance on subsequent reads.
3. **Efficient State Updates**: Delayed saving of state reduces unnecessary writes to `localStorage`, which can improve performance when state changes rapidly.
4. **`saveDelay`**: Optional delay before saving the state to `localStorage`, useful for debouncing frequent state changes.
5. **Automatic Cleanup**: Option to automatically clear state from `localStorage` when the component unmounts using the `clearStorageOnUnMount` option.
6. **Real-time Synchronization**: State updates are synchronized across all components and tabs in real-time when using the same key.
7. **Custom Serialization and Deserialization**: Provides flexibility to serialize and deserialize complex objects through custom functions.
8. **Reduced Re-renders**: Internal caching reduces re-renders by avoiding unnecessary reads from `localStorage`.
#### Usage Scenarios:
- **Cross-tab synchronization**: Ideal for state that needs to be consistent across multiple tabs or windows.
- **Form auto-save**: Keep form data persistent across sessions or tabs.
- **Optimizing performance**: Reduce frequent reads and writes to `localStorage` to enhance app performance.
---
#### API
```ts
const [state, setState] = usePersistentState<T>(
key: string,
initialState: T | () => T,
config?: {
saveDelay?: number,
clearStorageOnUnMount?: boolean,
useLayout?: boolean,
serialize?: SerializerFn<T>,
deserialize?: DeSerializerFn<T>
}
);
```
- **`key`**: A unique identifier for the stored state in `localStorage`.
- **`initialState`**: The initial state value or a function that returns the initial state.
- **`config`**: Optional configuration object:
- **`saveDelay`**: (Default: `300ms`) The delay before saving the state to `localStorage` after a state update. Useful for debouncing rapid state changes.
- **`clearStorageOnUnMount`**: (Default: `false`) Boolean flag indicating whether to clear the state from `localStorage` when the component unmounts.
- **`useLayout`**: (Default: `false`) If `true`, synchronizes state ( uses useLayoutEffect ) updates during the layout phase to immediately reflect updates in the UI.
- **`serialize`**: (Optional) Custom serialization function that converts state to a string before saving it to `localStorage`.
- **`deserialize`**: (Optional) Custom deserialization function that parses the string from `localStorage` back into the original state.
---
#### Basic Example
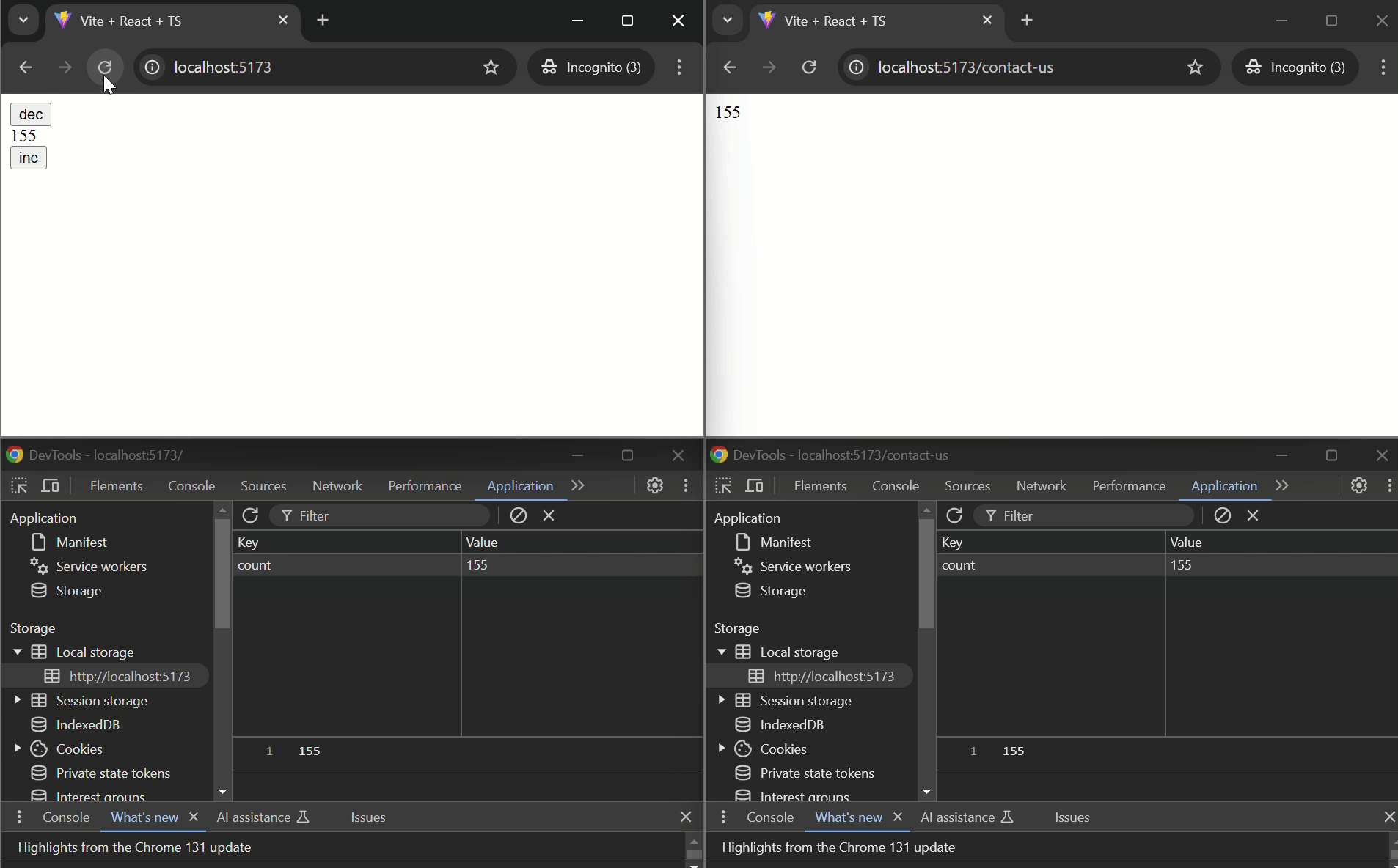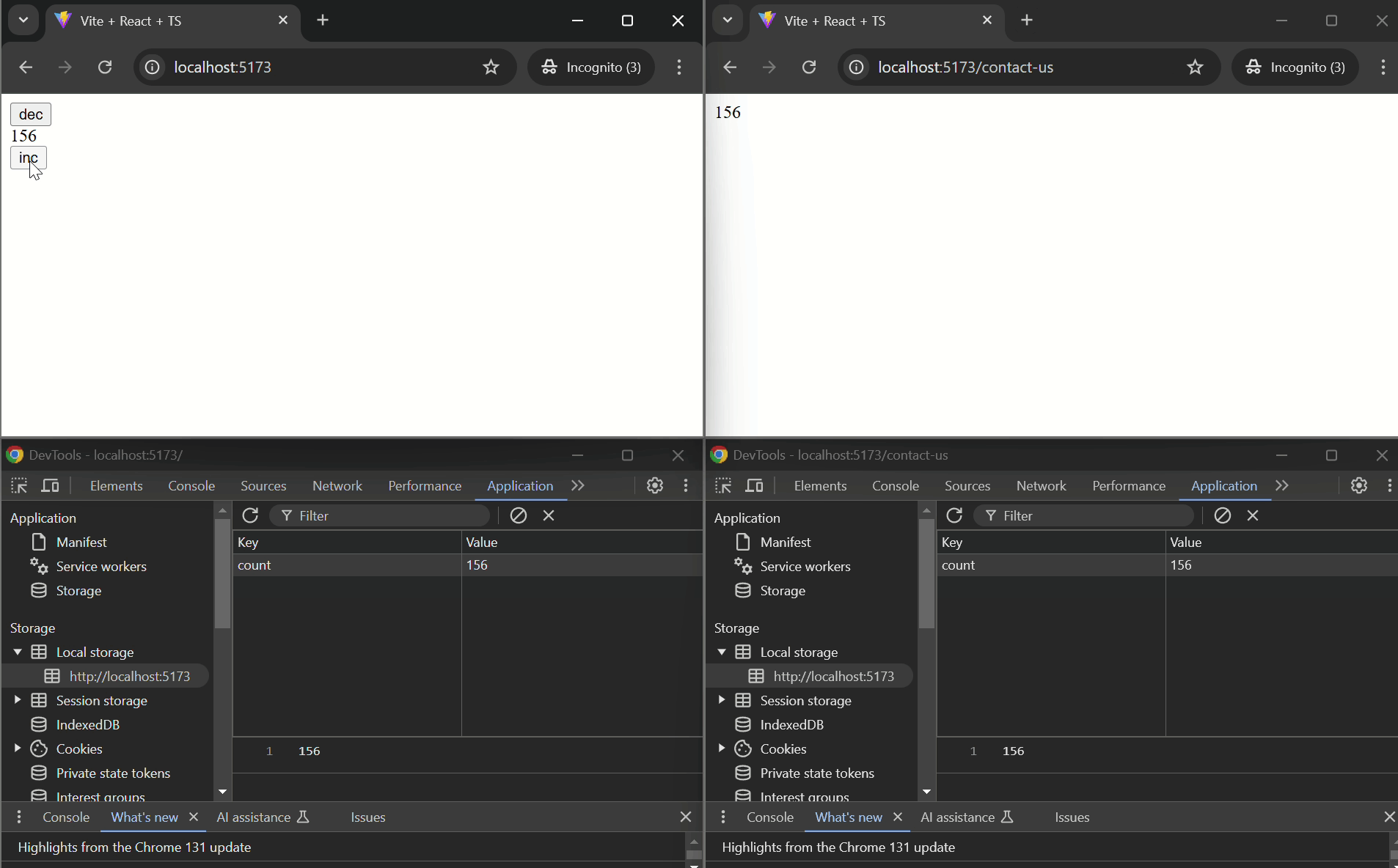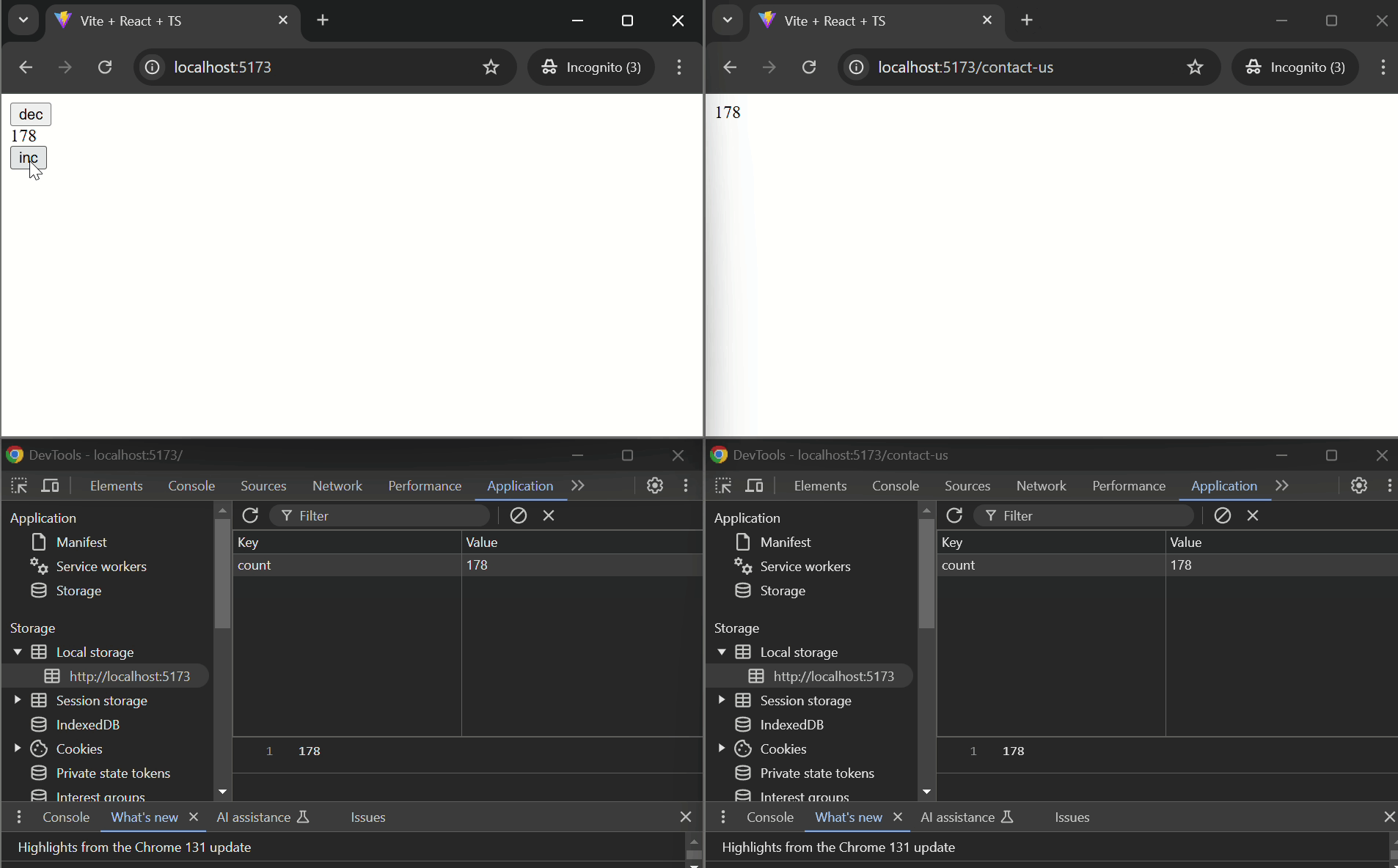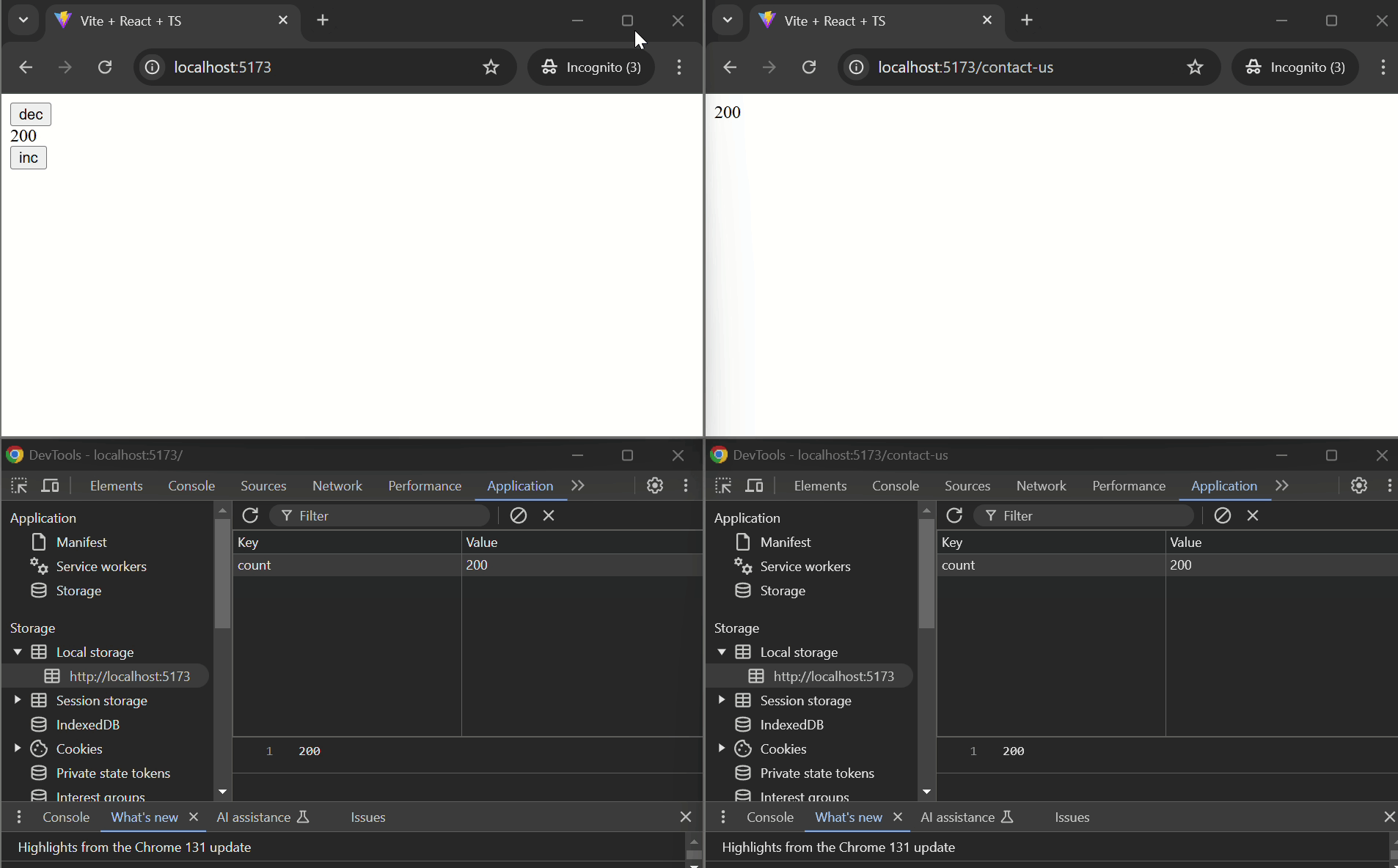
```tsx
import { usePersistentState } from "@d3vtool/hooks";
const CounterComponent: React.FC = () => {
const [count, setCount] = usePersistentState("count", 0);
function handleIncrement() {
setCount(prev => prev + 1);
}
function handleDecrement() {
setCount(prev => prev - 1);
}
return (
<div style={{
display: "flex",
alignItems: "center",
justifyContent: "center",
gap: "12px",
marginTop: "12rem"
}}>
<button onClick={handleDecrement}>DEC</button>
<p>{count}</p>
<button onClick={handleIncrement}>INC</button>
</div>
);
};
export default CounterComponent;
```
---
#### Example with `clearStorageOnUnMount` and `saveDelay`
```tsx
import { usePersistentState } from "@d3vtool/hooks";
// Define config outside or use useMemo to prevent re-creation on every render.
const pStateConfig = {
saveDelay: 200, // Save after 200ms delay
clearStorageOnUnMount: true
}
const SessionComponent: React.FC = () => {
const [sessionData, setSessionData] = usePersistentState('session', {}, pStateConfig);
return (
<div>
<p>Session Data: {JSON.stringify(sessionData)}</p>
<button onClick={() => setSessionData({ user: 'John Doe' })}>Set User</button>
<button onClick={() => setSessionData({})}>Clear Session</button>
</div>
);
};
export default SessionComponent;
```
---
#### Example with `useLayout` Option
```tsx
import { usePersistentState } from "@d3vtool/hooks";
const LayoutComponent: React.FC = () => {
const [layoutData, setLayoutData] = usePersistentState('layoutData', { theme: 'light' }, {
useLayout: true
});
return (
<div>
<p>Layout Data: {JSON.stringify(layoutData)}</p>
<button onClick={() => setLayoutData({ theme: 'dark' })}>Change Theme</button>
</div>
);
};
export default LayoutComponent;
```
---
#### Example with `serialize` and `deserialize` Functions
```tsx
import React from 'react';
import { usePersistentState } from "@d3vtool/hooks";
class Product {
public static selfInstance: Product | null = null;
constructor(name: string, price: number) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
static serialize(product: Product): string {
return `${product.name},${product.price}`;
}
static deserialize(serialized: string): Product {
const [name, price] = serialized.split(',');
return new Product(name, parseFloat(price));
}
static create(name: string, price: number): Product {
if (Product.selfInstance === null) {
Product.selfInstance = new Product(name, price);
} else {
Product.selfInstance.name = name;
Product.selfInstance.price = price;
}
return Product.selfInstance;
}
}
// Or you can define this `config` inside your component
// with useMemo hook in order to avoid re-creation on every re-render
const config = {
serialize: Product.serialize,
deserialize: Product.deserialize
}
const ProductComponent: React.FC = () => {
// Initializing product using the create method to ensure the singleton pattern
const [product, setProduct] = usePersistentState("product", Product.create("Laptop", 1200), config);
function updatePrice() {
setProduct(Product.create("Laptop", 1500)); // Update price of the product
}
return (
<div>
<p>Product: {product.name}, Price: ${product.price}</p>
<button onClick={updatePrice}>Update Price</button>
</div>
);
};
export default ProductComponent;
```
---
### Key Notes:
1. **Save Delay**: The `saveDelay` option allows you to debounce rapid state updates before saving to `localStorage`. This reduces unnecessary writes when the state is changing frequently, such as in form inputs.
2. **Clear on Unmount**: Use `clearStorageOnUnMount` to remove the stored state when the component unmounts, which is helpful for preventing stale data from persisting across sessions.
3. **Real-Time Syncing**: The state is automatically synced across all tabs and windows, providing real-time synchronization, which is ideal for managing state in applications with multiple browser tabs or windows.
---
### `useReadPersistentState`
`useReadPersistentState` is a custom hook that reads the persistent state from `localStorage` without providing the ability to update it across windows or tabs. This hook supports deserializing the state value from `localStorage` using an optional custom deserialization function.
#### API
```ts
const state = useReadPersistentState<T>(
key: string,
deserializerFn?: DeSerializerFn<T>
): T | undefined;
```
- **`key`**: A unique string to identify the stored state in `localStorage`.
- **`deserializerFn`**: (Optional) A custom function to deserialize the state value from `localStorage`. Defaults to a generic `deserialize` function.
- **Returns**: The deserialized state value if found in storage, or `undefined` if no value is found for the given key.
#### Example
##### Reading a primitive type (number):
```tsx
import { useReadPersistentState } from "@d3vtool/hooks";
const ReadCounterComponent: React.FC = () => {
const counter = useReadPersistentState<number>("counter");
return (
<div>
Read Counter: {counter}
</div>
);
};
export default ReadCounterComponent;
```
##### Reading a Special type (BigInt):
```tsx
import { useReadPersistentState } from "@d3vtool/hooks";
const ReadCounterComponent: React.FC = () => {
const counter = useReadPersistentState<BigInt>("counter");
return (
<div>
Read Counter: {counter}
</div>
);
};
export default ReadCounterComponent;
```
##### Reading an user-defined object value from persistent storage with a custom deserializer:
###### User.ts
```tsx
class User {
constructor(public name: string) {
this.name = name;
}
static serializerFn(user: User): string {
return user.name;
}
static deserializerFn(data: string): User {
return new User(data);
}
}
```
```tsx
import User from "./User.ts";
const ReadUserComponent: React.FC = () => {
const userState = useReadPersistentState<User>('user', User.deserializerFn);
return (
<div>
User: {userState?.name}
</div>
);
};
export default ReadUserComponent;
```
#### Notes
- `useReadPersistentState` allows reading data from `localStorage` but does not allow updating the state across windows or tabs.
- Custom deserialization functions are helpful when dealing with unsupported types in `localStorage`, such as custom classes or non json-serializable object.
- If no deserialization function is passed, a default deserialization is applied to parse the stored value.
---
### createHub
`createHub` creates a shared state hub that can manage and synchronize state across multiple components.
#### API
```ts
const myHub = createHub<T>(initialState: T | InitializerAction<T>);
```
- `initialState`: The initial state value or a function that returns the initial state.
- Returns a hub object that manages the shared state.
#### Example
```ts
import { createHub } from "@d3vtool/hooks";
const myHub = createHub({ count: 0 });
```
---
### createComputedHub
`createComputedHub` creates a new computed hub that derives its state from an existing hub using a compute action.
#### API
```ts
const computedHub = createComputedHub<T>(hub: Hub<T>, computeAction: ComputeAction<T>);
```
- `hub`: The original hub from which the state will be derived.
- `computeAction`: A function that computes the new state based on the current state of the original hub.
- Returns a new hub object that manages the computed state.
#### Example
```ts
import { createHub, createComputedHub } from "@d3vtool/hooks";
const countHub = createHub({ count: 0 });
// Create a computed hub that doubles the count value:
// Always use `createComputedHub` with `useReadHub`
const doubleComputedHub = createComputedHub(countHub, (state) => ({
count: state.count * 2
}));
export function DoubleCounter() {
// Always use computedHub with `useReadHub`
// Whenever 'countHub' is updated, 'doubleComputedHub' will automatically update as well.
const doubleCount = useReadHub<number>(doubleComputedHub);
return (
<>
<p>{doubleCount}</p>
</>
)
}
```
---
### useHub
`useHub` is a custom hook that subscribes to a shared state hub and provides access to the current state along with a function to update it.
#### API
```ts
const [state, setState] = useHub<T>(hub: Hub<T>);
```
- `hub`: The shared state hub that holds the state.
- Returns the current state and a function to update it.
#### Example
```tsx
import { useHub } from "@d3vtool/hooks";
// Always create `hub` outside of your component.
const myHub = createHub({ count: 0 });
const CounterComponent: React.FC = () => {
const [count, setCount] = useHub(myHub);
return (
<div>
<p>Count: {count}</p>
<button onClick={() => setCount(prev => prev + 1)}>Increment</button>
<button onClick={() => setCount(0)}>Reset</button>
</div>
);
};
export default CounterComponent;
```
---
### useReadHub
`useReadHub` is a custom hook that reads the current state from a shared state hub without providing a way to update it.
#### API
```ts
const state = useReadHub<T>(hub: Hub<T>);
```
- `hub`: The shared state hub that holds the state.
- Returns the current state.
#### Example
```tsx
import { useReadHub } from "@d3vtool/hooks";
const DisplayCounterComponent: React.FC = () => {
const count = useReadHub<number>(myHub);
return (
<div>
<p>Count: {count}</p>
</div>
);
};
export default DisplayCounterComponent;
```
---
### useComputeHub
`useComputeHub` is a custom hook that computes a derived state from a shared state hub using a provided compute action.
#### API
```ts
const computedState = useComputeHub<T>(hub: Hub<T>, computeAction: ComputeAction<T>);
```
- `hub`: The shared state hub that holds the state.
- `computeAction`: A function that computes a derived state based on the current state of the hub.
- Returns the computed state.
#### Example
```tsx
import { useComputeHub } from "@d3vtool/hooks";
// Always create `hub` outside of your component.
const myHub = createHub({ count: 0 });
const ComputedCounterComponent: React.FC = () => {
const doubleCount = useComputeHub(myHub, (state) => state.count * 2);
return (
<div>
<p>Double Count: {doubleCount}</p>
</div>
);
};
export default ComputedCounterComponent;
```
---
### useStoredHub
`useStoredHub` is a custom hook that synchronizes a shared state hub with persistent storage (like localStorage). This allows the state of the hub to persist across pages and tabs reloads or navigation.
#### API
```ts
const [state, setState] = useStoredHub<T>(key: string, hub: Hub<T>);
```
- `key`: The key used to store and retrieve the hub's state from persistent storage (e.g., localStorage).
- `hub`: The shared state hub that holds the state.
- Returns the current state and a function to update it.
#### Example
This example demonstrates how to use `useStoredHub` to manage and synchronize a counter across different pages across tabs. The counter state persists using localStorage and is shared between the `Home` and `ContactUs` components.
1. **countHub.ts:**
```ts
import { createHub } from "@d3vtool/hooks";
export const countHub = createHub(1);
```
2. **Page1 Component:**
```tsx
import { countHub } from "./countHub";
import { Link } from "react-router-dom";
import { useStoredHub } from "@d3vtool/hooks";
export default function Page1() {
const [count, setCount] = useStoredHub<number>("counter", countHub);
function handleInc() {
setCount(prev => prev + 1);
}
function handleDec() {
setCount(prev => prev - 1);
}
return (
<div style={{
display: "flex",
alignItems: "center",
justifyContent: "center",
gap: "12px",
marginTop: "12rem"
}}>
<button onClick={handleDec}>DEC</button>
<p>{count}</p>
<button onClick={handleInc}>INC</button>
<Link to="/page2">Page 2</Link>
</div>
);
}
```
3. **Page2 Component:**
```tsx
import { countHub } from "./countHub";
import { Link } from "react-router-dom";
import { useStoredHub } from "@d3vtool/hooks";
export default function Page2() {
const [count, setCount] = useStoredHub<number>("counter", countHub);
function handleInc() {
setCount(prev => prev + 1);
}
function handleDec() {
setCount(prev => prev - 1);
}
return (
<div style={{
display: "flex",
alignItems: "center",
justifyContent: "center",
gap: "12px",
marginTop: "12rem"
}}>
<button onClick={handleDec}>DEC</button>
<p>{count}</p>
<button onClick={handleInc}>INC</button>
<Link to="/">Page 1</Link>
</div>
);
}
```
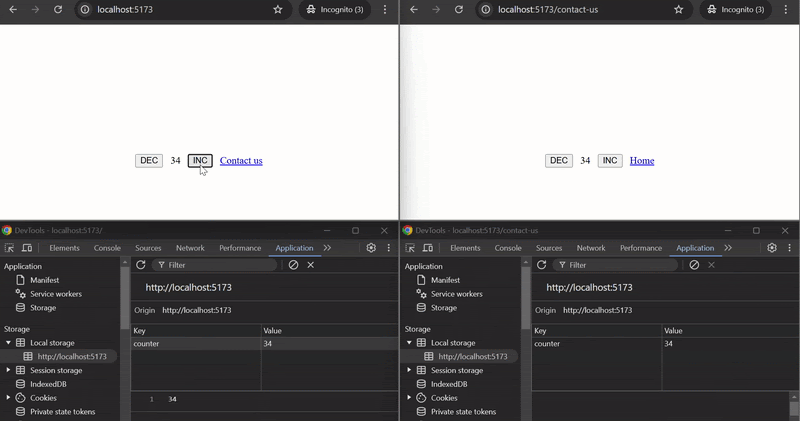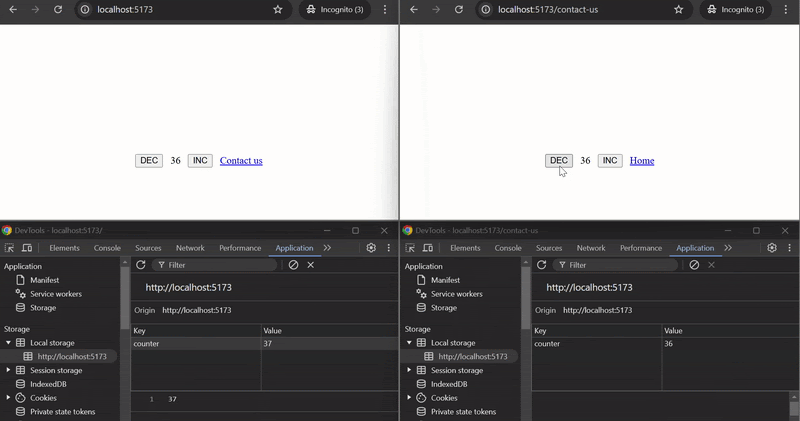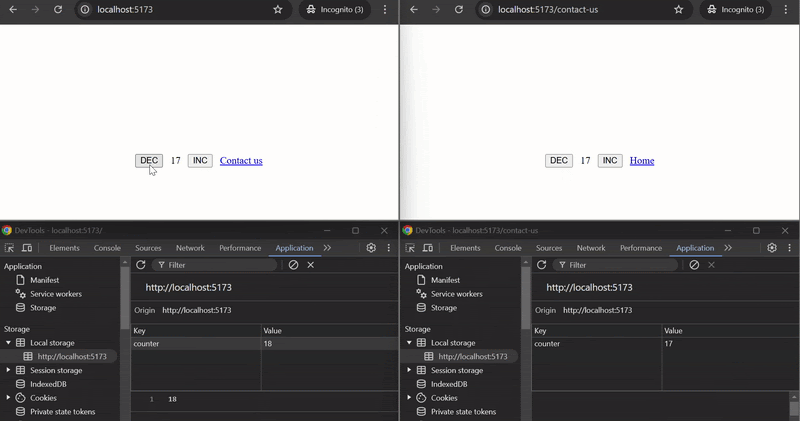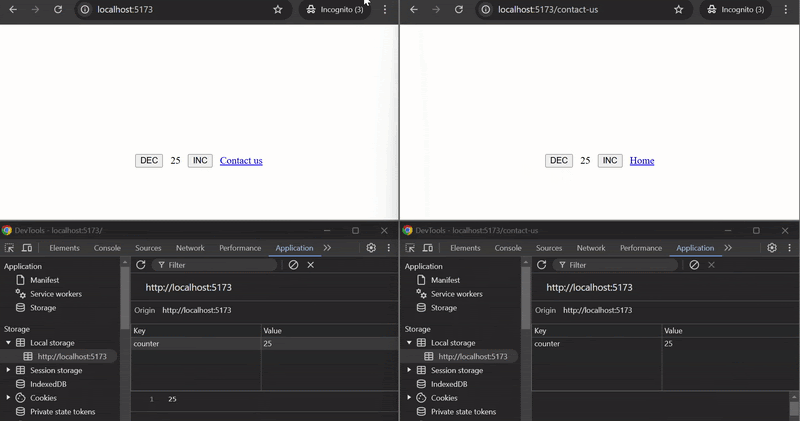
#### How it works:
- `useStoredHub` is used in both `Page1` and `Page2` components with the same key `"counter"`, ensuring that the counter value is shared and synchronized between the two pages or across tabs.
- The `counter` state is persisted using localStorage and can be incremented or decremented on either page. The updated state is reflected on both pages or in pages opend on different tabs.
---
### `createPromiseHub`
`createPromiseHub` is a function that creates a hub to manage state with a promise action. This hub can then be used with the `usePromiseHub` or `usePromiseReadHub` hooks.
#### API
```ts
const promiseHub = createPromiseHub(initialState, promiseAction);
```
- `initialState`: The initial state value or initializer function.
- `promiseAction`: The async function that will resolve to update the state.
#### Example
```ts
import { createPromiseHub } from "@d3vtool/hooks";
export const fetchUserDataHub = createPromiseHub(undefined, async (prevState) => {
const response = await fetch('/api/user');
const data = await response.json();
return data;
});
```
---
### `usePromiseHub`
`usePromiseHub` is a custom hook that helps manage asynchronous state using a promise hub. It provides the current state, loading status, error information, and a way to re-trigger the async action. The hook can be configured to either trigger the promise immediately or allow manual re-triggering, and optionally integrate with React Suspense.
#### API
```ts
const { data, error, isPending, reAction } = usePromiseHub(promiseHub, config?);
```
- `promiseHub`: The promise hub created using `createPromiseHub`.
- `config`: (Optional) Configuration object for the hook. It includes:
- `immediate`: If `true`, the promise action will be triggered immediately on hook initialization. Defaults to `true`.
- `suspense`: If `true`, the hook will integrate with React Suspense, suspending the component until the promise resolves. Defaults to `false`.
#### Example
```tsx
import { usePromiseHub } from "@d3vtool/hooks";
import { fetchUserDataHub } from "./userHub";
const UserProfile: React.FC = () => {
const { data, error, isPending, reAction } = usePromiseHub(fetchUserDataHub);
return (
<div>
{isPending ? <p>Loading user data...</p> : <p>User: {data?.name}</p>}
{error && <p>Error: {error.message}</p>}
<button onClick={reAction} disabled={isPending}>Retry</button>
</div>
);
};
export default UserProfile;
```
#### Example with Suspense
If you're using `suspense`, you don't need to use the `isPending` state, as React Suspense will handle the loading state for you.
```tsx
import { useMemo } from "react";
import { usePromiseHub } from "@d3vtool/hooks";
import { fetchUserDataHub } from "./userHub";
const UserProfile: React.FC = () => {
const config = useMemo(() => ({ suspense: true }), []); // Use useMemo to avoid recreating config on re-renders
const { data, error } = usePromiseHub(fetchUserDataHub, config);
return (
{error && <p>Error: {error.message}</p>}
<p>User: {data?.name}</p>
);
};
export default UserProfile;
```
```tsx
import { Suspense } from "react";
import UserProfile from "./UserProfile";
const App: React.FC = () => {
return (
<Suspense fallback={<p>Loading...</p>}>
<UserProfile />
</Suspense>
);
};
export default App;
```
---
### `usePromiseReadHub`
`usePromiseReadHub` is a custom hook that provides read-only access to the state managed by a promise hub. It returns the current state, any error, and the loading status.
#### API
```ts
const { data, error, isPending } = usePromiseReadHub(promiseHub);
```
- `promiseHub`: The promise hub managing the async state.
- `suspense`: (Optional) If `true`, integrates with React Suspense, suspending the component until the promise resolves.
#### Example
```tsx
import { usePromiseReadHub } from "@d3vtool/hooks";
import { fetchUserDataHub } from "./userHub";
const UserProfileReadOnly: React.FC = () => {
const { data, error, isPending } = usePromiseReadHub(fetchUserDataHub);
return (
<div>
{isPending ? <p>Loading user data...</p> : <p>User: {data?.name}</p>}
{error && <p>Error: {error.message}</p>}
</div>
);
};
export default UserProfileReadOnly;
```
### Example with Suspense
If you prefer to use React Suspense to handle the loading state automatically, you can enable it by passing `true` for the `suspense` flag.
```tsx
import { usePromiseReadHub } from "@d3vtool/hooks";
import { fetchUserDataHub } from "./userHub";
const UserProfileSuspense: React.FC = () => {
const { data, error } = usePromiseReadHub(fetchUserDataHub, true);
return (
<p>User: {data?.name}</p>
{error && <p>Error: {error.message}</p>}
);
};
export default UserProfileSuspense;
```
```tsx
import { Suspense } from "react";
import UserProfileSuspense from "./UserProfileSuspense";
const App: React.FC = () => {
return (
<Suspense fallback={<p>Loading...</p>}>
<UserProfileSuspense />
</Suspense>
);
};
export default App;
```
### Explanation:
- **Suspense**: If `suspense` is set to `true`, it will automatically suspend the component's rendering until the promise resolves, showing the fallback (`<p>Loading...</p>`) while loading.
- **Error Handling**: Any errors encountered during the promise execution are displayed using the `error`.
---
### `usePromiseHubAction`
`usePromiseHubAction` is a custom hook that allows you to manually trigger an asynchronous action within a `PromiseHub` from any other component and provides the current loading state and any errors.
#### API
```ts
const { reAction, error, isPending } = usePromiseHubAction(promiseHub, suspense?);
```
- **`reAction`**: A function to trigger the asynchronous action manually.
- **`error`**: The current error state if the action fails.
- **`isPending`**: A boolean indicating whether the action is currently loading.
- **`suspense`**: (Optional) If `true`, the hook will suspend rendering until the promise is resolved.
#### Example
#### Defining `productListHub`
The `productListHub` is created using `createPromiseHub`. It manages the asynchronous fetching of the product list from a REST API and stores the fetched data.
```ts
import { createPromiseHub } from "@d3vtool/hooks";
import { TResponse, IProduct } from "./types"; // Assume you have these types
export const productListHub = createPromiseHub<IProduct[] | undefined>(undefined, async () => {
const response = await fetch('http://localhost:4000/products');
const data = await response.json();
return data;
});
```
#### Example Usage
##### Without Suspense
```tsx
import { usePromiseHubAction } from "@d3vtool/hooks";
import { productListHub } from "./productListHub";
const ProductList: React.FC = () => {
const { reAction: refetchProducts, error, isPending } = usePromiseHubAction(productListHub);
return (
<div>
<button onClick={refetchProducts} disabled={isPending}>
{isPending ? 'Loading...' : 'Refetch Products'}
</button>
{error && <p style={{ color: 'red' }}>Error fetching products: {error.message}</p>}
</div>
);
};
export default ProductList;
```
##### With Suspense
```tsx
import { productListHub } from "./productListHub";
import { usePromiseHubAction } from "@d3vtool/hooks";
const ProductList: React.FC = () => {
const { reAction: refetchProducts, error } = usePromiseHubAction(productListHub, true);
return (
<div>
<button onClick={refetchProducts}>
Refetch Products
</button>
{error && <p style={{ color: 'red' }}>Error fetching products: {error.message}</p>}
</div>
);
};
export default ProductList;
```
```tsx
import { Suspense } from "react";
import ProductList from "./ProductList";
const App: React.FC = () => {
return (
<Suspense fallback={<p>Loading Products...</p>}>
<ProductList />
</Suspense>
);
};
export default App;
```

#### Explanation:
- **Without Suspense**:
- The button allows the user to manually trigger the `refetchProducts` action, which re-fetches the product list.
- The button text changes to "Loading..." when the promise is in progress, and the button is disabled to prevent multiple clicks.
- If an error occurs during the fetch, it is displayed below the button.
- **With Suspense**:
- The component is wrapped in a `Suspense` boundary, which will suspend rendering until the promise is resolved.
- The `fallback` prop is used to show a loading message while the promise is pending.
- If the `suspense` flag is set to `true`, the component suspends until the asynchronous action completes.
---
### `useSecId`
`useSecId` is a custom hook that returns a function to generate unique string identifiers with customizable length and character set.
#### API
```ts
const generateId = useSecId(length?: number, alphabets?: string);
```
- **`length`** *(optional)*: The desired length of the generated ID. Defaults to `8`.
- **`alphabets`** *(optional)*: A string representing the set of characters to use when generating the ID.
- **Returns**: A function that generates a new unique ID each time it is called.
#### Example
```tsx
import React from 'react';
import { useSecId } from "@d3vtool/hooks";
const IdGeneratorComponent: React.FC = () => {
const generateId = useSecId(); // Default: 8-character ID generator
const generateCustomId = useSecId(10, "ABC123"); // Custom: 10-character ID generator using "ABC123"
return (
<div>
<p>Generated ID: {generateId()}</p>
<p>Custom Generated ID: {generateCustomId()}</p>
</div>
);
};
export default IdGeneratorComponent;
```
In this example, `useSecId` is used to create two generators:
- The first generates a default 8-character ID.
- The second generates a custom 10-character ID using the characters `"ABC123"`.
---
### `useForm`
`useForm` is a custom React hook for managing form state, handling validation, and submitting forms with asynchronous logic. It provides an efficient way to bind form inputs to a schema, track validation errors, and perform custom submission actions. A notable feature is that it minimizes unnecessary re-renders: the component will only re-render when a validation error occurs, not when the input changes, improving performance.
#### API
```ts
const {
formData,
onSubmit,
formErrors,
listeners,
setFormData,
getFormData,
resetFields
} = useForm<FormSchema>(initialFormData);
```
- **`formData`**: The current form state object containing the values of the form fields, where each key matches a field from the form schema.
- **`onSubmit`**: A function to handle form submission. It supports middleware logic and triggers the submission process while handling form validation.
- **`formErrors`**: An object representing error messages for each form field, mapping field names to error strings.
- **`listeners`**: Event listeners to be spread onto form inputs. These include handlers such as `onChange` and `onBlur`, as well as a `ref` action to set input references.
- **`setFormData`**: A function to update the value of a specific form field. You can optionally hide error messages while setting data.
- **`getFormData`**: A function to retrieve the value of a specific form field from the form data.
- **`resetFields`**: A function that allows resetting all form fields. You can optionally hide error messages during the reset process.
---
#### Example
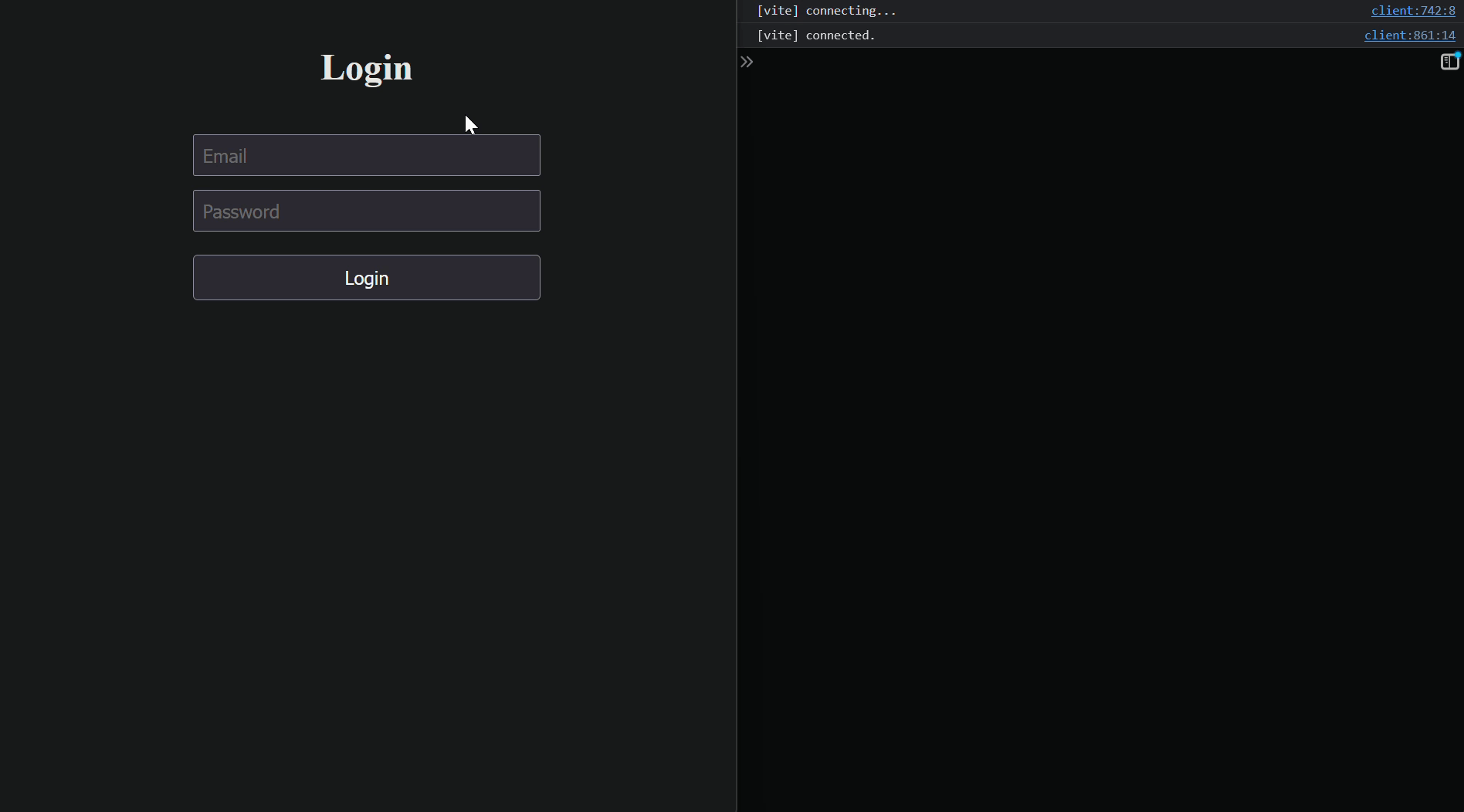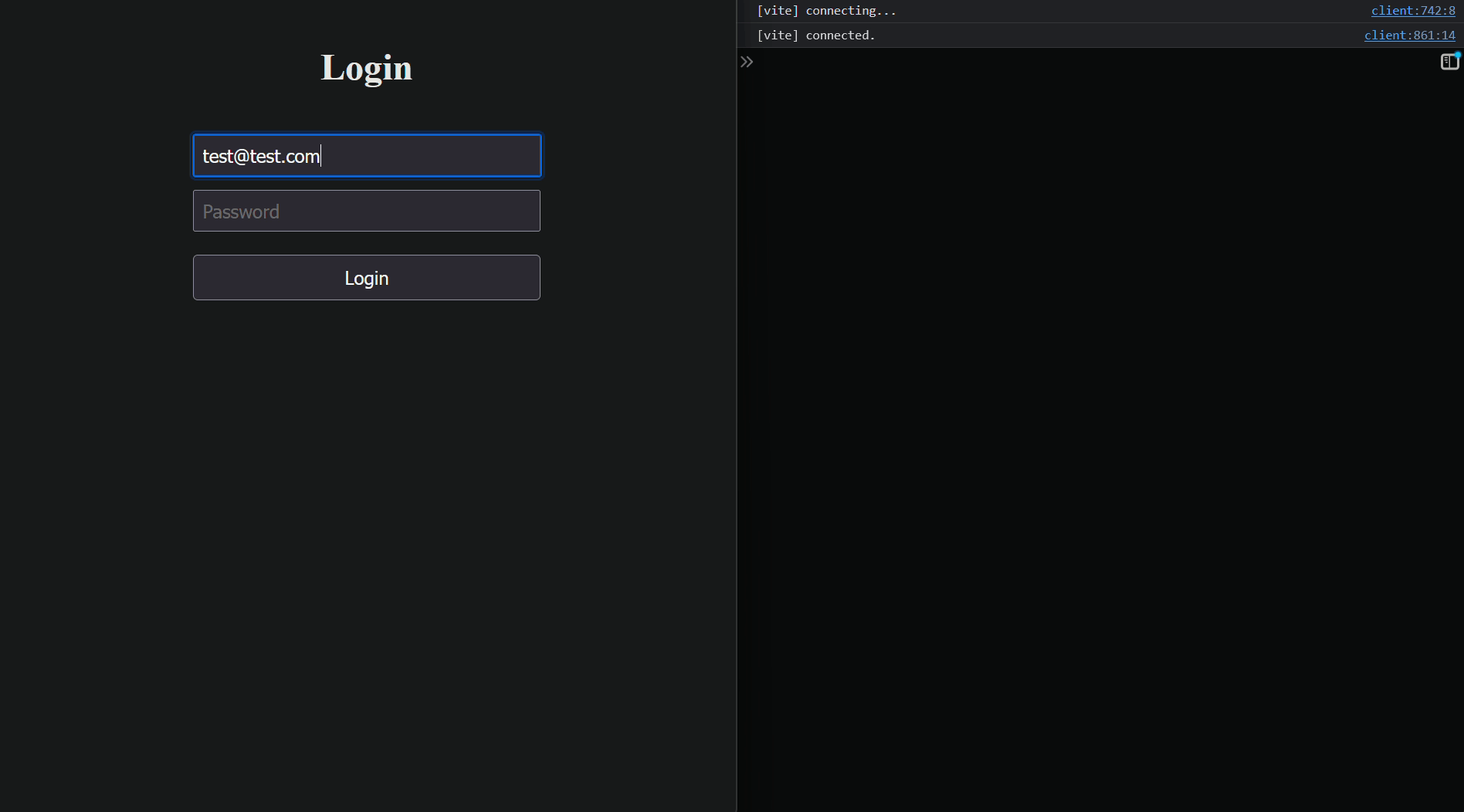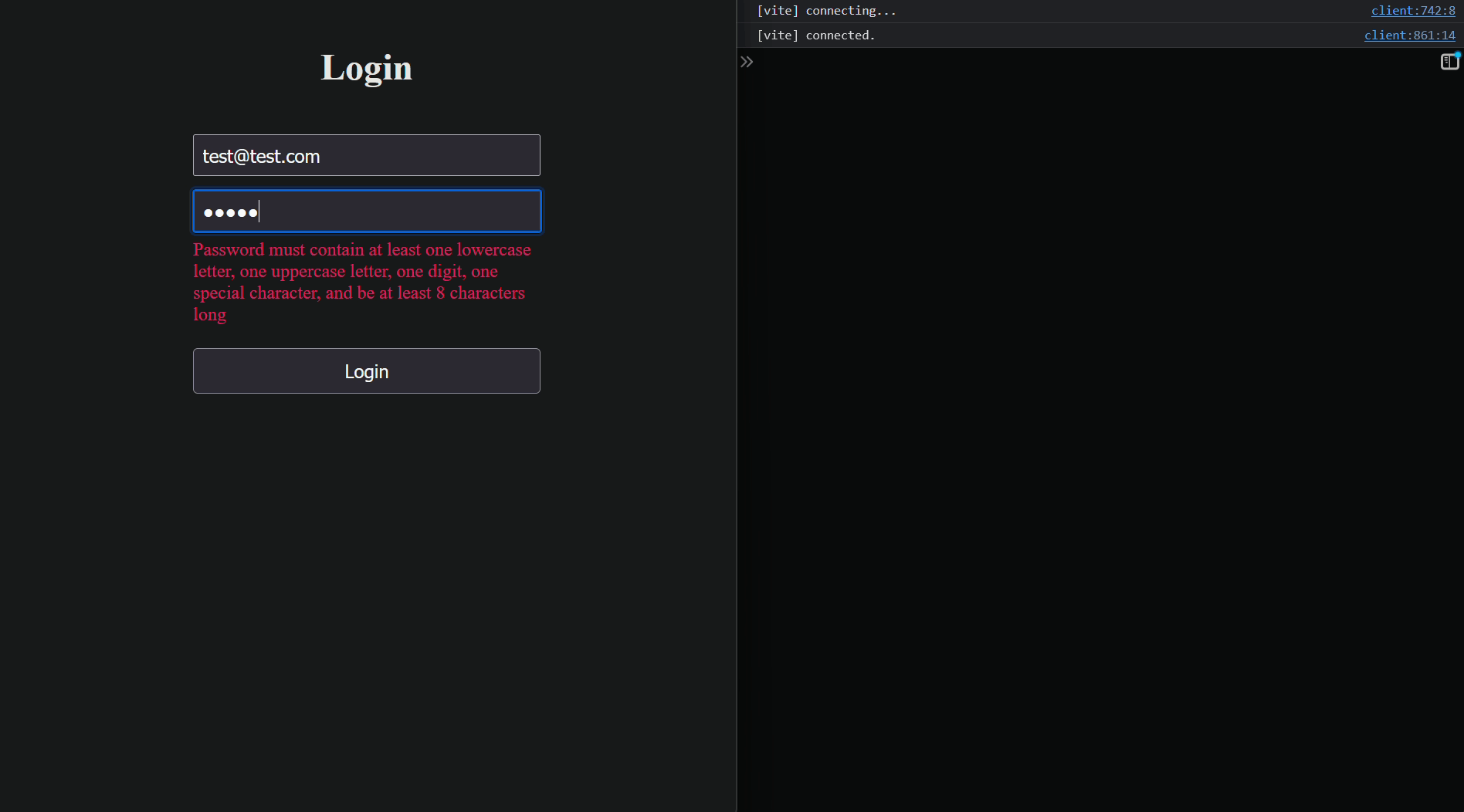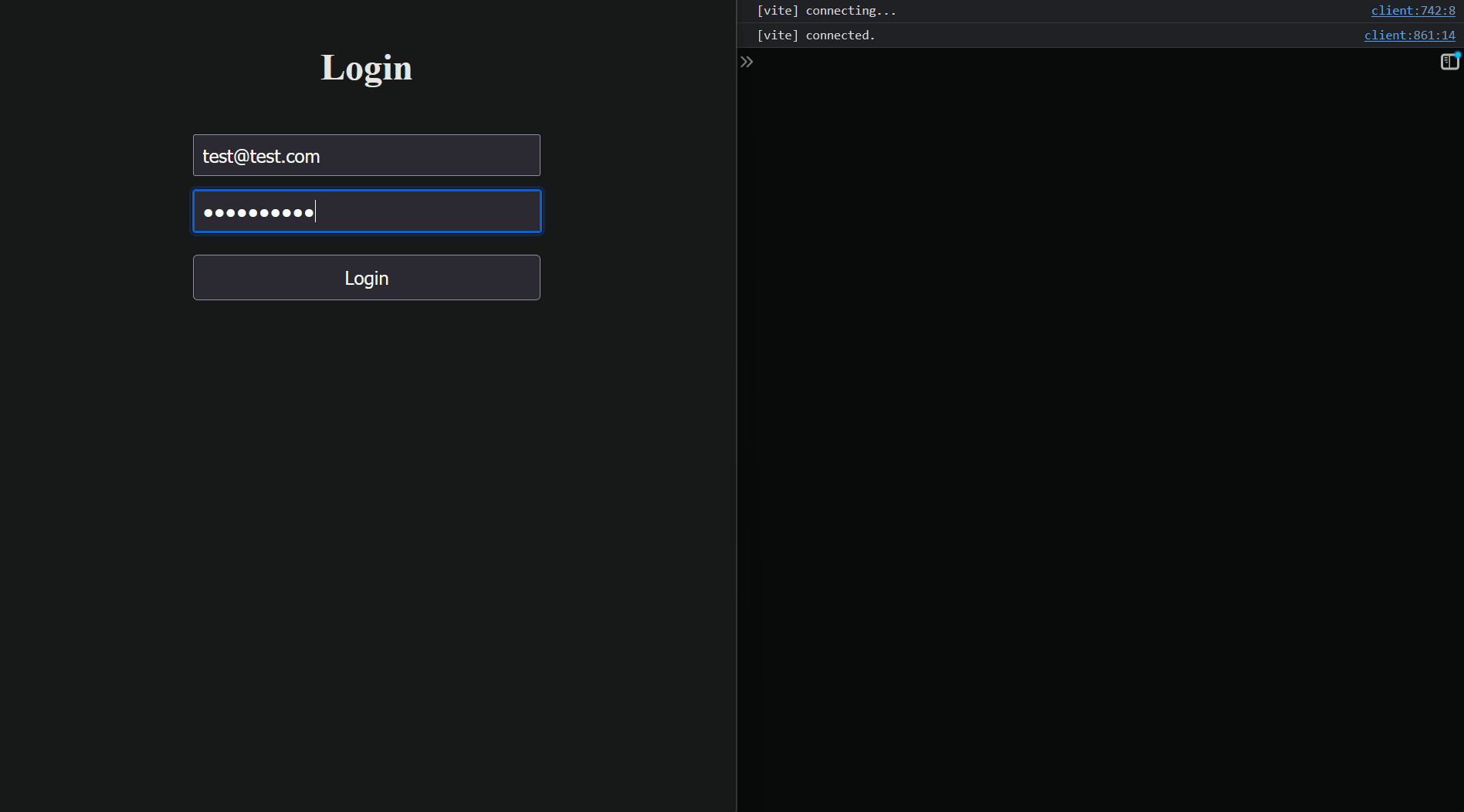
---
#### Step 1: **Import Required Libraries**
```tsx
import { useForm } from "@d3vtool/hooks";
import { Validator, VInfer, StringUtils } from "@d3vtool/utils";
```
- **`useForm`**: The main hook from the `@d3vtool/hooks` package that handles form state, validation, and submission.
- **`Validator`**: A utility from `@d3vtool/utils` for defining form validation rules.
- **`VInfer`**: A TypeScript helper to infer the type from a validation schema.
- **`StringUtils`**: A utility for manipulating strings, like transforming keys into a readable format (used later for field placeholders).
---
#### Step 2: **Define the Form Schema**
```tsx
const schema = Validator.object({
email: Validator.string().email(),
password: Validator.string().password(),
});
type SchemaType = typeof schema;
type FormSchema = VInfer<SchemaType>;
```
- **`schema`**: Defines the validation rules for the form using the `Validator.object` method. It includes:
- `email`: Must be a valid email string.
- `password`: Must follow password rules (defined by `Validator.string().password()`).
- **`SchemaType`**: A TypeScript type generated from the `schema`, allowing us to infer the shape of the form data.
---
#### Step 3: **Initialize Form Data**
```tsx
/**
* Alternatively, you can define it directly within the hook argument.
* This way, there's no need to use `VInfer` as it will automatically
* infer the type.
*/
const initialFormData: FormSchema = {
email: "",
password: "",
};
```
- **`initialFormData`**: Provides the initial state for the form fields (both `email` and `password` are empty strings by default). This state is tied to the schema using `VInfer` to ensure type safety.
---
#### Step 4: **Using `useForm` Hook in the Component**
```tsx
const {
formData, onSubmit,
formErrors, listeners
} = useForm<SchemaType>(initialFormData, schema);
```
- **`formData`**: Holds the current values of the form fields (`email` and `password`).
- **`onSubmit`**: Handles form submission logic and triggers validation.
- **`formErrors`**: Contains validation error messages for form fields, if any exist.
- **`listeners`**: An object that contains event listeners for input elements (e.g., `onChange`, `onBlur`, etc.).
---
#### Step 5: **Handling Form Submission**
```tsx
async function handleOnSubmit() {
// Handle form submission logic (e.g., send data to the server)
console.log(formData);
}
```
- **`handleOnSubmit`**: This function is called when the form is submitted. It logs the current form data but can be modified to perform any necessary actions like sending data to a server.
---
#### Step 6: **Render the Form**
```tsx
<main style={{ height: '100%', display: 'flex', flexDirection: 'column', alignItems: 'center', justifyContent: 'center', gap: '2.5rem', marginTop: '3rem' }}>
<h1>Login</h1>
<form
style={{ width: '300px', display: 'flex', flexDirection: 'column', alignItems: 'center', justifyContent: 'center', gap: '0.75rem' }}
onSubmit={onSubmit(handleOnSubmit)}
>
```
- **`onSubmit`**: When the form is submitted, `onSubmit` is called, triggering the validation and then it will callback the submission logic.
---
#### Step 7: **Rendering Form Inputs Dynamically**
```tsx
{
Object.keys(formData).map((key) => (
<div key={key} style={{ width: '100%' }}>
<input
name={key} // `name` should be the same as `schema key`
placeholder={StringUtils.toTitleCase(key)}
type={key.includes('password') ? 'password' : 'text'}
{...listeners} // Spread the input listeners here
style={{ width: '100%', fontSize: '1rem', padding: '0.4rem' }}
/>
{
formErrors[key as keyof typeof formErrors] && (
<span style={{ color: 'crimson' }}>
{formErrors[key as keyof typeof formErrors]}
</span>
)
}
</div>
))
}
```
- **Dynamic input fields**: The form fields (`email` and `password`) are rendered dynamically using `Object.keys(formData)`. For each field:
- The `input` field is created with the proper name and placeholder.
- **Type**: If the field is for `password`, the `input` type is set to `"password"`, otherwise, it's a text field.
- **Error messages**: If there are validation errors for a field, an error message is displayed below the corresponding input.
- **`listeners`**: The event listeners for each input are spread dynamically from `{...listeners}`.
---
#### Step 8: **Form Submission Button**
```tsx
<button
type="submit"
title="Login"
style={{ cursor: 'pointer', padding: '0.5rem 0', marginTop: '0.5rem', fontSize: '1rem', width: '100%' }}
>
Login
</button>
```
---
#### setFormData usage:
```tsx
const {
formData,
setFormData,
} = useForm<FormSchema>(initialFormData);
// Example 1: Update the 'email' field with a new value
setFormData('email', 'user@example.com');
// Example 2: Update the 'email' field and hide any associated error messages
setFormData('email', 'user@example.com', true);
```
---
#### getFormData usage:
```tsx
const {
formData,
getFormData,
} = useForm<FormSchema>(initialFormData);
// Example 1: Retrieve the value of the 'email' field
const emailValue = getFormData('email');
console.log(emailValue); // Outputs: user@example.com
// Example 2: Retrieve the value of the 'password' field
const passwordValue = getFormData('password');
console.log(passwordValue); // Outputs: ********
```
---
#### resetFields usage:
```tsx
const {
resetFields,
} = useForm<FormSchema>(initialFormData);
// Example 1: Reset all form fields and clear any error messages
resetFields();
// Example 2: Reset all form fields but retain the current error messages
resetFields(true);
```
---
#### Advantages
1. **Automatic Validation**: Validation is seamlessly integrated with the form state. You define a schema, and the hook automatically handles the validation of form data against it.
2. **Minimized Re-renders**: The component only re-renders when there is a validation error, significantly improving performance, especially for larger forms.
3. **Error Handling**: The hook provides a simple way to display validation errors for each field. You can easily bind error messages to form inputs, improving the user experience.
4. **Custom Submission Handling**: The `onSubmit` function allows you to add any custom logic on form submission, making it highly flexible for various use cases like API requests or complex business logic.
5. **Clean and Simple API**: The hook returns an intuitive object structure with form state, submission handler, error object, and input listeners, making it easy to integrate into any React form component.
---
### `useDebounce`
`useDebounce` is a custom React hook that delays the execution of a provided function until after a specified delay time has passed since the last time the function was invoked. This is especially useful for scenarios like handling user input (e.g., search bar) where you want to avoid triggering an action on every keystroke.
#### API
```ts
const debounce = useDebounce(delay: ms, debounceAction: DebounceAction): VoidFunction;
```
- **`delay`**: The debounce delay in milliseconds (`ms`). This defines how long to wait after the last invocation before calling the `debounceAction`.
- **`debounceAction`**: The action or function that you want to debounce. It will only be executed after the specified delay period.
#### Example Usage
```tsx
import React, { useCallback } from 'react';
import { useDebounce } from '@d3vtool/hooks';
export default function Search() {
// Memoize the trigger function
const memoizedTrigger = useCallback(() => {
console.log("Searching...");
// Your search logic here
}, []);
// Use the useDebounce hook to delay the trigger function
const debounce = useDebounce(800, memoizedTrigger);
return (
<div>
<input
type="text"
placeholder="Search..."
onChange={debounce} // Debounced onChange handler
/>
</div>
);
}
```
#### Why Use `useDebounce`?
- **Performance Optimization**: Prevents unnecessary function executions during frequent events (like typing) by waiting until the user stops interacting for a predefined period.
- **Customizable Delay**: You can adjust the delay time to suit your use case, giving you more control over how quickly the action should be triggered.
- **Easy Integration**: Works seamlessly with any function or event handler, making it easy to implement debouncing in forms, search bars, or other interactive UI elements.
### License
This package is open-source and licensed under the [MIT License](LICENSE).